Vereinigte Staaten von Amerika (USA) |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Vereinigte Staaten von Amerika (USA) |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
| Flaggen – Flags: | |
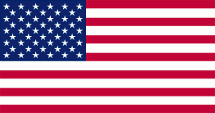 |
seit/since 1960, National-, Staats-, Handels- und Marineflagge – national, state, merchant and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 10:19, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4   |
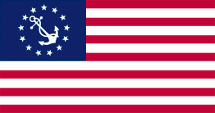 |
Flagge für Wassersportfahrzeuge (Yachtflagge) – flag for water sports vessels (yacht flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 10:19, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
1960–2002, seit/since 2019, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 71:100, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
2002–2019, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge des Heeres – flag of the Army, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 63:80 (?), Quelle/Source: United States Institute of Heraldry, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons   |
 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe – flag of the Air Force, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 63:80 (?), Quelle/Source: Dorothy G. Gatchell, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons   |
 |
Flagge der Marine – flag of the Navy, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 63:80 (?), Quelle/Source: United States Department of the Navy, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons   |
 |
Flagge der Küstenwache – flag of the Coast Guard, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 63:80 (?), Quelle/Source: U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge des Grenzschutzes – flag of the Border Patrol, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 7:12, Quelle/Source: United States Border PatrolVectored by FOX 52., Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge des Zoll – flag of Customs, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 11:18, Quelle/Source: Ibagli, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 7:10, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4   |
 |
Flagge des Vizepräsidenten – flag of the Vice President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 63:80, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
|
Die Flagge der USA, mit
ihren Sternen und Streifen, wurde in dieser Grundform am 14.06.1777
eingeführt. Sie zeigt heute dreizehn waagerechte weiße und rote Streifen.
Die Oberecke ist blau und zeigt fünfzig weiße fünfzackige Sterne. Die
dreizehn Streifen stehen für die dreizehn britischen Kolonien, die sich im
Jahre 1775 zur Wahrung der ihnen ihrer Meinung nach zustehenden Rechte
gegenüber Großbritannien in einer Union zusammenschlossen hatten. Seit 1818
wird die Anzahl der zur dieser Union gehörenden Staaten durch die Anzahl der
weißen Sterne im blauen Feld repräsentiert. Seit dem 04.07.1960 (Aufnahme
von Hawaii in die USA) sind es fünfzig Stück. Die Farben Blau, Weiß und Rot
haben ihren Ursprung im Britischen "Union Jack", der sogar noch ein Jahr
lang (bis 1777) in der Flagge der USA zu sehen war. Die Farben haben heute
folgende Bedeutung: Blau steht für Gerechtigkeit und Ausdauer, Weiß für
Reinheit und Bescheidenheit, Rot für Stärke und Mut. Die US-Vorschrift "DDD-F-416F" bestimmt die genauen Farbtöne für Rot, Weiß und Blau, so wie sie von Bundesbehörden verwendet und umgesetzt werden müssen. Es handelt sich dabei um Koordinaten des CIE-Farbraums, die in HEX-Werte übertragbar sind und folgende Werte ergeben: #FFFFFF für Weiß, #B22234 für Rot und #3C3B6E für Blau. Ergänzend gibt es die "Standard Color Reference of America", in ihrer 10. Ausgabe, eine Reihe von Mustern gefärbter Seidenstoffe, die als Referenz herangezogen werden. Die sich daraus ergebenden Echt-Farben sind folgende: Weiß Nr. 70001, Old Glory Red Nr. 70180 und Old Glory Blue Nr. 70075. Daraus lassen sich folgende Pantone-Farbtöne ableiten: Rot = pt 187 c und Blau = pt 5265 c, was aber keine offiziellen oder amtlichen Farbwerte sind. Die Flagge des Staates Texas muss farblich exakt der Flagge der USA entsprechen, von daher wurden für Texas offizielle Pantone-Farbtöne festgelegt: Rot = pt 193 c und Blau = pt 281 c. Die Yachtflagge ist keine offizielle Flagge und darf nur in den Küstengewässern benutzt werden. Sie war usprünglich eine im Jahre 1848 geschaffene Sonderflagge für Privatfahrzeuge, die damit kenntlich machen konnten, dass sie sich nicht bei den Zollbehörden eines Hafens melden müssen. Die Präsidentenflagge wurde in ihrer heutigen Form am 29.05.1946 eingeführt. Sie ist einfarbig blau und zeigt das Siegel des Präsidenten in einem Kreis aus fünfzig Sternen. Die Flagge des Vizepräsidenten wurde in ihrer heutigen Form am 07.10.1975 nach einigen Änderungen eingeführt. Sie ist weiß, zeigt das Siegel Präsidenten in der Mitte und in den Ecken der Flagge je einen dunkelblauen fünfzackigen Stern. |
The flag of the USA, with
its stars and stripes, was introduced in this basic form on 14th of June in
1777. Today it shows thirteen horizontal white and red stripes. The top
corner is blue and shows fifty white five-pointed stars. The thirteen
stripes symbolise the thirteen British colonies that formed a union in 1775
to protect the rights to which they believed they were entitled vis-à-vis
United Kingdom. Since 1818, the number of states belonging to this union has been represented by the number of white stars in the blue field. Since 4th of July in 1960 (admission of Hawaii to the USA), there have been fifty of them. The colours blue, white and red have their origin in the British "Union Jack", which could even be seen in the flag of the USA for one year (until 1777). Today, the colours have the following meaning: blue stands for justice and perseverance, white for purity and modesty, red for strength and courage. The US-regulation "DDD-F-416F" defines the exact colour tones for red, white and blue as they must be used and implemented by federal authorities. These are coordinates of the CIE colour space that can be translated into HEX values and result in the following values: #FFFFFF for white, #B22234 for red and #3C3B6E for blue. In addition, there is the "Standard Colour Reference of America", in its 10th edition, which provides a series of samples of dyed silk fabrics that are used as a reference. The resulting true colours are as follows: White No. 70001, Old Glory Red No. 70180 and Old Glory Blue No. 70075, from which the following Pantone colour shades can be derived: Red = pt 187 c and Blue = pt 5265 c, which are not official or official colour values. The flag of the state of Texas must correspond exactly to the flag of the USA in terms of colour, which is why official Pantone colour tones have been defined for Texas: Red = pt 193 c and Blue = pt 281 c. The yacht flag is not an official flag and may only be used in coastal waters. It was originally a special flag created in 1848 for private vessels to indicate that they did not have to report to the customs authorities in a harbour. The presidential flag was introduced in its current form on 29th of May in 1946. It is single-coloured blue and shows the presidential seal in a circle of fifty stars. The flag of the Vice-President was introduced in its present form on 7th of October in 1975 after a number of changes. It is white, shows the presidential seal in the centre and a dark blue five-pointed star in each corner of the flag. |
| → Flaggenschichte ← | → Flag History ← |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN), Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen der USA – coat of arms of the USA, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen der USA wurde am 20.06.1782, nach anderen Quellen am 20.07.1782, als Staatssiegel angenommen. Es wurde von William Barton und Charles Thomson geschaffen und zeigt einen Weißkopfadler mit einem Olivenzweig und dreizehn silbernen Pfeilen in seinen Krallen. Sie symbolisieren, dass der amerikanische Kongress über Krieg oder Frieden entscheiden kann, und, sie stehen, genau wie die dreizehn Sterne in dem blauen Feld über den Kopf des Adlers, für die dreizehn ursprünglichen Kolonien, aus denen die Vereinigten Staaten hervorgingen. Links und rechts des Adlerkopfes ein goldenes Spruchband mit der Inschrift "E pluribus unum" → "Aus vielen eines". | The
national emblem of the United States was adoped on 20th of June in 1782,
according to other sources on 20th of July in 1782, as the seal of the sate.
It was created by William Barton and Charles Thomson and shows a
white-headed eagle with an olive branch and thirteen silvery arrows in its
claws. They symbolize that the U.S. Congress is able to decide on war or peace, and they stand exactly like the thirteen stars in the blue field over the head of the eagle, for the thirteen original colonies, from which the United States emerged. To the left and to the right of the head of the eagle a golden banner with the inscription "E pluribus unum" → "Out of many, one". |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
seit/since 1947, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1918–1919, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1919–1942, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1942–1943, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1943, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1943–1947, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
|
|
Lage – Position: |
|
|
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Die Bundesstaaten – The Federal States: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.000 v.Chr.
· Besiedlung von Asien aus, über Alaska südwärts ca. 1000 n.Chr. · der Wikinger Leif Eriksson entdeckt Amerika 1394 · der venezianische Seefahrer Zeno entdeckt Amerika erneut 1492 · der genuesische Seefahrer in spanischen Diensten Christoph Kolumbus entdeckt Amerika erneut (Bahamas) 24.06.1497 · der italienische Seefahrer in englischen Diensten Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) entdeckt das amerikanische Festland (Labrador) 1498 · der italienische Seefahrer in englischen Diensten Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) segelt entlang der Ostküste der heutigen USA 1513 · Spanien nimmt Florida in Besitz 1542 · der spanische Seefahrer Cabrillo erreicht von Mexiko aus die Westküste der heutigen USA (Kalifornien), der spanische Forscher und Eroberer Coronado erreicht das heutige Neumexiko auf dem Landweg, der der spanische Forscher und Eroberer de Soto durchreist die heutigen Staaten Florida, Süd Carolina, Alabama und Mississippi auf dem Landweg 1565 · der spanische Seefahrer Urdaneta erreicht von den Philippinen aus die Westküste der heutigen USA (Kalifornien) 1578 · der englische Seefahrer Francis Drake erkundet die Westküste der heutigen USA (Kalifornien) 1578 · der englische Seefahrer Walter Raleigh erkundet die Ostküste der heutigen USA 1585 · der englische Seefahrer Walter Raleigh gründet am Roanoke River eine erste englische Kolonie an der Ostküste, sie wird später jedoch aufgegeben 1600–1670 · Frankreich kolonisiert entlang des St.-Lorenz-Stromes und erreicht von Norden kommend die Großen Seen 1607 · Gründung von Jamestown an der Küste Virginias, unter dem Namen Virginia die erste englische Kolonie an der Ostküste 1609 · der englische Seefahrer Henry Hudson erkundet die Ostküste der heutigen USA 1613 · Gründung von Neu Amsterdam (später Neu York) am Hudson River, die erste niederländische Siedlung im Norden der Ostküste der heutigen USA, später Mittelpunkt der niederländischen Kolonie Neu-Niederlande 1638 · Gründung von Neuschweden (später Delaware), die erste schwedische Siedlung an der Ostküste der heutigen USA 1650–1680 · Spanien nimmt den Süden heutigen USA in Besitz, in etwa die heutigen Staaten Kalifornien, Arizona, Neumexiko, Texas, Louisiana, das allmählich kolonisiert wird, ferner Land an der Westseite des Mississippi, in etwa die heutigen Staaten Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Minnesota, das nur mäßig, bzw. gar nicht kolonisiert wird 1655 · Neuschweden wird niederländischer Besitz 1664 · Neuschweden (Delaware) wird britischer Besitz 1664 · Neu-Niederlande wird britischer Besitz 1670–1690 · Frankreich kolonisiert südlich der Großen Seen und entlang des Mississippi, in etwa in den heutigen Staaten Michigan, Indiana, Wisconsin, Monnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Illinois, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi 1695–1720 · Frankreich kolonisiert an der Mündung des Mississippi 1733 · Gründung der königlichen Kolonie Georgia, damit gibt es an der Ostküste insgesamt dreizehn britische Kolonien, die sogenannten Neuenglandkolonien (Neu Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Insel), die Mittelkolonien (Neu York, Delaware, Neu Jersey, Pennsylvanien) und die Südkolonien (Virginia, Maryland, Nord- und Südkarolina, Georgia) 1754–1763 · Siebenjähriger Krieg, Auseinandersetzungen zwischen Großbritannien und Frankreich, Frankreich muss 1763 alle Gebiete in Kanada und östlich des Mississippi an Großbritannien abtreten, jedoch durften sich die dreizehn britischen Kolonien nicht nach Westen ausdehnen, und hatten die wirtschaftlichen Folgen des Krieges zu tragen 1764 · Molasses Act, Handelsverbot für die britischen Kolonisten mit Frankreich und Spanien 1765 · Großbritannien führt die Stempelsteuer ein 1765 · Gründung der Widerstandsbewegung "Sons of Liberty", ein Kongress der Kolonien beschließt den Boykott britischer Waren 16.12.1773 · "Bostoner Teesturm", britische Waren werden ins Meer geworfen 1774 · Großbritannien gliedert die ehemals französischen Besitzungen zum Ohio an Kanada an, Revolte in Massachusetts, Großbritannien verhängt den Ausnahmezustand (Aufhebung der Verfassung), die Kolonisten organisieren dagegen den 1. Kontinentalkongress, Beendigung des Handels mit Großbritannien, Bildung der Minutemen-Miliz, Terror gegen dem König loyale Kolonisten 19.04.1775 · Gefechte von Lexington und Concord, Beginn des Unabhängigkeitskrieges (bis 1783) 04.07.1776 · Unabhängigkeitserklärung 17.10.1777 · Schlacht von Saratoga, schwere Niederlage der britischen Truppen 15.11.1777 · Verabschiedung der Konföderationsartikel (Bildung der USA) 1778 · die USA verbünden sich mit Frankreich 1778 · die USA verbünden sich mit Spanien 1780 · die USA verbünden sich mit den Niederlanden 19.10.1781 · Schlacht von Yorktown, Kapitulation der britischen Truppen 30.11.1782 · der Separatvertrag mit Großbritannien erkennt die Unabhängigkeit der USA an 03.09.1783 · Vertrag von Paris, die Unabhängigkeit der USA wird bestätigt 1788 · erste Verfassung 1791 · Ergänzung der Verfassung um die "Bill of Rights" 1803 · die USA kaufen dessen Kolonie Louisiana von Frankreich (die heutigen Staaten Montana, der Südwesten von Nord-Dakota, der Nordosten von Wyoming, Süd-Dakota, Minnesota, Iowa, Nebraska, der Nordosten von Colorado, Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas und Louisiana) 1804–1807 · Versuche Neuengland mit britischer Unterstützung von den USA abzuspalten 1810–1813 · die USA annektieren Westflorida 1812–1814 · US-amerikanisch-britischer Krieg, ohne Ergebnisse 1814 · Hartfordkongress, erneuter Versuch Neuengland mit britischer Unterstützung von den USA abzuspalten 1818 · Großbritannien tritt den Nordosten des heutigen Nord-Dakota an die USA ab 1819 · die USA erwerben Florida von Spanien 1836 · die USA Unterstützen die Abspaltung des Staates Texas von Mexiko 1845 · Texas tritt der USA bei 1846 · Großbritannien tritt das Oregon Gebiet an die USA ab (die heutigen Staaten Oregon, Washington und Idaho) 1846–1848 · Krieg gegen Mexiko, Annexion mexikanischen Staatsgebiets (die heutigen Staaten Kalifornien, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, sowie Teile Wyomings, Colorados und Neumexikos) 1853 · die USA erwerben den Süden des heutigen Arizona von Mexiko (Gadsen-Kauf) 1854 · Gründung der Republikanischen Partei 06.11.1860 · Wahl von Abraham Lincoln (Republikaner) zum Präsidenten der USA 20.12.1860 · Südkarolina erklärt gemäß der Verfassung der USA seinen Austritt aus der Union Januar bis Februar 1861 · Austritt weiterer zehn Staaten 08.02.1861 · Gründung der Konföderierten Staaten von Amerika (CSA, Südstaaten) 04.03.1861 · Amtsantritt von Lincoln 12.–14.04.1861 · "Beschuss von Fort Sumter", in Wirklichkeit ein Schusswechsel mit einigen Leichtverletzten 15.04.1861 · Lincoln ruft 75.000 Freiwillige zu den Waffen, de facto Kriegserklärung an die CSA, Beginn des Sezessionskriegs 09.04.1865 · General Lee kapituliert bei Appomattox (Virginia) als Kommandeur der konföderierten Armee von Nord-Virginia, die anderen CSA-Armeen kapitulieren nach und nach bis Juli 1865 18.12.1865 · der im Januar 1865 vom US-Kongreß beschlossene 13. Zusatzartikel zur Verfassung erlangt Rechtskraft, damit wird die Sklaverei auf dem Gebiet der USA endgültig abgeschafft. 1865–1877 · "Rekonstruktion", erzwungene Rückkehr der CSA-Staaten in die Union 1867 · die USA erwerben Alaska von Russland April bis August 1898 · rätselhafte Explosion des US-amerikanischen Kriegsschiffs „Maine“ vor Havanna, US-amerikanische Militärintervention, spanisch-US-amerikanischer Krieg, Frieden von Paris: Spanien muss sein Kolonialreich zum größten Teil an die USA abtreten (Kuba, Philippinen, Puerto Rico) 07.07.1898 · Annexion von Hawaii 1903 · Kuba wird Protektorat der USA, Panama tritt die Kanalzone an die USA ab 1905 · US-Militärintervention in Honduras 1906–1909 · US-Militärintervention in Kuba 1907 · US-Militärintervention in Honduras 1911 · US-Militärintervention in Honduras 1912–1932 · US-Militärintervention in Nikaragua 1913 · US-Militärintervention in Honduras 1914 · US-Militärintervention in Mexiko 1915 · US-Militärintervention in Haiti 1916 · US-Militärintervention in Mexiko und in der Dominikanischen Republik, Kauf der Jungferninseln von Dänemark 06.04.1917 · Kriegserklärung an das Deutsche Reich, die USA beteiligen sich am Ersten Weltkrieg (bis November 1918) 1918 · US-Militärintervention in Sibirien 1919 · US-Militärintervention in Kostarika 1919–1924 · US-Militärintervention in Kuba 1924 · US-Militärintervention in Honduras 08.12.1941 · Kriegserklärung an Japan, die USA beteiligen sich am Zweiten Weltkrieg (bis September 1945) 25.06.1950 · US-Militärintervention in Korea (bis Juli 1953), US-Militärintervention in Taiwan 1958 · US-Militärintervention im Libanon 1962 · US-Militärintervention in Thailand 1963 · US-Militärintervention in Vietnam (bis 1973) 1983 · US-Militärintervention in Grenada 1989 · US-Militärintervention in Panama 1991 · US-Militärintervention im Irak (Zweiter Golfkrieg) 1994 · US-Militärintervention in Haiti 2001–2021 · US-Militärintervention in Afghanistan 20.03.2003 · US-Militärintervention im Irak (Dritter Golfkrieg) |
|
15.000 B.C.
· settlement from Asia via Alaska southward ca. 1000 A.D. · the Viking Leif Eriksson discoveres America 1394 · the Venetian seafarer Zeno discoveres America again 1492 · Christopher Columbus the Genoese seafarer in Spanish services discoveres America again (Bahamas) 24th of June 1497 · Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) the Italian seafarer in British services discovers the American mainland (Labrador) 1498 · Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) the Italian seafarer in British services sailes along the east coast of the today's USA 1513 · Spain takes Florida in possession 1542 · the Spanish seafarer Cabrillo reaches the west coast of the today's USA from Mexico (California), the Spanish researcher and conquistador Coronado reaches the today's New Mexico over land, the Spanish researcher and conquistador de Soto travels thorough today's Florida,South Carolina, Alabama and Mississippi 1565 · the Spanish seafarer Urdaneta reaches the west coast of the today's USA (California) from the Philippines 1578 · the English seafarer Francis Drake explores the west coast of the today's USA (California) 1578 · the English seafarer Walter Raleigh explores the east coast of the today's USA 1585 · the English seafarers Walter Raleigh founds the first English colony on the east coast at Roanoke River, but it is later abandoned 1600–1670 · France colonizes along the St. Lawrence river and reaches the north of the Great Lakes 1607 · founding of Jamestown on the coast of Virginia, under the name "Virginia" the first English colony on the east coast 1609 · the English seafarer Henry Hudson explores the east coast of the today's USA 1613 · founding of New Amsterdam (later New York) on the Hudson River, the first Dutch settlement in the north of the east coast of the today's USA, and later center of the Dutch colony of New Netherlands 1638 · formation of New Sweden (later Delaware), the first Swedish settlement on the east coast of the today's USA 1650–1680 · Spain in possession the south of today's, about the current states of California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Louisiana, which becomes gradually colonized, also land on the west side of the Mississippi, about the current states Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Minnesota, but it becomes only moderately or not colonized 1655 · New Sweden is owned by Dutch 1664 · New Sweden (Delaware) becomes a British possession 1664 · New Netherlands, becomes a British possession 1670–1690 · France colonizes in the south of the Great Lakes and along the Mississippi, in roughly the present states of Michigan, Indiana, Wisconsin, Monnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Illinois, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi 1695–1720 · France colonizes at the mouth of the Mississippi 1733 · founding of the royal Colony of Georgia, in this way there exist on the east coast thirteen British colonies, so the so named New England Colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island), the so named Middle Colonies (New York, Delaware, New Jersey, Pennsylvania) and the Southern Colonies (Virginia , Maryland, North and South Carolina, Georgia) 1754–1763 · Seven Years' War, conflict between United Kingdom and France, France has to cede all areas in Canada and east of the Mississippi to United Kingdom in 1763, but for the thirteen British colonies it is not allowed to extend to the west and they have to carry the economic consequences of this war 1764 · Molasses Act, prohibition of trade for te British colonies with France and Spain 1765 · United Kingdom introduces the stamp tax 1765 · establishment of the resistance movement "Sons of Liberty", a congress of the colonies decides to boycott British goods 16th of December 1773 · "Boston Tea Party", British goods are thrown into the sea 1774 · United Kingdom annexes the former French possessions on Ohio River to Canada, revolt in Massachusetts, United Kingdom imposed the state of emergency (repeal of the Constitution), on the other hand the colonists organize the 1st Continental Congress, termination of trade with United Kingdom, the establishment of the Minutemen Militia, terror against colonists which are loyal to the King 19th of April 1775 · battles of Lexington and Concord, the beginning of the independence war (until 1783) 4th of July 1776 · declaration of independence 17th of October 1777 · Battle of Saratoga, heavy defeat of the British troops 15th of November 1777 · adoption of the Articles of Confederation (establishment of the USA) 1778 · the USA ally with France 1778 · the USA ally with Spain 1780 · the USA ally with the Netherlands 19th of October 1781 · Battle of Yorktown, surrender of British troops 30th of November 1782 · the Separate Treaty with United Kingdom recognizes the independence of the United States 3rd of September 1783 · Treaty of Paris, the independence of the United States becomes confirmed 1788 · first constitution 1791 · supplementing of the constitution with the the Bill of Rights 1803 · the USA buy the Louisiana colony from France (the present states Montana, the southwest of North Dakota, the northeast of Wyoming, South Dakota, Minnesota, Iowa, Nebraska, the northeast of Colorado, Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas and Louisiana) 1804–1807 · attempts to separate New England from the USA with British support 1810–1813 · the USA annex West Florida 1812–1814 · US-american-British war, without results 1814 · Hartford Convention, new attempt to separate New England from the USA with British support 1818 · United Kingdom cedes the northeast of today's North Dakota to the USA 1819 · the USA acquire Florida from Spain 1836 · the USA support the secession of the State of Texas from Mexico 1845 · Texas joins the USA 1846 · United Kingdom cedes the Oregon territory to the United States (the today's states Oregon, Washington and Idaho) 1846–1848 · war against Mexico, annexation of Mexican territory (the today's states of California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and parts of Wyoming, Colorado and New Mexico) 1853 · the USA acquire the south of today's Arizona from Mexico (Gadson Purchase) 1854 · founding of the Republican Party 6th of November 1860 · election of Abraham Lincoln (Republican) as President of the USA 20th of December 1860 · South Carolina declares its withdrawal from the Union in accordance with the constitution of the USA January to February 1861 · withdrawal of ten further states 8th of February 1861 · founding of the Confederate States of America (CSA, Southern States) 4th of March 1861 · inauguration of Lincoln 12th to 14th of April 1861 · "bombardment of Fort Sumter", in reality a small battle with a few slight injuries 15th of April 1861 · Lincoln urges 75.000 volunteers to arms, a de facto declaration of war on the CSA, the beginning of the secession war 9th of April 1865 · General Lee surrenders at Appomattox (Virginia) as commander of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, the other CSA Armies capitulate gradually until July 1865 18th of December in 1865 · the in January 1865 by the US Congress adopted 13th amendment to the constitution becomes valid, so that slavery in the area of USA is finally abolished 1865–1877 · "Reconstruction", forced return of the CSA states in the Union 1867 · the USA acquire Alaska from Russia April to August 1898 · mysterious explosion of the U.S. warship "Maine" in Havana, US military intervention, Spanish-US-american War, Peace of Paris: Spain's has to cede its colonial empire for the most part to the United States (Cuba, Philippines, Puerto Rico) 7th of July 1898 · annexation of Hawaii 1903 · Cuba becomes a protectorate of the United States, Panama cedes the Canal Zone to the USA 1905 · US military intervention in Honduras 1906–1909 · US military intervention in Cuba 1907 · US military intervention in Honduras 1911 · US military intervention in Honduras 1912–1932 · US military intervention in Nicaragua 1913 · US military intervention in Honduras 1914 · US military intervention in Mexico 1915 · US military intervention in Haiti 1916 · US military intervention in Mexico and in the Dominican Republic, the USA buy the Virgin Islands from Denmark 6th of April 1917 · declaration of war against the German Empire, the USA will participate in the First World War (until November 1918) 1918 · US military intervention in Siberia 1919 · US military intervention in Costa Rica 1919–1924 · US military intervention in Cuba 1924 · US military intervention in Honduras 8th of December 1941 · declaration of war on Japan, the United States participate in the Second World War (until September 1945) 25th of June 1950 · US military intervention in Korea (until July 1953), US military intervention in Taiwan 1958 · US military intervention in Libanon 1962 · US military intervention in Thailand 1963 · US military intervention in Vietnam (until 1973) 1983 · US military intervention in Grenada 1989 · US military intervention in Panama 1991 · US military intervention in Iraq (Second Gulf War) 1994 · US military intervention in Haiti 2001–2021 · US military intervention in Afghanistan 20th of March 2003 · US military intervention in Iraq (Third Gulf War) |
|
Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte, Volker Preuß |

| Der Name "Vereinigte Staaten von Amerika" erinnert daran, dass die USA ein Staatenbund sind, und durch den Zusammenschluss von dreizehn britischen Kolonien entstanden sind. Die USA nennen sich selbst gern nur "Amerika", auch offiziell, als stünden sie für den ganzen Kontinent. | The name
"United States of America" recalled that the USA is a confederation of
states, and that they were created by union of thirteen British colonies. The United States call themselves just "America", even officially, as they would stand for the whole continent. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |