Amerikanische Jungferninseln |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Amerikanische Jungferninseln |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
seit/since 1921, National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national, state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: User:Dbenbenn, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
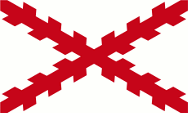 |
16. Jhd/cent., Die Inseln gehören zum spanischen Einflussbereich – The islands belongs to the Spanish sphere of influence, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
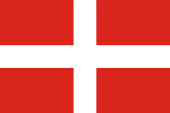 |
1651–1665, St. Croix ist im Besitz des Malteserordens – St. Croix a pssession of the Order of Malta |
 |
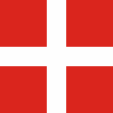
1665-1696, St. Croix ist eine Kolonie von Frankreich – St. Croix is a colony of France, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Sodacan [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons   |
 |
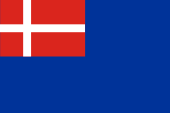
1680–1776(?), Flagge der Dänischen Westindien-Guinea-Kompanie – flag of the Danish West India Company, Quelle/Source, nach by: videnskab.dk |
 |
1754–1807, Flagge Dänemarks – flag of Denmark, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1798–1842, Flagge für dänische Schiffe auf dem Weg nach Dänisch-Westindien – Flag for Danish ships en route to the Danish West Indies, Quelle/Source, nach/by: World Statesmen, www.mgg.dk, ca.2010/dkflag/danske-flag, FOTW |
 |
1807–1815, |
 |
1815–1917, Flagge Dänemarks – flag of Denmark, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4  |
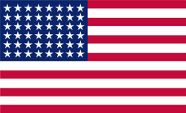 |
1917–1921, Flagge der USA – flag of the USA, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
| Die heutige Flagge der Jungferninseln der USA wurde von Percival Wilson Sparks geschaffen und am 17.05.1921 angenommen. Sie zeigt ein weißes Grundtuch und darauf vereinfachte Elemente des Wappens der USA: einen goldenen Weißkopfseeadler mit einem Brustschild in den Farben der USA, der in seinen Fängen einen Ölzweig und drei Pfeile hält. Die Pfeile stehen für die drei größten Inseln des Landes: Saint Thomas, Saint John und Saint Croix. Links und rechts des Adler die Buchstaben "V" und "I", sie verkörpern den Landesnamen "Virgin Islands". Unter dänischer Herrschaft wurden dänische Flaggen verwendet, eine Zeit lang auch einfarbige blaue oder sogar weiße Flaggen mit der dänischen Flagge in der Oberecke. Nach dem Verkauf der Inseln an die USA (31.03.1917) unterstanden sie zunächst der Marine der USA, und es wurde zunächst die Flagge der USA verwendet. Am 17.05.1921 wurde jedoch das heutige Modell eingeführt. |
The current flag of the
US Virgin Islands was created by Percival Wilson Sparks and was adopted on
17th of May in 1921. It shows a white bunting and on it simplified elements
of the coat of arms of the USA: a golden bald eagle with a breast shield in
the colours of the USA, holding an olive branch and three arrows in its
talons. The arrows represent the three largest islands in the country: Saint
Thomas, Saint John and Saint Croix. To the left and right of the eagle are
the letters "V" and "I", symbolising the country's name "Virgin Islands".
Under Danish rule, Danish flags were used, for a time also single-coloured
blue or even white flags with the Danish flag in the upper corner. After the
sale of the islands to the USA (31st of March in 1917), they were initially
under the control of the US Navy and the US flag was initially used. On 17th
of May in 1921, however, the current model was introduced. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
St. Croix: 14.11.1493 · der spanische Seefahrer Christoph Kolumbus entdeckt die Insel St. Croix, er nennt sie Isla de Santa Cruz (Heilig-Kreuz-Insel) und die umliegenden Inseln nennt er Las Islas Once Mil Virgenes (Inseln der 11.000 Jungfrauen) 1587 · erste englische Kolonie auf St. Croix 1625 · erste niederländische Kolonien auf St. Croix 1645 · die Niederländer verlassen St. Croix 1650 · die englischen Kolonien auf St. Croix werden von spanischen Truppen zerstört, Franzosen kommen auf die Insel und übernehmen die Herrschaft 1651–1665 · der Malteserorden beherrscht St. Croix 1665 · Franzosen kommen erneut auf die Insel und übernehmen die Herrschaft 1696 · die Franzosen verlassen St. Croix 13.06.1733 · die Dänische Westindien-Guinea-Kompanie kauft St. Croix von Frankreich St. Thomas: 1493 · der spanische Seefahrer Christoph Kolumbus entdeckt die Insel 1665 · erste dänische Kolonie auf St. Thomas 1667 · die Dänen verlassen St. Thomas 25.05.1672 · St. Thomas wird dänische Kolonie 1685–1693 · das Kurfürstentum Brandenburg betreibt einen Handelsstützpunkt St. John: 1684 · St. John wird nach Kämpfen mit England dänische Kolonie 24.08.1754 · Dänemark übernimmt Dänisch-Westindien von der Dänischen Westindien-Guinea-Kompanie, die Jungferninseln werden Kronkolonie 1801–1802 · die Inseln werden von britischen Truppen besetzt 1807–1815 · die Inseln werden von britischen Truppen besetzt 12.12.1916 · Dänemark verkauft die Jungferninseln an die USA 31.03.1917 · die Hoheit Dänemarks endet, die Inseln werden von der US-Marine übernommen 30.01.1931 · die Verwaltung der Inseln geht an das Innenministerium der USA über |
|
St. Croix: 14th of November 1493 · the Spanish navigator Christopher Columbus discovers the island of St. Croix, he named it Isla de Santa Cruz (Holy Cross Island) and the surrounding islands, he named Las Islas Once Mil Virgenes (Islands of 11.000 Virgins) 1587 · first English colony on St. Croix 1625 · first Dutch colony on St. Croix 1645 · the Dutch leave St. Croix 1650 · the English colonies on St. Croix will be destroyed by Spanish troops, the French come to the island and take over the reigns 1651–1665 · the Order of Malta dominates St. Croix 1665 · the French come back to the island and take over the reigns 1696 · the French to leave St. Croix 13th of June 1733 · the Danish West India Company buys St. Croix from France St. Thomas: 1493 · the Spanish navigator Christopher Columbus discovers the island 1665 · first Danish colony of St. Thomas 1667 · the Danes leave St. Thomas 25th of May 1672 · St. Thomas becomes a Danish colony 1685–1693 · the Electorate of Brandenburg operates a trading post St. John: 1684 · St. John becomes a Danish colony, after fights with England 24th of August 1754 · Denmark takes over the Danish West Indies from the Danish West India Company, the Virgin Islands become a Crown Colony 1801–1802 · the islands are occupied by British troops 1807–1815 · the islands are occupied by British troops 12th of December 1916 · Denmark sells the Virgin Islands to the United States 31st of March 1917 · the sovereignty of Denmark ends, the islands come under the control of the U.S. Navy 30th of January 1931 · the administration of the islands goes on to the Ministry of Interior of the United States |
| Quelle/Source: Meyers Konversationslexikon, World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Volker Preuß |
| Kolumbus nannte die Inseln "Las Islas Once Mil Virgenes" (Inseln der 11.000 Jungfrauen), zu Ehren der Heiligen Ursula und Ihrer Begleiterinnen. Von diesem langen Namen hat sich nur "Jungferninseln" erhalten. | Columbus named the islands "Las Islas Once Mil Virgenes" (Islands of the 11.000 Virgins), in honor of St. Ursula and her female companions. From this long name only remained "Virgin Islands". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |