Puerto Rico |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Puerto Rico |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, |
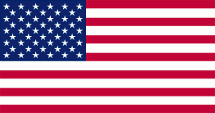 |
National-, Handels- und Marineflagge der USA – national, merchant and naval flag of the USA, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 10:19, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (ES)  |
 |
Flagge des Gouverneurs |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
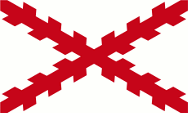 |
1521–1785, Flagge Königreich Neu-Spanien – flag of the Kingdom of New Spain, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
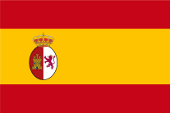 |
1785–1821, Flagge Königreich Neu-Spanien – flag of the Kingdom of New Spain, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
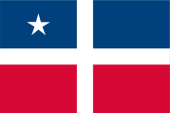
1821–1898, Flagge von Spanisch-Amerika – flag of Spanish America, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
1930(?)–1990(?), |
 |
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge Puerto Ricos zeigt fünf gleich breite, waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Weiß, Rot, Weiß und Rot, sowie am Mast ein blaues gleichschenkliges Dreieck mit einem weißen fünfzackigen Stern darin. Sie wurde am 22.12.1895 erstmals gehisst, war jedoch nur inoffiziell. Es durfte ausschließlich die Flagge der USA zu verwendet werden. Am 24.07.1952 wurde die offiziell als Flagge des assoziierten Freistaats angenommen, darf jedoch nur zusammen mit der Flagge der USA gehisst werden. | The flag
of Puerto Rico shows five identical broad horizontal stripes in red, white,
red, white and red, as soon as a blue isosceles triangle on the pole with a
white five-pointed star in it. It was hoisted for the first time on 22nd of December in 1895, but had only an unofficial status. There was to use solely the flag of the USA. On 24th of July in 1952 became that flag officially tooken over as flag of the associated free state, but it is just allowed to hoist it together with the flag of the USA. |
| Die Flagge von Puerto Rico hat ihre Wurzeln in der Flagge von Kuba: | The flag of Puerto Rico has its roots in the flag of Cuba: |
| Die Flagge Kubas wurde im Jahre 1849 – exakt im gleichen Design wie die heutige Flagge von Puerto Rico – von dem venezoelanischen General Narciso López in seinem Neu Yorker Exil für den kubanischen Freiheitskampf entworfen. Im gleichen Jahr wurden die Farben dieser Flagge von dem kubanischen Dichter Miguel Teurbe Tolon umgekehrt. Diese Flagge wurde erstmals bei dem großen anti-spanischen Aufstand in Kuba im Jahre 1850 benutzt. | It was
created for Cuba in the year 1849 – in exactly the same design like the
today's flag of Puerto Rico – by the Venezuelan General Narciso López in his
New York exile for the Cuban fight for freedom. In the same year the colours of the flag became inverted by the Cuban poet Miguel Teurbe Tolon. That Cuban flag was in use for the first time at the great Anti-Spanish riot in Cuba in the year 1850. |
| Das Dreieck ist freimaurerischen Ursprungs und steht für Freiheit, Gleichheit und Brüderlichkeit. Die Farbe Rot steht für das im Kampf gegen die Spanier vergossene Blut, und Weiß steht für Reinheit, Gleichheit und Frieden. Der weiße Stern (La Estrella Solitaria) ist ein Symbol für Freiheit und Gleichheit, und sollte ursprünglich ausdrücken, dass den USA ein weiterer Staat hinzugefügt werden sollte. Auch das Rot, Weiß und Blau sind eindeutige Bezüge auf die "Stars and Stripes" der USA. | The red
triangle of Masonic origin and stands for freedom, equality and
brotherliness. The colour red stands for the in the struggle against the
Spaniards given blood and white stands for purity, equality and peace. The white star (La Estrella Solitaria) is a symbol for freedom and equality, and should initially express that there has to add a further state to the USA. Red, white and blue are also clear references to the "Stars and Stripes" of the USA. |
| Die puertorikanische Abteilung der Kubanischen Revolutionären Partei nahm aus Solidarität mit dem Freiheitskampf der Kubaner gegen die Spanier im Jahre 1890 eine Flagge an, die in ihrer Gestaltung der Flagge Kubas entsprach, jedoch wurden die Farben umgekehrt um eine besondere, nationale und puertorikanische Identität zu zeigen. | The Puertorican division of the Cuban Revolutionar Party adoped because of solidarity with the fight for freedom of the Cubans against the Spanish in the year 1890 a flag, which corresponded in its designing to the flag of Cuba, but the colours became inverted to show a special, national and Puertorican identity. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind per Gesetz von 1952 festgelegt, allerdings nur als als Rot und Blau, ohne genauer zu spezifizieren. Seit dem wurde das Dreieck in einem dunklen Blau dargestellt, welches dem der Flagge der Vereinigten Staaten ähnelte. Seit 1995 werden jedoch hellere Blautöne verwendet. Die heutigen Farben scheinen aus der Praxis heraus definiert zu sein und könnten folgendermaßen dargestellt werden: Rot = pt 1788, Blau = pt 2728. Die Flagge ist in der Praxis in unterschiedlichsten Farbtönen anzutreffen. |
The colours of the flag
are defined by law in 1952, but only as red and blue, without specifying
more precisely. Since then, the triangle has been depicted in a dark blue
similar to that of the United States flag. Since 1995, however, lighter
shades of blue have been used. Today's colours seem to be defined from practice and could be represented as follows: Red = pt 1788, Blue = pt 2728. The flag is found in practice in a wide variety of shades. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D), Wikipedia (ES) | |
| Die Flagge (und gleichzeitig das Logo) der Reederei DSD wurde im Jahre 1903 im Rahmen eines firmeninternen Wettbewerbs vom Steuermann Ommund Thingbø geschaffen, der den Wettbewerb gewann. Die Schiffe der DSD wurden entsprechend beflaggt und auch die Schornsteine bekamen drei rote Ringe. Puerto Rico, das im Jahre 1900 als nicht-organisiertes Territorium an die USA angegliedert worden war beanspruchte die Rechte am Design der Flagge für sich. Man ging dabei davon aus, dass das Design das Gleiche ist und in Puerto Rico schon im Jahre 1895 geschaffen worden war und damit ältere Rechte vorlägen. | The flag
(and in the same way the logo) of the shipping company DSD was created in
the year 1903 on the occasion of an internal competition by the helmsman
Ommund Thingbø, who won the competition. The ships of the DSD were flaged
accordingly and the chimneys were also painted with three red rings. Puerto Rico, which became affiliated to the United States in 1900 as a non-organized territory, claimed the rights for the design of the flag. It was assumed that the design was the same and that it had already been created in Puerto Rico in the year 1895 and thus had older rights. |

Quelle/Foto: Volker Preuß, DSD-Shipping |
Det Stavangerske Dampskibsselskap (DSD) Die Flagge der DSD, links auf ihrem Gebäude im Hafen von Stavanger in Norwegen am 23.08.2018, oben als Grafik umgesetzt. – On the left the flag of the DSD on its building in the port of Stavanger in Norway on 23rd of August in 2018. Above it is realized as a graphic. |
| In den 1950-er Jahren forderte Puerto Rico das erste Mal über das norwegische Außenministerium die Änderung der Flagge. Auf dem Rechtsweg wurde entschieden, dass es keinen Verstoß gegen internationale Regeln gibt, auch wenn die Flagge viele Jahre vor der Einführung der DSD in Puerto Rico in Gebrauch war, denn diese Flagge wurde erst am 24.07.1952 im Zusammenhang mit der neuen Verfassung offiziell eingeführt, als Puerto Rico ein Assoziierter Freistaat der USA (auch Dominion, oder Commonwealth) wurde. Jedoch ist Puerto Rico bis heute kein unabhängiger und souveräner Staat, und seine Flagge darf auf öffentlichen Gebäuden auch nur zusammen mit der Flagge der USA gehisst werden. Ebenso weicht das Design bei DSD und Puerto Rico in einem nicht unwichtigen Detail voneinander ab. Der weiße Stern im blauen Dreieck ist bei Puerto Rico etwas kleiner und gerade, bei DSD etwas größer und schräg. | In the
years of 1950, Puerto Rico first claimed via the Norwegian Ministry of
Foreign Affairs to change the flag.
A court ruled that there was no break of international rules, even if the flag was in use many years before its launch in the DSD in Puerto Rico, where this flag was officially approved not until 24th of July in 1952 in occasion of the introduction of a new constitution, when Puerto Rico became an Associated Free-State of the United States (also called Dominion, or Commonwealth). However, Puerto Rico is not an independent and sovereign state until today, and its flag may be hoisted on public buildings only along with the flag of the United States. Further, the design of DSD and Puerto Rico differs from each other in a not unimportant detail. The white Star in the blue triangle in Puerto Rico is slightly smaller and straight, at DSD slightly larger and slanted. |
| Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Puerto Rico – coat of arms of Puerto Rico, Quelle/Source: unbekannt/unknown |
| Das Hauptelement des Wappens von Puerto Rico ist das Lamm Gottes mit einer Kreuzfahne auf einem grünen Schild, es sind die Symbole von Johannes dem Täufer. Das Grün repräsentiert die Vegetation der Insel. Obwohl Puerto Rico ein US-Territorium ist, weist der Schild weiterhin Elemente auf, die an die Präsenz Spaniens in der Neuen Welt erinnern. Es wuerde 1511 gestiftet, 1899 abgeschafft und 1905 wiederhergestellt. Die aktuelle Version wurde von der Regierung von Puerto Rico am 03.06.1976 offiziell eingeführt. Im Schildrand wechseln sich Felder ab, mit der Heraldik von Kastilien, León, Kastilien-León und Jerusalem. Links und rechts des Wappens erscheinen die Buchstaben "F" (Ferdinand II. von Aragon) und "Y" (Ysabel, Isabella I. von Kastilien). Das Spruchband zeigt den Spruch: "JOANNES EST NOMEN EJUS" → "Johannes ist sein Name". Ein Verweis auf Johannes den Täufer, aber auch auf den alten Namen der Insel: "San Juan Bautista". |
The main element of
Puerto Rico's coat of arms is the Lamb of God with a cross flag on a green
shield, they are the symbols of John the Baptist. The green represents the
vegetation of the island. Although Puerto Rico is a US territory, the shield still has elements that recall Spain's presence in America. It was awarded in 1511, abolished in 1899 and restored in 1905. The current version was officially adopted by the government of Puerto Rico on 3rd of June in 1976. In the shield border, fields alternate with the heraldry of Castile, León, Castile-León and Jerusalem. To the left and right of the coat of arms appear the letters "F" (Ferdinand II. of Aragon) and "Y" (Ysabel, Isabella I. of Castile). The banner shows the saying: "JOANNES EST NOMEN EJUS" → "John is his name". A reference to John the Baptist, but also to the old name of the island: "San Juan Bautista". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN) | |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Die Lage des Landes – position of the Country: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1493 ·
Entdeckung der Insel durch Christoph Kolumbus 1508 · beginnende Kolonisierung durch Spanien unter Juan Ponce de León 1511 · Indianeraufstand, Ausrottung der Indianer 1518 · Einfuhr von Negersklaven 1521 · Gründung von San Juan (damals: San Juan Bautista de Puerto Rico) 1815 · Puerto Rico wird Handelsfreiheit gewährt 1835 · anti-kolonialer Aufstand 1838 · anti-kolonialer Aufstand 1867–1868 · anti-kolonialer Aufstand 1873 · Abschaffung der Sklaverei 1897 · Gewährung innerer Autonomie 21.04.–10.12.1898 · Spanisch-Amerikanischer Krieg (01.05.1898: Sieg der USA in der Seeschlacht in der Manila-Bucht, 12.06.1898: die Philippinen proklamieren die Unabhängigkeit, Juni 1898: Eroberung von Puerto Rico durch US-amerikanische Truppen, 03.07.1898: Sieg der USA in der Seeschlacht von Santiago de Cuba, 13.08.1898: US-Truppen besetzen Manila, 14.08.1898: Kapitulation der spanischen Truppen auf den Philippinen) 10.12.1898 · Frieden von Paris, Spanien tritt die Philippinen, Kuba, Puerto Rico und Guam an die USA ab 1900 · Angliederung an die USA als "nicht-organisiertes Territorium" 1917 · Gewährung der Staatsbürgerschaft der USA und von beschränkter Selbstverwaltung (Jones-Act) 1926 · anti-kolonialer Aufstand 1936–1937 · anti-kolonialer Aufstand 1948 · Erweiterung der beschränkten Selbstverwaltung (Recht zur Wahl eines eigenen Gouverneurs) 1950 · bewaffneter, anti-kolonialer Widerstand 1952 · neue Verfassung, Puerto Rico wird Assoziierter Freistaat der USA (Dominion, Commonwealth) 1967 · Volksabstimmung, Ablehnung der Unabhängigkeit mit großer Mehrheit 14.12.1973 · die UNO erkennt das Recht Puerto Ricos auf Unabhängigkeit an 13.12.1998 · Volksabstimmung: 50,2% lehnen eine Eingliederung in die USA als 51. Bundesstaat ab |
History: |
| 1493 ·
discovery of the island by Christoph Columbus 1508 · beginning colonization by Spain under Juan Ponce de León 1511 · Indian revolt, eradication of the Indians 1518 · import of Negro slaves 1521 · foundation of San Juan (at that time: San Juan Bautista de Puerto Rico) 1815 · Puerto Rico becomes granted freedom of trade 1835 · anti-colonial revolt 1838 · anti-colonial revolt 1867–1868 · anti-colonial revolt 1873 · abolition of slavery 1897 · granting of internal autonomy 21st of April to 10th of December 1898 · Spanish-American War (1st of May 1898: victory of the USA in the sea-battle in the Manila Bay, 12th of June 1898: the Philippines proclaim the independence, June 1898: conquest of Puerto Rico by US-American troops, 3rd of July 1898: victory of the USA in the sea-battle of Santiago de Cuba, 13th of August 1898: US troops occupy Manila, 14th of August 1898: surrender of the Spanish troops on the Philippines) 10th of December 1898 · Peace of Paris, Spain cedes the Philippines, Cuba, Puerto Rico and Guam to the USA 1900 · affiliation to the USA as "non-organized territory" 1917 · granting of the citizenship of the USA and of limited self administration (Jones-Act) 1926 · anti-colonial revolt 1936–1937 · anti-colonial revolt 1948 · extension of the limited self administration (right for the election of an own governor) 1950 · armed, anti-colonial resistance 1952 · new constitution, Puerto Rico becomes an associated free state of the USA (Dominion, Commonwealth) 1967 · plebiscite, rejection of the independence with a big majority 14th of December 1973 · the UNO recognizes the right of Puerto Rico for its independence 13th of December 1998 · plebiscite: 50,2% reject an incorporation in the USA as 51st federal state |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Ursprung des Namens der Insel liegt im Namen der im Jahre 1521 gegründeten Stadt " San Juan Bautista de Puerto Rico", dem heutigen "San Juan". Der Name der Stadt übertrug sich sehr schnell auf die ganze Insel. "Puerto Rico" heißt "reicher Hafen". | The name of the island has its roots in the name of the in 1521 established town of " San Juan Bautista de Puerto Rico", the today’s "San Juan". The name of the town became very quickly transfered over the whole island. "Puerto Rico" means "rich harbor". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |