Westindische Föderation |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Westindische Föderation |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
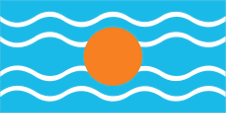 |
1958–1962, Flagge der Westindischen Föderation – flag of the Federation of the West Indies, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1958–1962, Flagge des Generalgouverneurs – flag of the Governor General, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
seit/since 1999, Flagge des Cricket Teams der Westindischen Inseln – flag of West Indies Cricket Team, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN), www.gettyimages.ca |
| Großbritannien fasste nahezu alle seine Besitzungen im Bereich der Karibik am 03.01.1958 zur "Westindischen Föderation" zusammen. Dieses politische Projekt war ein Versuch die Verwaltung zusammenzufassen und einen Staat nach dem Vorbild Kanadas zu schaffen, aber auch um den Unabhängigkeitsbestrebungen der zugehörigen Inseln und Kolonien entgegenzuwirken. Jedoch kam es zu Eifersüchteleien zwischen großen und kleinen Inseln, bis hin zum offenen Streit. Jamaika initiierte 1961 eine erfolgreiche Volksabstimmung für das Verlassen der Westindischen Föderation, in Trinidad und Tobago wurde das auch angestrebt, so dass die Föderation am 31.05.1962 aufgelöst wurde. Jamaika wurde am 06.08.1962 von Großbritannien unabhängig und Trinidad und Tobago am 31.08.1962. Die Flagge der "Westindische Föderation" war ein hellblaues Flaggentuch mit vier waagerechten weißen Wellenlinien und einer goldenen Scheibe in der Mitte. Sie symbolisierte die Sonne über der Karibischen See. Über den Farbton des Blau ist man sich im Zweifel, es wird oft das übliche Britische Heraldikblau angenommen. Eine Zeitgenössische Beschreibung nennt jedoch ein "kaiserliches Blau" was Hellblau wäre und auch viele zeitgenössische Drucke zeigen dieses helle Blau. Bis heute haben die Westindischen Inseln ihr eigenes, gemeinsames Cricket Team, das auch eine eigene Flagge hat. Dazu gehören: Antigua und Barbuda, Barbados, Dominika, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaika, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent und die Grenadinen, Trinidad und Tobago, Saint Kitts, Nevis, Anguilla, Montserrat, Britische Jungferninseln, Sint Maarten, US-amerikanische Jungferninseln. |
On 3rd of January in
1958, United Kingdom merged almost all of its possessions in the Caribbean
to form the "Federation of the West Indies". This political project was an attempt
to unify the administration and to create a state modelled on Canada, but
also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and
colonies. However, jealousies arose between the large and small islands and even led to open dispute. In 1961, Jamaica initiated a successful referendum to leave the West Indies Federation, which was also sought in Trinidad and Tobago, with the result that the federation was dissolved on 31st of in May 1962. Jamaica became independent from United Kingdom on 6th of August and Trinidad and Tobago on 31st of August in 1962. The flag of the "Federation of the West Indies" was a light blue bunting with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the centre. It symbolised the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the colour shade of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldic blue. However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue", which would be light blue, and many contemporary prints also show this light blue. To this day, the West Indies have their own joint cricket team, which also has its own flag. These include: Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Saint Kitts, Nevis, Anguilla, Montserrat, British Virgin Islands, Sint Maarten, US Virgin Islands. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN), alamy.com, Volker Preuß | |
|
interaktive Landkarte der Westindischen Föderation – interactive Map of the Federation of the West Indies |
 |
| Quelle/Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Antigua Barbados Caymaninseln (als Teil Jamaikas) Dominika Grenada Jamaika Montserrat St. Kitts, Nevis Anguilla St. Lucia St. Vincent Trinidad und Tobago Turks- und Caicos-Inseln (als Teil Jamaikas) |
Antigua Barbados Cayman Islands (as part of Jamaica) Dominica Grenada Jamaica Montserrat St. Kitts, Nevis Anguilla St. Lucia St. Vincent Trinidad and Tobago Turks and Caicos Islands (as part of Jamaica) |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN) | |
|
Großbritannien fasste nahezu alle seine Besitzungen im Bereich der Karibik am 03.01.1958 zur "Westindischen Föderation" zusammen. Dieses politische Projekt war ein Versuch die Verwaltung zusammenzufassen und einen Staat nach dem Vorbild Kanadas zu schaffen, aber auch um den Unabhängigkeitsbestrebungen der zugehörigen Inseln und Kolonien entgegenzuwirken. Jedoch kam es zu Eifersüchteleien zwischen großen und kleinen Inseln, bis hin zum offenen Streit. Es mussten viele Zugeständnisse an die einzelnen Inseln gemacht und häufig mehr Selbstverwaltung zugestanden werden. Jamaika initiierte 1961 eine erfolgreiche Volksabstimmung für das Verlassen der Westindischen Föderation, in Trinidad und Tobago wurde das auch angestrebt, so dass die Föderation am 31.05.1962 aufgelöst wurde. Jamaika wurde am 06.08.1962 von Großbritannien unabhängig und Trinidad und Tobago am 31.08.1962.
03.01.1958
· Bildung der Westindischen Föderation (unter Zusammenfassung der
Besitzungen St. Kitts/Nevis/Anguilla, Montserrat, Antigua, Dominika,
Barbados, Caymaninseln, Grenada, Jamaika, St. Lucia, St. Vincent, Trinidad
und Tobago, Turks- und Caicos-Inseln) |
|
On 3rd of January in 1958, United Kingdom merged almost all of its possessions in the Caribbean to form the "West Indies Federation". This political project was an attempt to unify the administration and to create a state modelled on Canada, but also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and colonies. However, jealousies arose between the large and small islands and even led to open dispute. Many concessions had to be made to the individual islands and often more self-government had to be granted. In 1961, Jamaica initiated a successful referendum to leave the West Indies Federation, which was also sought in Trinidad and Tobago, with the result that the federation was dissolved on 31st of in May 1962. Jamaica became independent from United Kingdom on 6th of August and Trinidad and Tobago on 31st of August in 1962. 3rd of January 1958
· establishment of the Federation of the West Indies (by unification of the
possessions of St. Kitts/Nevis/Anguilla, Montserrat, Antigua, Dominica,
Barbados, Cayman Islands, Grenada, Jamaica, St. Lucia, St. Vincent, Trinidad
and Tobago, Turks and Caicos Islands) |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN) |
| Der Name "Westindische Föderation" widerspiegelt die geographische Lage und die föderale Struktur des Landes. Manchmal wird es auch als "Karibische Föderation" oder "Britische Karibische Föderation" bezeichnet. | The name "Federation of the West Indies" mirrors the geographic position and the federal structure of the country. Sometimes it is also called "Caribbean Federation" or "British Caribbean Federation". |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |