Lettland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Lettland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D)  |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
Präsidentenflagge – flag of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
historische Flaggen / Flaggengeschichte
|
|
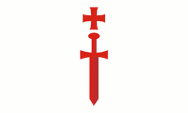 |
1230–1237, Flagge des Schwertbrüderordens – flag of the Order of the Sword Brothers, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
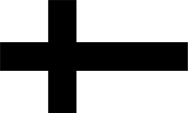 |
1237–1561, Flagge des Deutschen Ordens – flag of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1595–1621, |
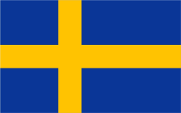 |
1621–1721, Flagge von Schweden – flag of Sweden, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1721–1795, |
 |
1795–1858, Nationalflagge von Russland – national flag of Russia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1858–1915, Nationalflagge von Russland – national flag of Russia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
ca. 1870-1916, inoffizielle Nationalflagge – unofficial national flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt |
 |
1916, inoffizielle Nationalflagge – unofficial national flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1916–1917, inoffizielle Nationalflagge – unofficial national flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt |
 |
1918–1940, Nationalflagge – national flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939  |
 |
1918–1940, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
1918–1940, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
Lotsen(ruf)flagge – pilot flag (Pilot Call flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 Diese Art Flaggen wurde im 20. Jahrhundert abgeschafft, heute gilt – This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is: |
 |
1918–1920, Flagge der Lettischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik – flag of the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia.de |
 |
1940–1953, Flagge der Lettischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik – flag of the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach by: World Statesmen |
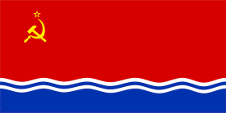 |
1953–07.10.1988 |
|
siehe auch – look also: Flaggengeschichte der Sowjetrepubliken der UdSSR – flag history of the soviet republics of the USSR |
|
|
|
|
 |
seit/since 1945(?), Flagge der Deutsch-Balten – flag of the Baltic Germans, Quelle/Source, nach/by: photo, www.db-kulturwerk.de |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge Lettlands zeigt einen schmalen weißen Streifen in der Mitte eines karminroten Flaggentuches (Pantone 201 C), so dass drei horizontale Streifen im Verhältnis 2:1:2 entstehen. Das Rot steht für das Blut, das für das Erreichen der Selbständigkeit in der Vergangenheit vergossen wurde. Das Weiß steht für das Recht, die Gerechtigkeit, die Wahrheit und die Ehre des Volkes. | The flag
of Latvia shows a slender white stripe in the middle of a carmine bunting
(Pantone 201 C). In this way arise three horizontal stripes in ratio 2:1:2. The red stands for the blood which was given for the achieve
of the independence in the past. |
| Eine rote Flagge mit einem weißen Streifen hat in Lettland eine sehr lange Tradition. Eine solche Flagge wurde bereits im 13. Jhd. erstmals erwähnt. | A red flag with a white stripe has a long tradition in Latvia. Such a flag was mentioned for the first time already in the 13th century. |
| Die Livländische Reimchronik aus dem 14. Jahrhundert berichtet über ein Gefecht im Jahre 1279 in welchem Lettische Stämme aus der Gegend von Wenden (Cesis) eine solche Flagge bei sich trugen. | The Rhymed Chronicle of Livonia from the 14th century reports about a battle in the year 1279, in which Latvian tribes from Wenden (Cesis) beared such a flag. |
| Eine Legende besagt, dass ein tödlich verwundeter Häuptling der Letten auf ein weißes Laken gebettet worden war. Dort wo er lag bliebt das Laken weiß, jedoch links und rechts von ihm wurde das Laken von seinem Blut getränkt. Ab dem nächsten Gefecht, dass wie alle folgenden siegreich verlief, wurde das Laken als Flagge benutzt, und von allen Lettischen Stämmen als Flagge akzeptiert. | A legend
tells about to a mortally wounded Latvian chief who was laid on a white
sheet. There where he was lying the sheet remained white, but to the left
and to the right the sheat was stained with his blood. From the next battle on, which was victorious like all the following, this sheet was used as a flag, and got accepted by all Latvian tribes as flag. |
| Als Flagge des Volkes tauchte sie über die Jahrhunderte immer wieder auf, zuletzt 1915, während des Ersten Weltkriegs. Im Zusammenhang mit der sich ankündigenden Unabhängigkeit des Landes sollte diese Flagge die Nationalflagge werden, jedoch gab es Bedenken, das die Flagge mit derjenigen von Österreich verwechselt werden könnte. So hat der lettische Künstler Ansis Cirulis im Mai des Jahres 1917 vorgeschlagen Karmesinrot anstelle von normalem Rot zu verwenden. Diese Flagge wurde am 18.11.1918 offiziell für Lettland angenommen. Beschlüsse des Parlaments bestätigten das am 15.06.1921 und offenbar noch einmal am 20.01.1923. | As flag
of the people it arises in the course of the centuries again and again,
finally in 1915 during the First World War. In context with the signs of the
coming independence of the country this flag should be the national flag,
but there were qualms that this flag could be confounded with the flag of
Austria. Because of that the Latvian artist Ansis Cirulis proposed in May of
the year 1917 to use crimson instead of normal red. This flag was officially adoped on 18th of November in 1918 for Latvia. Resolutions of the Parliament confirmed that on 15th of June in 1921 and apparently again on 20th of January in 1923. |
| Diese Flagge wurde am 07.10.1988 als Nationalflagge und am 20.02.1990 auch als Staatsflagge wieder eingeführt. Die tiefrote Farbe soll angeblich auf charakteristische, landestypische Färbemittel zurückgehen. | This flag became re-introduced on 7th of October in 1988 as national flag and on 20th of February in 1990 also as state flag. The deep red colour should ostensibly go back to characteristic, locally typical dye-substances. |
| Zwischen 1940 und 1941, sowie 1944 und 1953 verwendete Lettland, als Lettische Sozialistische Sowjetrepublik und Teil der Sowjetunion, ein sowjetisches Einheits-Modell. Am 17.01.1953 wurde eine neue Sowjetflagge für Lettland angenommen. Es war ein Entwurf von dem Maler Arturs Lapinsch. Logischerweise zeigte diese Flagge wieder Stern, Hammer und Sichel in Gold auf rotem Grund, am unteren Ende der Flagge jedoch ein dunkelblauer Streifen, vom roten Feld durch eine Wellenline getrennt. Ab dem 07.10.1988 war sie nur noch als Staatsflagge gültig, und wurde am 20.02.1990 endgültig abgeschafft. | Between
1940 and 1941, as well as 1944 and 1953 used Latvia as Latvian Socialistic
Soviet Republic and a part of the Soviet Union a soviet unity-model.
On 17th of January in 1953 was adoped a new Soviet flag for Latvia. It was a design by the painter Arturs Lapinsch. Of course that flag showed again star, hammer and sickle in gold on red ground, but there was on the lower end of the flag a dark blue stripe, separated from the red field by a wave line. Since the 7th of October in 1988 it was still valid as state flag, and was abolished ultimately on 20th of February in 1990. |
| Quelle/Source: Jürgen Kaltschmitt, Volker Preuß, Wikipedia (EN), Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen Lettlands – coat of arms of Latvia, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
historische Wappen – historical Coat of Arms: |
|
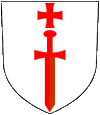 |
1230–1237, Wappenschild des Schwertbrüderordens – blazon of the Order of the Sword Brothers, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1237–1561, Wappenschild des Deutschen Ordens – blazon of the Teutonic Order (teutonic knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
Wappen von Kurland – coat of arms of Kurland, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
ca.1880–1918, Wappen von Livland – coat of arms of Livonia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
Wappen von Lettgallen – coat of arms of Latgale, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das lettische Staatswappen wurde von Rihards Zarins geschaffen und im Jahre 1921 eingeführt. Es war bis zur Machtübernahme durch die Bolschewisten im Jahre 1940 gültig, und wurde unter deren Herrschaft durch ein sowjetisches Modell ersetzt. Im Zusammenhang mit dem Erreichen der Unabhängigkeit von der Sowjetunion wurde das Wappen von 1921 am 27.02.1990 wieder eingeführt. | The
Latvian coat of arms was created by Rihards Zarins and introduced in the
year 1921. It was valid until the takeover by the Bolshevists in the year
1940 and was substituted under their rule by a soviet model. In context with the achieve of the independence from the Soviet Union the coat of arms of the year 1921 was intoduced again on 27th of February in 1990. |
| Es zeigt einen geteilten und halbgespaltenen Schild. In der oben Hälfte eine goldene, aufgehende Sonne mit siebzehn Strahlen auf blauem Grund. Es ist ein Symbol für ganz Lettland und seine siebzehn Landkreise. Im Feld unten links ein roter Löwe auf Silber. Es steht für die Landschaften Kurland und Semgallen. Im Feld unten rechts ein silbernes Fabeltier (Greif) mit einem Schwert auf Rot. Es steht für die Landschaften Livland und Lettgallen. Oberhalb des Schildes befinden sich drei goldene Sterne. Sie stehen für die historischen Landschaften und Landesteile Lettlands: das Herzogtum Kurland, Livland und die Landschaft Lettgallen. Schildhalter sind der rote Löwe und der silberne Greif aus dem Schild. Sie stehen auf Eichenzweigen. Unterhalb ein Band in den Landesfarben. | It shows
a divided and half clefted shield. In the upper half a golden rising sun
with seventeen beams on blue ground. This is a symbol for whole Latvia and
its seventeen districts. In the field left below a red lion on silver. It
stands for the countrysides Kurland and Semigallia. In the field right below
a silvery fable beast (griffin) with a sword on red. It stands for the
countrysides Livonia and Latgale. Above the shield are positioned three golden stars. The stars stand for the historical countrysides and landscapes of Latvia: the Duchy of Kurland, Livonia and the countryside of Latgale. Shield holders are the red lion and the silvery griffin from the shield. They stand on oak twigs. Below a banner in the colours of the country. |
| Während des Zweiten Weltkriegs, in der Zeit der deutschen Besetzung zwischen 1941 und 1944 hatte Lettland offiziell keine eigenen Hoheitszeichen. Es gehörte zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, in dem die Staaten den Baltikums und Teile des heutigen Nordwestens von Weißrussland zusammengefasst waren. | During the Second World War – in the time of the German occupation between 1941 and 1944 – Latvia had officially no own national emblems. It belonged to the Empire's Commissionership of Ostland, in which have been summarized the countries of the Balticum and parts of the today's northwest of White Russia (Belarus). |
| Die Lettische Legion, die im Zweiten Weltkrieg freiwillig an der Seite des Deutschen Reiches gegen die Sowjetunion kämpfte trug als Ärmelabzeichen einen roten Schild mit einem schmalen weißen Diagonalstreifen. | The Latvian Legion, which voluntary fought on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union in the Second World War used as sleeve-insignia a red shield with a slender white diagonal stripe. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Nationalflaggen der Welt, Avantgarde für Europa | |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Der Löwe in der Heraldik". Ausführungen, Varianten, Entwicklung sowie Panther und Leoparden. |
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde
– aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1918–1940, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1993–2000, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel (Nationalgarde – National Guard) Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Landkarte des Baltikums – Map of the Balticum: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 9. Jhd. ·
Besiedlung durch die ostbaltischen Stämme der Lettgallen, Selonen,
Semgallen, Kuren und Liven 1202 · Gründung des "Schwertbrüderordens" in Dünamünde 1230 · Eroberung Kurlands, Livlands, Lettgallens und Semgallens durch den Schwertbrüderorden 1236 · Niederlage des Schwertbrüderordens gegen die Litauer 1237 · Vereinigung des Schwertbrüderordens mit dem Deutschen Orden, Kurland, Livland, Lettgallen und Semgallen kommen als Livländischer Bund mit einem eigenen Ordensmeister an den Staat des Deutschen Ordens 1346 · Estland wird durch den Deutschen Orden von Dänemark abgekauft und dem Livländischen Bund des Deutschen Ordens angegliedert 1558–1595 · Livländischer Krieg, der livländische Ordensmeister des Deutschen Ordens wandelt Kurland und Semgallen in ein Herzogtum als polnisches Lehen um, Estland musste an Schweden und teilweise an Dänemark abgetreten werden, Livland und Lettgallen kamen direkt an Polen 1621 · Schweden erobert Livland 1629 · Livland kommt offiziell an Schweden 1710 · Nordischer Krieg, Russland erobert Livland 1721 · Frieden von Nystad, Livland und Estland kommen an Russland, Kurland, Semgallen und Lettgallen bleiben bei Polen 1795 · Aufteilung Polens → Kurland, Semgallen und Lettgallen kommen zu Russland 19. Jhd. · Entstehen der lettischen Nationalbewegung 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg: 1915 das Deutsche Reich erobert Kurland und Semgallen, 1918 das Deutsche Reich erobert Lettgallen und Livland 07.11.1917 · bolschewistische Revolution in Russland, Machtergreifung durch die Sowjets 03.03.1918 · Sowjetrussland kapituliert gegenüber dem Deutschen Reich, Friedensvertrag von Brest-Litovsk, Herausbildung eines lettischen Staates (einschließlich Kurland, Semgallen, Lettgallen und dem Süden Livlands) 18.11.1918 · Lettland erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit von Sowjetrussland, Proklamation der Republik Lettland, Proklamation der Lettischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik, Bürgerkrieg bis 1920 18.03.1921 · Friede von Riga, Sowjetrussland erkennt die Unabhängigkeit Lettlands an 1934 · Errichtung der Präsidialdiktatur durch K. Ulmanis 23.08.1939 · deutsch-sowjetischer Nichtangriffspakt, Lettland wird sowjetische Interessensphäre und von der Sowjetunion besetzt, die seit dem 12. Jahrhundert im Land lebenden Deutsch-Balten (auch Baltendeutsche genannt), dürfen – wenn sie wollen – das Land in Richtung Deutsches Reich verlassen 12.07.1940 · Proklamation der Lettischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik (LSSR) 05.08.1940 · Aufnahme der LSSR in die Sowjetunion, Deportation von Tausenden von Einwohnern nach Sibirien 1939–1945 · Zweiter Weltkrieg: Juni/Juli 1941 Eroberung Lettlands durch deutsche Truppen, Lettland kommt zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, 36.000 Letten kämpfen freiwillig in einer Lettischen Legion an der Seite des Deutschen Reiches gegen die Sowjetunion, Dezember 1944 Eroberung Lettlands (außer Kurland) durch sowjetische Truppen, Flucht und Vertreibung der allermeisten Deutsch-Baltischen Einwohner, viele werden ermordet oder sterben auf der Flucht, 09.05.1945 die deutschen Truppen in Kurland kapitulieren, Lettland wird wieder LSSR und wird der Sowjetunion wieder angegeliedert, gewaltsame Russifizierung, Deportation von Tausenden von Letten nach Sibirien 1988 · Gründung der "Lettischen Volksfront“ 29.07.1989 · Unabhängigkeitserklärung 04.05.1990 · Proklamation der Republik Lettland 06.09.1991 · die Sowjetunion erkennt die Unabhängigkeit Lettlands an 1993 · erste Freie Wahlen 1994 · Abzug der russischen Truppen März 2004 · Lettland wird Mitglied der NATO Mai 2004 · Lettland wird Mitglied der Europäischen Union |
History: |
| 9th cent.
· settlement by the East Baltic tribes of the Lettgalles, Selones,
Semgalles, Kures and Lives 1202 · establishment of the "Order of the Sword Brothers" in Duenamuende 1230 · conquest of Kurland, Livonia, Latgale and Semigallia by the Order of the Sword Brothers 1236 · defeat of the Order of the Sword Brothers against the Lithuanians 1237 · unification of the Order of the Sword Brothers with the Teutonic Order, Kurland, Livonia, Latgale and Semigallia come as Livonian Federation with an own Master to the State of the Teutonic Order 1346 · Estland gets purchased by the Teutonic Order from Denmark and incorporated to the Livonian Federation of the Teutonic Order 1558–1595 · Livonian War, the Livonian Master of the Teutonic Order transforms Kurland and Semigallia in a duchy as a Polish enfeoffment, Estland was to cede to Sweden and partially to Denmark, Livonia and Latgale came directly to Poland 1621 · Sweden conquers Livonia 1629 · Livonia comes officially to Sweden 1710 · Nordic War, Russia conquers Livonia 1721 · Peace of Nystad, Livonia and Estland come to Russia, Kurland, Semigallia and Latgale remain at Poland 1795 · division of Poland → Kurland, Semigallia and Latgale come to Russia 19th cent. · nascence of the Latvian national movement 1914–1918 · First World War: 1915 the German Empire conquers Kurland and Semigallia, 1918 the German Empire conquers Latgale and Livonia 7th of November 1917 · bolshevistic revolution in Russia, seizure of power by the Soviets 3rd of March 1918 · Soviet Russia capitulates towards the German Empire, Peace Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, development of an Latvian state (including Kurland, Semigallia, Latgale and the south of Livonia) 18th of November 1918 · Latvia declares its independence from Soviet Russia, proclamation of the Republic of Latvia, proclamation of the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic, civil war until 1920 18th of March 1921 · Peace of Riga, Soviet Russia recognizes the independence of Latvia 1934 · establishment of the presidial dictatorship by K. Ulmanis 23rd of August 1939 · German-Soviet non aggression pact, Latvia becomes a soviet sphere of interest and gets occupied by the Soviet Union, the Baltic Germans who had been living in the country since the 12th century were allowed to leave the country for the German Reich if they wished to do so 12th of July 1940 · proclamation of the Latvian Socialistic Soviet Republic (LSSR) 5th of August 1940 · inclusion of the LSSR into the Soviet Union, deportation of thousands of inhabitants to Sibiria 1939–1945 · Second World War: June/July 1941 conquest of Latvia by German troops, Latvia comes to the empire`s commissionership of Ostland, 36.000 Latvians fight voluntary in a Latvian Legion on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union, December 1944 conquest of Latvia (except Kurland) by soviet troops, escape and expulsion of the vast majority of German-Baltic inhabitants, many are murdered or die while fleeing, 9th of May 1945 the German troops in Kurland surrender, Latvia becomes once more LSSR and incorporated into the Soviet Union again, forcible russification, deportation of thousands of Latvians to Sibiria 1988 · foundation of the "Latvian People's Front“ 29th of July 1989 · declaration of independence 4th of May 1990 · proclamation of the Republic of Latvia 6th of September 1991 · the Soviet Union recognizes the independence of Latvia 1993 · first free elections 1994 · withdrawal of the Russian troops March 2004 · Latvia becomes member of the NATO May 2004 · Latvia becomes a member in the European Union |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97 |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Die Bezeichnung "Lettland" ist erst mit der Entstehung der lettischen Nationalbewegung und der Lösung von der russischen Herrschaft aufgekommen. Das Land besteht aus vier historischen Landschaften, welche die Heimat von vier historischen Völkern waren: Kurland (lettisch: Kurzeme), Semgallen (lettisch: Zemgale) Lettgallen (lettisch: Latgale) und Livland (lettisch: Vidzeme). Das Volk der "Letten", welches sich selbst "Latvieschi" nennt, entstand durch die Verschmelzung der Stämme der Lettgaller und der Semgaller. Die Kuren sind in den Letten aufgegangen, und die Liven fast ausgestorben. So kam es, dass die vier Landschaften mehrheitlich von Letten bewohnt waren, und zu einem Lettland vereinigt wurden. | The
designation "Latvia" was usual not until the nascence of the Latvian
national movement and the detachment from the Russian control. The country
consists of four historical countrysides, which were the home of four
historical peoples: Kurland (Latvian: Kurzeme), Semigallia (Latvian: Zemgale)
Latgale (Lettgallen) and Livonia (Latvian: Vidzeme). The people of the "Latvians", which names itself "Latvieshi", came into beeing by the fusion of the tribes of the Lettgalles and the Semgalles. The Kures are dissolved into the Latvians, and the Lives are nearly extincted. In this way it came, that the four countrysides were mostly inhabited by Latvians and became united to one Latvia. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |
historische Landkarten zur Geschichte des Baltikums
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|