Estland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Estland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National- und Handelsflagge |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, |
 |
Flagge des Grenzschutzes |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the president, |
 |
Flagge des Verteidigungsministers |
 |
Flagge des Oberbefehlshabers |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
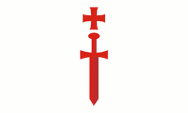 |
1230–1237, Flagge Schwertbrüderorden – flag of the Order of the Sword Brothers (Livonian Order), Quelle/Source, nach/by (Speculation): Wikipedia (EN) |
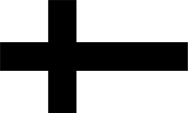 |
1237–1561, Flagge Deutscher Orden – flag of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1940, 1944–1953, |
 |
1953–1991, |
|
siehe auch – look also: Flaggengeschichte der Sowjetrepubliken der UdSSR – flag history of the soviet republics of the USSR |
|
|
|
|
 |
seit/since 1945(?), Flagge der Deutsch-Balten – flag of the Baltic Germans, Quelle/Source, nach/by: photo, www.db-kulturwerk.de |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die blau-schwarz-weiße Flagge Estlands war ursprünglich die Flagge einer Studentenverbindung, und wurde im Jahre 1881 das erste mal gehisst, und schließlich 1896 verboten. Im Zuge der Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit von Russland wurde sie am 21.11.1918 als Nationalflagge angenommen und mit der Verfassung vom 04.07.1920 bestätigt. | The blue-black-white flag of Estonia was initially the flag of a scholar fellowship, and was hoisted up for the first time in the year 1881, and finally banned in 1896. In context with the achievement of the independence from Russia the flag was re-introduced in the year 1917, and confirmed with the constitution from the 4th of July in 1920. |
| Zur Erklärung der Bedeutung der Farben gibt es viele Theorien: 1.) Das Blau steht für Treue und Vertrauen, das Schwarz für die Ahnen und die Vergangenheit und das Weiß für den Schnee und die Zukunft. Quelle: Flaggen-Atlas Erde; 2.) Es handelt sich um die Farben des finnischen Brudervolkes Blau und Weiß, ergänzt um Schwarz, um an die dunkle Zeit der Leibeigenschaft zu erinneren. Quelle: unbekannt; 3.) Blau steht für den Himmel, Schwarz für das Land und Weiß für den Schnee. Quelle: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt; 4.) Blau steht für Loyalität, den Himmel, das Meer und die Seen, Schwarz für die Unterdrückung in der Vergangenheit, die Erde des Landes und die traditionelle Farbe der Jacken der Landarbeiter, Weiß steht für den Kampf und die Freiheit, Tugend, Schnee und ist die Frabe der Birkenrinde. Quelle: Nationalflaggen der Welt. |
There are many theories
to explain the meaning of the colours: 1.) The blue stands for loyalty and trust, the black for the ancestors and the past and the white for the snow and the future. Source: Flaggen-Atlas Erde; 2.) These are the colours of the Finnish fraternal people, blue and white, supplemented by black to remind of the dark time of serfdom. Source: unknown; 3.) Blue stands for the sky, black for the land and white for the snow. Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt; 4.) Blue stands for loyalty, the sky, the sea and the lakes, black for the oppression in the past, the soil of the country and is the traditional color of the jackets of the farm workers, white stands for the struggle for freedom, virtue, snow and is the colour of the birch bark. Source: Nationalflaggen der Welt. |
| In den Jahren der sowjetischen Okkupation (1940 und 1944–1990) wurde bis 1953 eine einfarbige rote Flagge verwendet, darauf Hammer, Sichel und die Initialen des Landes in Gold. Im Jahre 1953 wurde eine neue Sowjetflagge eingeführt, die offiziell noch bis 1991 verwendet wurde, obwohl die alte Flagge bereits seit 1988 wieder erlaubt war. Durch den estnischen Historiker Indrek Kiverik wurde festgestellt, dass im internationalen Gebrauch, und teilweise auch in Estland selbst, bei der Gestaltung der estnischen Flagge ein viel zu dunkles Blau verwendet wird. Hier ein Verweis auf die Estnische Reichskanzlei, wo die Farbgebung der Flagge im CMYK-Farbraum vorgegeben ist. (=> hier klicken) | In the
years of the soviet occupation (1940 and 1944–1990) was in use until 1953 a
single colour red flag, on it hammer, sickle and the initials of the country
in gold. In the year 1953 was introduced a new soviet flag, which was
officialliy
in use even until 1991, although the old flag was already allowed since
1988. By the Estonian historian Indrek Kiverik was detected, that
international and partial even in Estonia, is in use a much to dark blue at
the styling of the estonian flag. The representation in the
Flag-Encyclopaedia was amended from there. Here is a Link to the Estonian
Reich Chancery |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen-Atlas Erde, Alle Flaggen alle Staaten | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Estland – coat of arms of Estonia, Quelle/Source: Riigikantselei, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Wappen – historical Coats of Arms: |
|
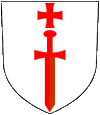 |
1230–1237, Wappenschild des Schwertbrüderordens – blazon of the Order of the Sword Brothers (Livonian Order), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1237–1561, Wappenschild des Deutschen Ordens – blazon of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1629–1721, Wappen von Livland – coat of arms of Livonia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1942–1945, Ärmelabzeichen der Esten in der Waffen-SS – Sleeve insignia of the Estonians in the Waffen-SS, Quelle/Source, nach/by: axishistory.com |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen von Estland stammt aus dem Jahre 1918 und zeigt einen goldenen Schild mit drei untereinander angeordneten Löwen, umgeben von Eichenzweigen. Es ist ursprünglich das Wappen der Stadt Reval (Tallin), welches wiederum vom Wappen des Staates Dänemark entlehnt ist. | The coat of arms of Estonia descents from the year 1918 and shows a golden shield with three among themselves grouped lions, surrounded by oak twigs. It is originally the coat of arms of the town Reval (Tallin), which is borrowed again from the coat of arms of the state Denmark. |
| In der Zeit, in der Estland zur Sowjetunion gehörte, war ein sowjetisches Modell in Verwendung, welches dem Wappen der Sowjetunion ähnelte. 1989 wurde das Wappen von 1918 wieder gültig. | In the times where Estonia belonged to the Soviet Union was in use a soviet model, which equals the coat of arms of the Soviet Union. In 1989 they re-introduced the coat of arms of 1918. |
| Während des Zweiten Weltkriegs, in der Zeit der deutschen Besetzung zwischen 1941 und 1944 hatte Estland offiziell keine eigenen Hoheitszeichen. Es gehörte zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, in dem die Staaten den Baltikums und Teile des heutigen Nordwestens von Weißrussland zusammengefasst waren. | During the Second World War – in the time of the German occupation between 1941 and 1944 – Estonia officially had no own national emblems. It belonged to the Empire's Commissionership of Ostland, in which have been summarized the countries of the Balticum and parts of the today's northwest of White Russia (Belarus). |
| Die Estnische Legion, die im Zweiten Weltkrieg freiwillig an der Seite des Deutschen Reiches gegen die Sowjetunion kämpfte trug als Ärmelabzeichen einen goldenes Schild mit drei schwarzen Löwen und dem Namen des Landes darüber. | The Estonain Legion, which voluntary fought on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union in the Second World War used as sleeve-insignia a golden shield with three black lions and above them the name of the country. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen-Atlas Erde, Alle Flaggen alle Staaten, Avantgarde für Europa | |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Der Löwe in der Heraldik". Ausführungen, Varianten, Entwicklung sowie Panther und Leoparden. |
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
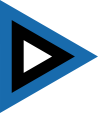 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country:
|
Landkarte des Baltikums – Map of the Balticum:
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 2000 v.Chr. ·
Besiedlung des heutigen Estlands durch die Esten 1202 · Gründung des "Schwertbrüderordens" in Dünamünde (heutiges Lettland) 1202–1230 · Eroberung Kurlands, Livlands, Lettgallens, Semgallens und des südlichen Estlands durch den Schwertbrüderorden, das nördliche Estland wird durch den dänischen König Waldemar II. unterworfen 1236 · Niederlage des Schwertbrüderordens gegen die Litauer 1237 · Vereinigung des Schwertbrüderordens mit dem Deutschen Orden, Kurland, Livland, Lettgallen, Semgallen und das südliche Estland kommen als Livländischer Bund mit einem eigenen Ordensmeister an den Staat des Deutschen Ordens 1346 · das nördliche Estland wird durch den Deutschen Orden von Dänemark abgekauft und dem Livländischen Bund des Deutschen Ordens angegliedert 1558–1595 · Livländischer Krieg, der livländische Ordensmeister des Deutschen Ordens wandelt Kurland und Semgallen in ein Herzogtum als polnisches Lehen um, Estland muss an Schweden und teilweise an Dänemark abgetreten werden, Livland und Lettgallen kommen direkt an Polen 1621 · Schweden erobert Livland 1629 · Livland kommt offiziell an Schweden 1710 · Nordischer Krieg, Russland erobert Livland 1721 · Frieden von Nystad, Livland und Estland kommen an Russland, Kurland, Semgallen und Lettgallen bleiben bei Polen, Estland wird ein eigenes russisches Gouvernement (bestehend aus dem nördlichen ehemals schwedischen Teil von Estland) 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg: 1918 das Deutsche Reich erobert Livland und Estland 07.11.1917 · bolschewistische Revolution in Russland, Machtergreifung durch die Sowjets 24.02.1918 · Estland erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit, der Staat Estland umfasst nun das alte Gouvernement Estland einschließlich des Nordens von Livland 03.03.1918 · Russland kapituliert gegenüber dem Deutschen Reich, Friedensvertrag von Brest-Litovsk, Anerkennung des estnischen Staates durch Sowjetrussland 1924 · Niederschlagung eines kommunistischen Putsches 23.08.1939 · deutsch-sowjetischer Nichtangriffspakt, Estland wird sowjetische Interessensphäre und von der Sowjetunion besetzt, die seit dem 12. Jahrhundert im Land lebenden Deutsch-Balten (auch Baltendeutsche genannt), dürfen – wenn sie wollen – das Land in Richtung Deutsches Reich verlassen 21.07.1940 · Proklamation der Estnischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik (ESSR) 06.08.1940 · Aufnahme der ESSR in die Sowjetunion, Deportation von Tausenden von Einwohnern nach Sibirien 1939–1945 · Zweiter Weltkrieg: Juni/Juli 1941 Eroberung Estlands durch deutsche Truppen, Estland kommt zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, 20.000 Esten kämpfen freiwillig in einer Estnischen Legion an der Seite des Deutschen Reiches gegen die Sowjetunion, Dezember 1944 Eroberung Estlands durch sowjetische Truppen, Flucht und Vertreibung der allermeisten Deutsch-Baltischen Einwohner, viele werden ermordet oder sterben auf der Flucht, Estland wird wieder ESSR und wird der Sowjetunion wieder angegeliedert, gewaltsame Russifizierung, Deportation von Tausenden von Esten nach Sibirien 1945–1988 · gezielte Einwanderung von Russen 1988 · Entstehung der Autonomiebewegung 30.03.1990 · Proklamation der Unabhängigkeit 1991 · die Sowjetunion erkennt die Unabhängigkeit Estlands an 1992 · neue Verfassung 1994 · Abzug der russischen Truppen 2004 · Estland wird Mitglied der Europäischen Union |
History: |
| 2000 B.C.
· settlement of the today's Estonia by the Estonians 1202 · establishment of the "Order of the Sword Brothers" in Duenamuende (today's Latvia) 1202–1230 · conquest of Courland, Livonia, Lettgallia, Semigallia and the southern Estonia by the Order of the Livonian Order, the northern Estonia becomes subjected by the Danish King Waldemar II. 1236 · defeat of the Order of the Sword Brothers against the Lithuanians 1237 · unification of the Order of the Sword Brothers with the Teutonic Order, Courland, Livonia, Lettgallia, Semigallia and the southern Estonia come as Livonian Federation with an own Master to the State of the Teutonic Order 1346 · the northern Estonia gets purchased by the Teutonic Order from Denmark and incorporated to the Livonian Federation of the Teutonic Order 1558–1595 · Livonian War, the Livonian Master of the Teutonic Order transforms Courland and Semigallia in a duchy as a Polish enfeoffment, Estonia becomes ceded to Sweden and partially to Denmark, Livonia and Lettgallia come directly to Poland 1621 · Sweden conquers Livonia 1629 · Livonia comes officially to Sweden 1710 · Nordic War, Russia conquers Livonia 1721 · Peace of Nystad, Livonia and Estonia come to Russia, Courland, Semigallia and Lettgallia remain at Poland, Estonia becomes an own Russian gouvernement (consists of the northern former Swedish part of Estonia) 1914–1918 · First World War: 1918 the German Empire conquers Livonia and Estonia 7th of November 1917 · bolshevist revolution in Russia, seizure of power by the Soviets 24th of February 1918 · Estonia declares its independence, the state of Estonia includes now the old Gouvernement of Estonia inclusive the north of Livonia 3rd of March 1918 · Russia capitulates towards the German Empire, Peace Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, recognition of the Estonian state by Soviet Russia 1924 · suppression of a communist coup d'état 23rd of August 1939 · German-Soviet non aggression pact, Estonia becomes a soviet sphere of interest and gets occupied by the Soviet Union, the Baltic Germans who had been living in the country since the 12th century were allowed to leave the country for the German Reich if they wished to do so 21st of July 1940 · proclamation of the Estonian Socialistic Soviet Republic (ESSR) 6th of August 1940 · inclusion of the ESSR into the Soviet Union, deportation of thousands of inhabitants 1939–1945 · Second World War: June/July 1941 conquest of Estonia by German troops, Estonia comes to the empire`s commissionership of Ostland, 20.000 Estonians fight voluntary in a Estonian Legion on the side of the German Empire against the Soviet Union, December 1944 conquest of Estonia by soviet troops, escape and expulsion of the vast majority of German-Baltic inhabitants, many are murdered or die while fleeing, Estonia becomes once more ESSR and incorporated into the Soviet Union again, forcible russification, deportation of thousands of Estonians to Sibiria 1945–1988 · enforced immigration of Russians 1988 · nascence of the autonomy movement 30th of March in 1990 · proclamation of independence 1991 · the Soviet Union recognizes the independence of Estonia 1992 · new constitution 1994 · withdrawal of the Russian troops 2004 · Estonia becomes a member in the European Union |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Avantgarde für Europa |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Estland" geht auf das Volk der "Esten" zurück. Sie nennen sich selbst "Eestlased", was auf das Wort "Aueist" zurückgeht und "Küstenbewohner" heißt. | The name "Estonia" has its roots in the people of the "Estonians". They name themselves "Eestlased", what descents from the word "Aueist" and means "Coastal Residents". |
| Quelle/Source: Die Völker der Erde, Atlas der wahren Namen | |
| Landkarten zur Geschichte des Baltikums – historical Maps of the Balticum: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |
Mit freundlicher |
Indrek Kiverik |