Japan |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Japan |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
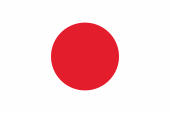 |
National- und Handelsflagge, Gösch – national and merchant flag, and jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
Marine- und Kriegsflagge – naval and war flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
Zollflagge – customs flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Das Flaggenbuch |
 |
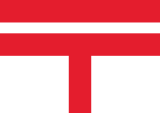
Flagge der Hafenpolizei – flag of the Harbour Police, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Das Flaggenbuch |
 |
Postflagge – postal flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:7, Quelle/Source: By Zscout370 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge des Premierministers – flag of the Premier, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:7, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge des Kaisers – flag of the Emperor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
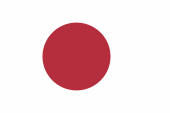
1870–1999, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 7:10, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
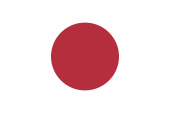
1870–1999, Handelsflagge und Gösch – merchant flag and jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1999–2008, National- und Handelsflagge, Gösch – national and merchant flag, and jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1945–1952, Handels- und Marineflagge unter Alliierter Besatzung – Merchant and naval flag under Allied occupation, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die "Hinomaru" genannte Flagge Japans ist weiß mit einer roten Sonnenscheibe in der Mitte, und wurde offiziell am 08.08.1854 zur Benutzung auf See eingeführt, und am 27.02.1870 auch an Land. | Japan’s flag, called the "Hinomaru" is white with a red sun disk in the centre, and was officially introduced on the 8th of August, 1854 for use at sea, and on the 27th of February, 1870 on land. |
| Andere Quellen nennen als Datum der Einführung der Flagge den 05.08.1854, den 09.07.1954, und offizielle (amtliche) japanische Quellen nennen sogar das Jahr 1856. Am 27.02.1870 wurde ein Gesetz erlassen, welches die Verwendung der Sonnenscheiben-Flagge an Land erlaubte, und auch deren Verwendung als Handelsflagge in der Seefahrt. Für Kriegsschiffe wurde an diesem Datum die Marineflagge eingeführt, und eine Reihe weiterer Sonderflaggen. Dieses Gesetz regelte auch das genaue Aussehen der Nationalflagge: Proportionen 7:10, der Durchmesser der roten Scheibe wurde auf 3/5 der Höhe der Flagge festgelegt. Für die Handelsflagge wurde ferner festgelegt: Proportionen 2:3 und die rote Scheibe ist ein Zwanzigstel der Flaggenläng in Richtung Mast verschoben. Am 13.08.1999 wurde das Gesetz über die Nationalflagge und die Nationalhymne verabschiedet, dabei die Proportionen der Flagge auf 2:3 abgeändert. Der rote Farbton wurde nicht genau definiert, nur als "tief" beschrieben. Die Farben sind in einem Schriftstück des Verteidigungsministeriums festgelegt worden, und zwar zuerst 1973, Rot als "Munsell 5R 4/12" und Weiß "Munsell N9". Das würde für das Rot bedeuten, dass es in etwa entsprechen würde: RGB 180|46|61, CMYK 6|95|67|25, Pantone 703. Jenes Schriftstück wurde am 21.03.2008 geändert, nicht zuletzt um den Forderungen des Gesetzes von 1999 Folge zu leisten. Hier wird das Rot als "Munsell 5.7R 3.7 / 15.5" für das Bedrucken von Acryl benannt und als "Munsell 6.2R 4/15.2" für das Bedrucken von Nylon. Das diese Farbspezifikationen ausschließlich dem Herstellungsprozess dienen, jedoch kaum verdeutlichen was eine korrekte Darstellung ausmacht, hat die japanische Entwicklungshilfe (ODA), die dem Außenministerium untersteht, das Rot als "DIC 156" klassifiziert. Die DIC Corporation ist ein japanischer Chemie-Konzern mit eigenen Farbstandards. Insofern interpretiert die ODA die Farbe Rot als CMYK 0|100|90|0, was in etwa entsprechen würde: RGB 228|29|45, bzw. Pantone 1788. | Other
Sources name as datum of the introduction of the flag the 5th of August in
1854, the 9th of July in 1854, and formal (official) Japanese Sources name
even the year 1856. On 27th of February in 1870 a law was passed which allowed the use of the sun disk flag ashore and even its use as merchant flag in the navigation. For warships on that datum was introduced the naval flag and series of further special flags. This law also regulated the exact appearance of the national flag: proportions 7:10, the diameter of the red disc was set at 3/5 of the height of the flag. For the merchant flag it was further stipulated: Proportions 2:3 and the red disc is shifted one twentieth of the flag's length towards the mast. On 13th of August in 1999, the Law on the National Flag and the National Anthem was adopted, changing the proportions of the flag to 2:3. The shade of red was not precisely defined, only described as "deep". The colours have been defined in a Ministry of Defence document, first in 1973, red as "Munsell 5R 4/12" and white "Munsell N9". This would mean for the red that it would roughly correspond to: RGB 180|46|61, CMYK 6|95|67|25, Pantone 703. That document was amended on 21st of March in 2008, not least to comply with the requirements of the 1999 Act. Here the red is designated as "Munsell 5.7R 3.7 / 15.5" for printing on acrylic and as "Munsell 6.2R 4/15.2" for printing on nylon. As these colour specifications only serve the manufacturing process, but hardly clarify what constitutes a correct representation, the Japanese Development Agency (ODA), which reports to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, has classified the red as "DIC 156". The DIC Corporation is a Japanese chemical company with its own colour standards. In this respect, the ODA interprets the colour red as CMYK 0|100|90|0, which would roughly correspond to: RGB 228|29|45, or Pantone 1788. |
| Banner mit Sonnen- oder Mondscheiben haben in Japan eine bis zu 1300 Jahre zurückreichende Tradition. Die rote Sonnenscheibe versinnbildlicht die Japanischen Kaiser als direkte Abkömmlinge der Sonnengöttin. Weiß symbolisiert Rechtschaffenheit, Aufrichtigkeit und Reinheit, Rot steht für Mut, Offenheit und Leidenschaft. | Banners
with sun or moon disks have a tradition going back about 1300 years in
Japan. The red sun disk symbolizes the Japanese Emperors as direct descendant of the sun-goddess. White stands for honesty, sincerity and cleanliness, and red for courage, openness and passion. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Wikipedia (EN) | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
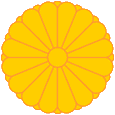 |
Staats- und Kaiserwappen – states's and emperor's coat of arms, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen von Japan ist das kaiserliche Reichswappen. Es zeigt eine stilisierte, goldene, 16-blättrige, Chrysantheme. Dieses Symbol ist ein sogenanntes Mon, ein japanisches Familiensymbol, jedoch darf die goldene Chrysantheme nur von der kaiserlichen Familie benutzt werden. Sie wird so z.B. auch auf der Standarte des Kaisers verwendet. | The coat
of arms of Japan is the imperial coat of arms. It shows a stylized, golden,
16-leaved chrysanthemum. This symbol is a so-called Mon, a Japanese family symbol, but the golden chrysanthemum may be used only by the imperial family. Is in this way also used on the standard of the emperor. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
sonstige Flaggen – other Flags: |
|
| Okinawa (Ryukyu-Islands): | |
 |
Flagge der Präfektur Okinawa |
| Ainu: | |
 |
Flagge der Ainu-Ureinwohner auf der Insel Hokkaido – flag of the native people on Hokkaido, the ”Ainu”, |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
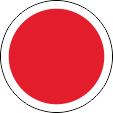 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.Jhd.
v.Chr. · über 100 Kleinstaaten verschiedener Stämme im heutigen Japan 2.–3. Jhd. · Entstehung von größeren Stammesbünden 645–702 · Taika Reform, Herausbildung des Kaiserreichs 1192 · Errichtung des Shogunats (Militärherrschaft) 1637 · Japan isoliert sich von der Welt 1853 · eine militärische Aktion der USA erzwingt von Japan die Öffnung seiner Häfen und Märkte 1867 · Beseitigung des Shogunats, Wiederherstellung der Macht des Kaisers 1872 · Modernisierung nach dem Vorbild des Westens 1873 · Erwerb der Bonin-Inseln und der Marcus-Inseln 1875 · Erwerb der Kurilen-Inseln 1876–1879 · Eroberung der Ryukyu-Inseln (Okinawa) 1889 · neue, am Deutschen Reich orientierte Verfassung 1894–1895 · Chinesisch-Japanischer Krieg, Sieg Japans, Erwerb von Formosa (Taiwan) und den Pescadores-Inseln, China muss Korea in die Unabhängigkeit entlassen 29.04.1901 · Geburt des späteren Kaisers Hirohito 1904–1905 · Russisch-Japanischer Krieg, Sieg Japans, Erwerb von Südsachalin und der Halbinsel Liaotung (Port Arthur), Errichtung der japanischen Schutzherrschaft über Korea 1910 · Japan annektiert Korea 1914–1918 · Japan beteiligt sich der Seite der Alliierten im Ersten Weltkrieg 1919 · das Diktat von Versailles überträgt Japan die Verwaltung pazifischer deutscher Kolonien (Marshall-, Karolinen- und Marianen-Inseln) und es erhält die deutsche Kolonie Kiautschou 1921 · Hirohito wird Regent (in Vertretung seines kranken Vaters Taischo) 1926 · Tod von Taischo, sein Sohn Hirohito wird neuer Kaiser 1927 · Beginn der Ära des radikalen Nationalismus, im Pazifik Interessenkonflikte mit den USA 1931 · militärische Intervention Japans in der Mandschurei, Errichtung des japanischen Satellitenstaats Mandschukuo 1937 · militär. Intervention Japans in China 1938 · Gleichschaltung des öffentlichen Lebens in Japan, Herrschaft des Militärs 1939 · Japanisch-Sowjetischer Grenzkrieg, Japan erleidet eine Niederlage 1940 · Japan besetzt Franz.-Indochina 1941 · totales Handelsembargo der USA gegen Japan, daraufhin absehbarer Zusammenbruch der japanischen Wirtschaft 07.12.1941 · Japan antwortet mit einem Angriff auf den US-amerikanischen Flottenstützpunkt Pearl Harbor und beginnt mit der Besetzung US-amerikanischer, britischer und niederländischer Besitzungen im Pazifik 04.–07.06.1942 · Seeschlacht von Midway, Niederlage Japans, allmähliche Zurückdrängung der Japanischen Truppen 06. und 09.08.1945 · die USA werfen Atombomben auf Hiroshima und Nagasaki und ermorden dabei 150 000 Zivilisten 02.09.1945 · Kapitulation Japans, Japan verliert alle seine Besitzungen, die Ryukyu-Inseln, sowie die Bonin- und Marcus-Inseln werden von den USA besetzt 1945–1947 · US-amerikanische Militärregierung 1947 · neue, an den USA orientierte Verfassung, der Kaiser wird entmachtet 1952 · Friedensvertrag von San Francisco, Japan erhält sein Selbstbestimmungsrecht zurück 1968 · Japan erhält die Bonin- und Marcus-Inseln zurück 1972 · Japan erhält die Ryukyu-Inseln (Okinawa) zurück 1989 · Tod des Kaisers Hirohito 1997 · Beginn einer schweren Wirtschaftskrise, in den Folgejahren allmähliche wirtschaftliche Erholung |
| 1st cent.
B.C. · over 100 small states of various tribes in the today's Japan 2nd–3rd cent. · nascence of bigger tribe federations 645–702 · Taika reform, development of the empire 1192 · establishment of the Shogunate (military rule) 1637 · Japan isolates itself from the world 1853 · a military campaign of the USA forces Japan to open its ports and markets 1867 · elimination of the Shogunate, re-establishment of the Emperor's reign 1872 · modernization patterned after the West 1873 · purchase of the Bonin Islands and the Marcus Islands 1875 · purchase of the Kurile Islands 1876–1879 · conquest of the Ryukyu Islands (Okinawa) 1889 · new constitution following the style of the German Empire 1894–1895 · Chinese-Japanese war, victory of Japan, purchase of Formosa (Taiwan) and the Pescadores Islands, China has to grant Korea independence 29th of April 1901 · birth of the later emperor Hirohito 1904–1905 · Russian-Japanese war, victory of Japan, purchase of South Sakhalin and the Liaotung peninsula (Port Arthur), establishment of Korea as a Japanese protectorate 1910 · Japan annexes Korea 1914–1918 Japan participates in the First World War on the side of the allies 1919 · the dictate of Versailles assigns to Japan the administration of German colonies in the Pacific (Marshall-, Caroline- and Mariana-Islands) and Japan receives the German colony of Kiaochow 1921 · Hirohito becomes regent (in substitution of his diseased father Taisho) 1926 · death of Taisho, his son Hirohito becomes the new emperor 1927 · start of the era of radical nationalism, in the Pacific conflicts of interests with the USA 1931 · military intervention of Japan in Manchuria, establishment of the Japanese satellite state of Manchoukuo 1937 · military intervention of Japan in China 1938 · phasing of public live in Japan, rule of the military 1939 · Japanese-Soviet frontier war, Japan suffers a defeat 1940 · Japan occupies French Indochina 1941 · total trade embargo of the USA against Japan, a cause for a foreseeable collapse of the Japanese economy 7th of December 1941 · Japan answers with an attack on the US-american naval base Pearl Harbor and starts with the occupation of US-american, British and Dutch possessions in the Pacific 4th–7th of June 1942 · sea battle of Midway, defeat of Japan, gradual back push of the Japanese troops 6th and 9th of August in 1945 · the USA drop atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki and kill 150 000 civilians 2nd of September 1945 · capitulation of Japan, Japan loses its possessions, the Ryukyu Islands, and the Bonin and Marcus Islands are occupied by the USA 1945–1947 · US military government 1947 · new constitution, following the style of the US-american constitution, ousting of the emperor from the rule 1952 · peace treaty of San Francisco, Japan gets back its right of self-determination 1968 · Japan gets back the Bonin and Marcus Islands 1972 · Japan gets back the Ryukyu Islands (Okinawa) 1989 · death of Emperor Hirohito 1997 · start of a severe economic crisis, gradual economic recovery in the following years |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der weltweit für das Land verbreitete Name "Japan" stammt aus Quellen außerhalb Japans. Er geht auf wahrscheinlich auf das malaiische Wort "Jepang" für das heutige Land Japan zurück. Portugiesische Seefahrer brachten diese Landesbezeichnung im 16. Jahrhundert mit nach Europa, von wo aus es weltweite Werbreitung gefunden hat. | The worldwide common name for the country, "Japan", comes from sources outside of Japan. He probably goes back to the Malay word "Jepang" for the today's country of Japan. Portuguese sailors brought this country name to Europe in the 16th century, from where it has found worldwide commonness. |
| Die Japaner selbst nennen ihr Land "Nihon", ein Wort das sich aus den Silben "ni" und "hon" zusammensetzt, die sich mit "Tag/Sonne" und "Ursprung/Beginn" übersetzen lasen. Japan ist darum als das "Land der aufgehenden Sonne" bekannt. Der Name "Nihon" wurde im 6./7. Jahrhundert gewählt, um in Briefen an die chinesischen Kaiser klarzumachen, wo das das Land der Absender liegt. Die Bezeichnung "Nippon" (gleichbedeutend mit Nihon) ist eher offziell und wird auf Briefmarken und Banknoten oder im internationalen Verkehr verwendet. | The Japanese themselves call their country "Nihon", a word composed of the syllables "ni" and "hon",
which are to translate with "day / sun" and "origin / beginning". Japan is therefore known as the "Land of the Rising Sun".
The name "Nihon" was chosen in 6th/7th century to clarify in letters to the Chinese emperors, where the country of the sender is placed. The name "Nippon" (synonymous with Nihon) is more official and is used on stamps and banknotes or in international traffic. |
| Ursprünglich hieß das Land "Wakoku", ein Name der auf die chinesischen Nachbarn zurückgeht und "Land der Kleinwüchsigen" bedeutet. | Originally the country was called "Wakoku", a name that goes back to the Chinese neighbors and means "land of the short people". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Stanisław Meyer | |
|
Mit freundlicher Unterstützung von: Kindly supported by: |
Rainer Bertram |
|
teilweise
Übersetzung des englischen Textes: partial Translator of the English text: |
Joachim Nuthack |