Südkorea |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Südkorea |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National-, Handels- und Marineflagge – national, merchant and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D)   |
 |
Gösch der Marine – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Präsidentenflagge – flag of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
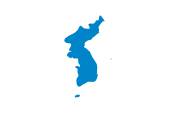 |
Flagge der Vereinigung – flag of unification, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: By File:Unification flag of Korea (pre 2006).svg: Variousderivative work: Valentim (File:Unification flag of Korea (pre 2006).svg) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Flagge – historical Flag: |
|
 |
1882–1910, |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge von Südkorea basiert auf der Flagge des ehemaligen Königreichs (bis 1910) und zeigt auf einem weißen Flaggentuch ein rot-blaues Yin-Yang-Symbol, welches auf Koreanisch T'aeguk – "Große Polarität" – genannt wird, und in jeder Ecke jeweils drei, teils ganze, teils durchbrochene schwarze Balken, sogenannte Trigramme, die auf Koreanisch Kwae genannt werden. | The flag of South Korea is based on the flag of the former kingdom (to 1910) and shows on a white bunting a red-blue Yin-Yang symbol, which is named in Korean T'aeguk, what means "big polarity" – and in every corner each three, partly complete, partly interrupted black bars, so named trigrams. They are named in Korean Kwae. |
| In dieser Form wurde diese Flagge erstmals im Jahre 1882 verwendet und ein Jahr später offiziell als Landessymbol anerkannt. Am 15.08.1948 wurde die Flagge für die Republik Korea (Südkorea) erneut angenommen. Am 25.01.1950 wurde sie ein wenig verändert, indem die Größe der Trigramme und auch die Größe des T'aeguk geändert wurden. Die Bezeichnung T'aeguk ist im Laufe der Zeit auf die gesamte Flagge übergegangen. | In this form the flag was for the first time in use in the year 1882 and one year later officially recognized as the symbol of the country. On the 15th of August in 1948 the flag was adoped again for the Republic of Korea (South Korea). On the 25th of January in 1950 it was changed a little bit by modifying of the size of the trigrams and also the size of the T'aeguk. The denomination T'aeguk was transfered in the times for the whole flag. |
|
Die Farbe Weiß steht für die Reinheit der Gedanken, ist aber auch die
traditionelle Farbe der koreanischen Nation. Das T'aeguk ist als Yin-Yang-Zeichen in der gesamten Weltanschauungssymbolik des Ostens bekannt. Es soll die Verschmelzung der Gegensätze symbolisieren. Trigramme sind kultische Schriftzeichen aus dem Buch "I Ging" mit weltanschaulichen und kosmologischen Bezügen (Sonne, Mond, Erde, Himmel oder Frühling, Sommer, Herbst, Winter oder Süden, Westen, Norden, Osten). Die Farben Blau und Rot sind angeblich hexadezimal definiert, als Blau = #CD2E3A und Rot = #0047A0. Daraus lassen sich die Pantone-Farben Blau = pt 294 und Rot = pt 711 ableiten. |
The color white stands for the purity of the thoughts, but is also the
traditional colour of the Korean nation. The T'aeguk is known as Yin-Yang symbol in the whole philosophical symbolism of the East. It should symbolize the fusion of the antithesis. Trigrams are cultic characters from the book "I Ging" with philosophical and cosmological relations (sun, moon, earth, heaven or spring, summer, autumn, winter or south, west, north, east). The colours blue and red are supposedly defined hexadecimally, as blue = #CD2E3A and red = #0047A0, from which the Pantone colours blue = pt 294 and red = pt 711 can be derived. |
| Die Flagge des Präsidenten ist blau und zeigt eine goldene Hibiskusblüte, sowie links und rechts davon zwei sogenannte "Wundervögel". Die Marineflagge Südkoreas ist blau mit einer weißen Oberecke, mit zwei gekreuzten schwarzen Ankern und darauf das T'aeguk. | The flag of the president is blue and shows a golden hibiscus blossom as well as to the left and on the right two so named "wonder-birds". The naval flag of South Korea is blue with white upper staff quadrant with two crossed black anchora and thereupon the T'aeguk. |
| Die "Flagge der Vereinigung" wurde anderem zur Winterolympiade 2018 gebraucht, als die Teams beider Korea unter dieser gemeinsamen Flagge auftraten. | The "flag of unification" was used, among other things, for the Winter Olympics 2018, when the teams of both Korea appeared under this common flag. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flags of the World, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Südkorea – coat of arms of South Korea, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen zeigt ein rot-blaues T'aeguk (Yin-Yang-Symbol), umgeben von den gelben Blättern der Sharon-Blüte. Sie steht für Kraft und Beständigkeit. Nach einer anderen Interpretation handele es sich jedoch um eine Hibiskusblüte, die Gastfreundschaft ausdrücken soll. In dem blauen Feld des Bandes der Name des Staates in Hangul-Schrift. | The coat
of arms shows a red-blue T'aeguk (Yin-Yang Symbol), surrounded by the yellow
leafs of the Sharon blossom. It stands for energy and constancy. But by an other interpretation this should be a Hibiscus blossom, which should express hospitality. In the blue field of the banner the name of the state in Hangul fonts. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
seit/since 2005, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1949–2005, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Die Lage des Landes – position of the Country: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| ca. 1100
v.Chr. · Gründung des koreanischen Staates Choson durch Kitscha, dem ersten
König des Landes und Begründer der Kitscha-Dynastie 108 v.Chr. · Unterwerfung von Choson durch China 194 v.Chr. · Herausbildung von drei koreanischen Staaten im Süden unter der Herrschaft der chinesischen Han, im Norden entsteht ein chinesischer Vasallenstaat 1. Jhd. v.Chr. · Herausbildung von drei koreanischen unabhängigen Königreichen (Goguryeo, Baekje und Silla) 668 n.Chr. · das Königreich Silla vereinigt alle drei Königreiche, Silla zerfällt jedoch nach 250 Jahren wieder in die Reiche Silla, Baekje und Madjin, Kriege zwischen den Reichen, Madjin setzt sich durch, Einigung der Reiche unter Madjin, Japan besetzt jedoch vorübergehend einen Küstenstreifen im Süden (Land Karak) 935 · General Wang Gon (Wang Kon) begründet in Madjin die Koryo-Dynastie, das vereinigte Reich wird Koryo genannt 1229 · Mongoleninvasion, Herrschaft der Mongolen bis 1280 1392 · Inthronisation der Yi-Dynastie, die von General Yi Sungye (T'aejo) begründet worden war, Umbenennung des Landes in Choson 1592–1598 · Japan versucht Choson (Korea) zu erobern 1637 · Choson (Korea) muss die Oberhoheit der chinesischen Mandschu-Kaiser anerkennen, das Land beginnt sich zu isolieren 1866 · französischer Versuch der Eroberung des Landes 1871 · US-amerikanischer Versuch der Eroberung des Landes 1876 · Japan erzwingt die Aufhebung der Isolation, Öffnung der Häfen für fremde Mächte 1894–1895 · chinesisch-japanischer Krieg um den Einfluss in Korea, China unterliegt und muss die japanische Oberherrschaft in Korea anerkennen 1904–1905 · russisch-japanischer Krieg um den Einfluss in Korea, Russland unterliegt 1910 · Japan annektiert Korea als Generalgouvernement Chôsen (Choson), Ende der Yi-Dynastie 1945 · Ende des Zweiten Weltkriegs, Japan kapituliert, Korea wird längs des 38. Breitengrads geteilt, der Norden wird von der Sowjetunion besetzt, der Süden durch die USA 06.09.1945 · in der Sowjetischen Besatzungszone wird die "Volksrepublik Korea" gegründet, deren Kompetenzen für ganz Korea geplant waren, im Süden werden alle ihre Aktivitäten am 12.12.1945 verboten 08.02.1946 · das Projekt "Volksrepublik Korea" wird beendet 10.05.1948 · Wahlen in ganz Korea für eine handlungsfähige Regierung, Nordkorea boykottiert die Wahlen Juli 1948 · neue Verfassung für Korea 15.08.1948 · in Folge der Wahl wird (nur in Südkorea) die Republik Korea proklamiert 09.11.1948 · in Nordkorea wird die Volksdemokratische Republik Korea proklamiert 25.06.1950 · nordkoreanische Truppen marschieren in Südkorea ein, es entwickelt sich ein größerer Konflikt, in den außer Südkorea auch China die USA und jeweilige Verbündete mit hineingezogen werden 27.07.1953 · Waffenstillstand von Panmundjom, das Land bleibt entlang der Waffenstillstandslinie zwischen Nord- und Südkorea geteilt 1961 · Militärputsch 1963 · Präsidentenwahlen 1965 · Wiederaufnahme diplomatischer Beziehungen zu Japan 1966 · Südkorea beginnt sich am Vietnamkrieg zu beteiligen 1972 · Kriegsrecht, neue Verfassung, Präsidialdiktatur 1979 · Militärputsch 1985 · kleinere Abkommen zwischen beiden Koreas 1988 · neue Verfassung, Mehr-Parteien-System 1990 · Kontakte beider koreanischer Regierungen 1991 · Südkorea tritt der UNO bei 1992 · Wiederaufnahme diplomatischer Beziehungen zu China 1992 · "Vertrag über Versöhnung, Nichtangriff, Austausch und Zusammenarbeit" zwischen beiden Koreas, jedoch Zunahme der Spannungen zwischen beiden Staaten 1997 · Friedensverhandlungen zwischen Nord- und Südkorea unter Beteiligung der USA und Chinas 2000 · verschiedene humanitäre Verbesserungen der Beziehungen zwischen beiden Koreas ab 2008 · Verschlechterung der Beziehungen zwischen beiden Koreas ab 2013 · Verbesserung der Beziehungen zwischen beiden Koreas |
History: |
| ca. 1100
B.C. · establishment of the Korean state of Choson by Kitcha, the first king
of the country and founder of the Kitcha-Dynasty 108 B.C. · subjection of Choson by China 194 B.C. · evolution of three Korean states in the south under the rule of the Chinese Han, in the north arises a Chinese vassal state 1st cent. B.C. · arise of three Korean independent kingdoms (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) 668 A.D. · the Kingdom of Silla joines all three kingdoms, but Silla disintegrates after 250 years in the empires Silla, Baekje and Madjin, wars between the empires, Madjin asserts oneself, unification of the empires under Madjin, Japan occupies transitionally a coastal stripe in the south (Karak country) 935 · General Wang Gon (Wang Kon) establishes in Madjin the Koryo-Dynasty, the united empire is named Koryo 1229 · Mongolian invasion, rule of the Mongols until 1280 1392 · enthronement of the Yi-Dynasty, which was established by General Yi Sungye (T'aejo), rename of the country in Choson 1592–1598 · Japan attempts to conquer Choson (Korea) 1637 · Choson (Korea) has to recognize the supremacy of the Chinese Mandju emperors, the country begins to insulate itself 1866 · French attempt to conquer the country 1871 · US-American attempt to conquer the country 1876 · Japan coerces the repeal of the isolation, opening of the ports for foreigner mights 1894–1895 · Chinese-Japanese War for the influence in Korea, China succumbs and has recognize the Japanese supremacy in Korea 1904–1905 · Russian-Japanese Krieg for the influence in Korea, Russia succumbs 1910 · Japan annexes Korea as General Government of Chôsen (Choson), end of the Yi-Dynasty 1945 · end of the Second World War, Japan surrenders, Korea becomes partitioned alon the 38th degree of latitude, the north becomes occupied by the Soviet Union, the south by the USA 6th of September 1945 · In the Soviet occupation zone, the "People's Republic of Korea" is founded, whose powers were planned for the whole of Korea; in the South, all its activities are banned on 12.12.1945 8th of February 1946 · the "People's Republic of Korea" project is terminated 10th of May 1948 · election in whole Korea for a employable government, North Korea boycotts the elections July 1948 · new constitution for Korea 15th of August 1948 · in result of the election gets proclaimed (only in South Korea) the Republic of Korea 9th of November 1948 · in North Korea gets proclaimed the People's Democratic Republic of Korea 25th of June 1950 · North Korean troops invade South Korea, increase into a bigger conflict in which embroil except South Korea even China the USA and respective allies 27th of July 1953 · Armistice of Panmundjom, the country remains separated along the armistice line between North and South Korea 1961 · military coup d'état 1963 · presidental elections 1965 · continuance of diplomatical connections to Japan 1966 · South Korea begins with its engagement in the Vietnam War 1972 · war law, new constitution, presidial dictatorship 1979 · military coup d'état 1985 · small agreements between both Koreas 1988 · new constitution, multy-party-system 1990 · contacts of both Korean governments 1991 · South Korea joines the UNO 1992 · continuance of diplomatical connections to China 1992 · "Treaty of reconciliation, non-aggression, interchange and cooperation" between both Koreas, but increase of the tensions between both states 1997 · discussions about peace between North and South Korea under participation of the USA and China 2000 · diverse humanitarian improvements of the connections between both Koreas from 2008 · deterioration in relations between the two Koreas from 2013 · improvement in relations between the two Koreas |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Korea" wurde im Mittelalter durch Handelsreisende nach Europa gebracht. Entweder bezog sich diese Bezeichnung auf den koreanischen Staat "Koguryo" der zwischen dem 1. Jhd. v.Chr. und dem 7. Jhd. n.Chr. auf der koreanischen Halbinsel bestand, oder die Bezeichnung geht zurück auf die Dynastie "Koryo", welche die koreanischen Staaten im Jahre 936 vereingte, und dem Land "Koryo" seinen Namen gab. Im Jahre 1392 kam die Dynastie "Yi" an die Macht (bis 1910), welche das Land im gleichen Jahr in "Choson" (Land der Morgenfrische) umbenannte. Diese Bezeichnung wird heute noch von Nordkorea verwendet. Südkorea nennt sich "Dachan Minkuk". International wird jedoch ausschließlich Korea (Nordkorea oder Südkorea) verwendet. | The name
"Korea" came to Europe in the middle ages by trading travelers. Either
refered this designation to the Korean state of "Koguryo", which exists
between the 1st cent. B.C. and the 7th cent. B.C. on the Korean peninsula,
or the designation goes back to the dynasty "Koryo", which united the
countries in the year 936 und gave the country "Koryo" its name. In the year 1392 the Dynastie "Yi" came to power (until
1910), which renamed the country in the same year in "Choson" (country of
the morning freshness). |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Wikipedia (D) | |