Israel |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Israel |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag,   |
 |
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, |
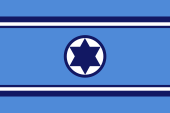 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe |
 |
Standarte des Präsidenten an Land |
 |
Flagge der autonomen palästinensischen Gebiete – flag of the autonomous Palestinian territories,   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
bis/to 1916, Flagge Osmanisches Reich – flag of the Ottoman Empire, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1916–1927, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
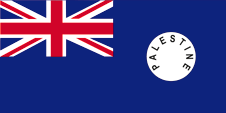 |
1927–1948, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2 Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
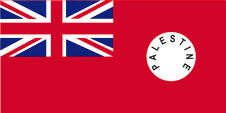 |
1927–1948, |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge Israels ist weiß mit einem blauem Davidstern in der Mitte, und zeigt oben und unten je einen blauen Streifen. Die Breite der dadurch entstehenden weißen und blauen Streifen verhält sich wie 14:30:85:30:14. Sie wurde von dem zionistischen Führer David Wolfsohn entworfen und erstmals am 21.07.1891 bei der Einweihung der Zion-Halle in Boston (USA) in der Öffentlichkeit gezeigt. Am 14.05.1948 wurde sie erstmals in Palästina gehisst, und am 12.09.1948 offiziell als Flagge des jüdischen Staates bestätigt. Der Davidstern ist ein jüdisches Symbol. Er entsteht durch das Kombinieren von zwei gleichschenkligen Dreiecken. Blau und Weiß sind Farben jüdischer Ritualkleidung und die Flagge geht laut David Wolfsohn auf den jüdischen Gebetsschal (Talit) zurück. | The flag of Israel is white with a blue David's star in the middle and shows above and below per one blue stripe. The ratio of the breadth of the thereby arising white and blue stripes is like 14:30:85:30:14. It was designed by the zionist leader David Wolfsohn and was showed for the first time in the public on the 21th of July in 1891 at the official opening of the Zion hall in Boston (USA). On the 14th of May in 1948 it was hoisted up for the first time in Palestina and on the 12th of September in 1948 it was officially confirmed as the flag of the jewish state. The David's star is a jewish symbol. It is formed by the combination of two isosceles triangles. Blue and white are colours of jewish ritual clothing and the flag has, ccording to David Wolfsohn, it's roots in the jewish prayer scarf (Talit). |
| Oft wird jedoch folgendes unterstellt: Da die Flagge von einem Zionisten geschaffen wurde, sei es wahrscheinlicher, dass kein äußeres Zeichen jüdischer Religion wiedergegeben wurde, sondern eine auf das Land Israel selbst bezogene Aussage dargestellt ist. So sei die Flagge als eine Interpretation des Kapitels 15 Vers 18 des 1. Buches Mose (Genesis 15:18) zu sehen, in der die Lage des von Abraham den Juden versprochenen Landes zwischen Nil und Euphrat versinnbildlicht wird: An dem Tage schloss der Herr einen Bund mit Abraham und sprach: "Deinen Nachkommen will ich dieses Land geben, von dem Strom Ägyptens bis an den großen Strom Euphrat." |
Often, however, the following is said: Seeing that the flag was created by a Zionist is it likelyer that there is
not reproduced an outward sign of jewish religion, but it is pictured an
about the country Israel itself refered declaration. In this way the flag should be to see as an interpretation of the chapter 15 verse 18 of the 1st book of Moses (Genesis 15:18) in which is symbolized the position of the by Abraham to the jews promised land between Nile and Euphrat: On that day the Lord made a covenant with Abram, saying, "To your descentants I give this land, from the river of Egypt to the great river, the river Euphrates." |
| Es liegen keine Angaben oder Quelle vor, die den Farbton Blau exakt definieren. Das betrifft alle drei Farbtöne, das Mittelblau der Nationalflagge, das Marineblau der Seeflaggen und das Hellblau der Flagge der Luftwaffe. Für die Nationalflagge lässt sich Pantone 300 finden, Pantone 281 und Pantone 286. Das Blau in den Seeflaggen wird Marineblau genannt, gemäß der Farbtafel des Flaggenkatalogs der Britischen Streitkräfte "Flags of all Nations" wäre Marineblau als Pantone 282 zu definieren, das Hellblau der Luftwaffe als Azurblau Pantone 549. |
There is no information
or source that precisely defines the shade of blue. This applies to all
three shades, the medium blue of the national flag, the navy blue of the sea
flags and the light blue of the air force flag. For the national flag, Pantone 300 can be found, Pantone 281 and Pantone 286. The blue in the sea flags is called navy blue, according to the colour chart of the British Armed Forces flag catalogue "Flags of all Nations", navy blue would be defined as Pantone 282, the light blue of the air force as azure Pantone 549. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Wikipedia (DE), Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World, Flags of all Nations | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Israel – coat of arms of Israel, Quelle/Source: nach by: Flaggen und Wappen |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das
Staatswappen wurde am 11.02.1949 offiziell eingeführt. Es zeigt die Menorah, den siebenarmigen Leuchter des alten Jerusalemer Tempels, und wird links und rechts von zwei Olivenzweigen eingefasst. Darunter in hebräischer Schrift der Name des Landes. |
The coat of arms of the state was officially introduced on the 11th of February in 1949. It shows the Menorah, the seven-armed candelabra of the ancient Jerusalem temple and is bordered to the left and to the right by two olive twigs. Underneath in Hebrew fonts the name of the country. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel, Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte bis 1862 siehe → Palästina 1862 · Herausbildung des Zionismus als jüdische Nationalbewegung 1917 · Balfour-Deklaration – Großbritannien beansprucht große Teile des Osmanischen Reiches nach dem bevorstehenden Kriegsende, und erklärt sich mit der Bildung einer „nationalen Heimstätte“ für die Juden in diesem Gebiet einverstanden 1920 · der Vertrag von San Remo spricht Großbritannien Palästina, Transjordanien und Irak als Mandatsgebiete des Völkerbundes zu 1922 · Palästina (einschließlich Jordanien) wird britisches Völkerbundsmandat 1923 · Jordanien wird als Emirat Transjordanien abgetrennt 1929 · blutige Auseinandersetzungen zwischen Arabern und Juden 1936 · nach jahrelanger starker jüdischer Einwanderung und keinerlei Reaktion der britischen Mandatsmacht, und keinerlei Garantien für Unabhängigkeit eines arabischen Palästina kommt es zu einem Arabischen Nationalaufstand 1939 · Niederschlagung des letzten arabischen Widerstands, britische Zusage auf einen gemeinsamen jüdisch-arabischen Staat binnen 10 Jahren 1942 · Zionisten fordern in New York die Bildung eines jüdischen Staats in Palästina 29.11.1947 · VN-Beschluss über die Bildung eines jüdischen Staates (Israel) und eines arabischen Staates (Palästina) auf dem Territorium des Mandatsgebietes Palästina → Ablehnung durch die Araber → Bürgerkrieg 14.05.1948 · das britische Mandat für Palästina endet, Proklamierung des Staates Israel 1948–1949 · israelisch-arabischer Krieg, Annexion von 6.700 km² arabischen Territoriums durch Israel, Vertreibung der dort ansässigen arabischen Bevölkerung, die Palästinenser verzichten auf die Proklamation eines arabischen Staates, da er die Anerkennung der Teilung des Landes und der israelischen Annexionen bedeutet hätte 11.05.1949 · Israel wird Mitglied der VN 1950 · "Rückkehrgesetz", alle Juden die sich in Israel ansiedeln erhalten sofort die Staatsbürgerschaft, 1,7 Millionen Juden kommen ins Land 24.04.1950 · Transjordanien übernimmt die Verwaltung des Westjordanlands und nennt sich jetzt Jordanien, Ägypten übernimmt die Verwaltung des Ghazastreifens 29.10.1956 · israelische Aggression gegen Ägypten, Besetzung der Halbinsel Sinai und des Ghazastreifens → Intervention der USA, der Sowjetunion und der VN 25.12.1956 · die israelischen Truppen müssen den Sinai räumen, Stationierung von VN-Tuppen 08.03.1957 · die israelischen Truppen müssen den Ghazastreifen räumen, Stationierung von VN-Tuppen 1967 · Abzug der VN-Truppen 05.06.1967 · Israel greift Ägypten, Syrien und Jordanien an und besetzt innerhalb von sechs Tagen ("Sechstagekrieg") die ganze Sinaihalbinsel, den Gazastreifen, das Westjordanland, Ostjerusalem und die syrischen Golanhöhen 1969–1970 · Kampfhandlungen mit Ägypten am Suezkanal 06.10.1973 · Ägypten und Syrien greifen Israel zur Rückgewinnung der besetzten Gebiete erfolglos an (Jom-Kippur-Krieg) 1974 · Israelisch-Ägyptisches Friedensabkommen 1974 · israelisch-syrisches Abkommen, Teilrückzug der israelischen Truppen von den Golanhöhen 1975 · Israelisch-Ägyptisches Friedensabkommen, Teilrückzug der israelischen Truppen von der Sinaihalbinsel 1978 · Israelisch-Ägyptisches Friedensabkommen von Camp David 26.03.1979 · Israelisch-Ägyptischer Friedensvertrag 1982 · Abzug der letzten israelischen Truppen von der Sinaihalbinsel 06.06.1982 · gegen palästinensische Truppen (PLO) gerichteter Angriff Israels auf Libanon, die PLO muss Libanon verlassen 1985 · Teilrückzug der israelischen Truppen aus dem Libanon, ein breiter Grenzstreifen bleibt besetzt 1988 · Jordanien trennt sich vom Westjordanland 13.09.1993 · Abkommen zwischen Israel und der PLO, Abzug der israelischen Truppen aus dem Gazastreifen und Jericho, Herstellung einer begrenzten lokalen palästinensischen Selbstverwaltung 1994 · Israelisch-Jordanischer Friedensvertrag, Errichtung erster palästinensischer Selbstverwaltungen in Jericho und im Gazastreifen 1995 · Teilrückzug der israelischen Truppen aus dem Westjordanland, palästinensische Selbstverwaltungen in weiteren Städten 1996 · Wahl des palästinensischen Autonomierates mit einem Präsidenten an der Spitze 2001 · Rückzug der israelischen Truppen dem südlibanesischen Grenzstreifen August 2006 · Israelische Truppen marschieren im Libanon ein, in 34 Tagen Krieg gelingt es nicht die Hisbolla-Miliz zu schwächen, der Süden Libanon wird druch die Aktionen der Israelis weitgehend zerstört 2007 · Kämpfe zwischen den Palästinenser-Fraktionen Hamas und Fatah, die Hamas erobert den gesamten Ghazastreifen und beansprucht die Führung Palästinas 2008–2009 · israelische Militäroperation im Gazastreifen 2014 · israelische Militäroperation im Gazastreifen 07.10.2023 · die Hamas überfällt aus dem Ghazastreifen heraus das umliegende israelische Gebiet und überzieht die Region mit religiös aufgeladenem Terror, binnen zwei Tagen erkämpft Israel die Kontrolle über seine Gebiete zurück und bekämpft in den folgenden Wochen Strukturen der Hamas im Ghazastreifen |
|
History to 1862 look → Palestina 1862 · development of the Zionism as jewish national movement 1917 · Balfour-Declaration – United Kingdom demands large parts of the Ottoman Empire after the forthcoming end of the war and is in agreement with the idea of the creation of a „national homestead“ for the jews in this area 1920 · the treaty of San Remo assignes United Kingdom as a mandate of the League of Nations the countries Palestina, Transjordan and Iraq 1922 · Palestina (including Jordan) becomes a British mandate of the League of Nations 1923 · Jordan becomes separated es Emirate of Transjordan 1929 · bloody quarrels between Arabs and Jews 1936 · after a many years lasting strong jewish immigration and none reaction of the British mandate force and none guaranties for the independence of an Arabian Palestina arises an Arabian national rebellion 1939 · annihilation of the last Arabian resistance, British promise for a common jewish-arabian state within 10 years 1942 · Zionists claim in New York the formation of a jewish state within Palestina 29th of November in 1947 · UN-Resulution about the formation of a jewish state (Israel) and an arabian state (Palestina) on the area of the mandate territory of Palestina → dismissed by the Arabs → civil war 14th of May in 1948 · the British mandate for Palestina ends, proclamation of the State of Israel 1948–1949 · Israeli-Arabian war, annexation of 2.587 square miles of Arabian territory by Israel, expulsion of the here resident Arabian population, the Palestinians disclaim the proclamation of an Arabian state because this will imply the recognition of the partition of the country and the Israeli annexations 11th of May in 1949 · Israel becomes a member of the UN 1950 · "return law", all jews which settle in Israel get immediately the citizenship, 1,7 millions of jews come into the country 24th of April in 1950 · Transjordan assumes the administration of the Western Jordan Land and nominates itself now Jordan, Egypt assumes the administration of the Ghaza Stripe 29th of October in 1956 · Israeli aggression against Egypt, occupation of the Sinai Peninsula and the Ghaza Stripe → intervention of the USA, the Soviet Union and the UN 25th of December in 1956 · the Israeli troops have to leave the Sinai, stationing of UN-troops 8th of March in 1957 · the Israeli troops have to leave the den Ghaza Stripe, stationing of UN-troops 1967 · withdrawal of the UN-troops 5th of June in 1967 · Israel attacks Egypt, Syria and Jordan and occupies within six days ("Six Days War") the whole Sinai Peninsula, the Ghaza Stripe, the Western Jordan Land, East Jerusalem and the Syrian Golan Heights 1969–1970 · battles with Egypt near the Suez channel 6th of October in 1973 · Egypt and Syria attack Israel unsuccessfully to win back the occupied territories (Jom Kippur War) 1974 · Israeli-Egyptian peace agreement 1974 · Israeli-Syrian agreement, partial withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Golan Heights 1975 · Israeli-Egyptian peace agreement, partial withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Sinai Peninsula 1978 · Israeli-Egyptian peace agreement of Camp David 26th of March in 1979 · Israeli-Egyptian peace treaty 1982 · withdrawal of the last Israeli troops from the Sinai Peninsula 6th of June in 1982 · against Palestinian troops (PLO) addressed Israeli attack against Lebanon, the PLO has to leave Lebanon 1985 · partial withdrawal of the Israeli troops from Lebanon, a broad frontier stripe stays occupied 1988 · Jordan disconnects itself from the Western Jordan Land 13th of September in 1993 · arrangement between Israel and the PLO, withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Ghaza Stripe and Jericho, establishing of a limited local Palestinian self administration 1994 · Israeli-Jordanian peace treaty, establishment of first Palestinian Autonomy Administrations in Jericho and in the Ghaza Stripe 1995 · partial withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the Western Jordan Land, Palestinian Autonomy Administrations in further towns 1996 · election of the Palestinian Autonomy Counsel with a President on the top 2001 · withdrawal of the Israeli troops from the south Lebanese frontier stripe August 2006 · Israeli troops invade in Lebanon, in 34 days of war there was no success to weaken the Hisbolla Militia, the south of Lebanon becomes appreciably destroyed by the campaigns of the Israeli 2007 · struggles between the Palestinian factions of Hamas and Fatah, Hamas conquers the whole Ghaza Stripe and claims the leadership in Palestine 2008–2009 · Israeli military operation in the Gaza Strip 2014 · Israeli military operation in the Gaza Strip 7th of October in 2023 · Hamas invades the surrounding Israeli territory from the Ghaza Strip and covers the region with religiously charged terror; within two days, Israel regains control over its territories and fights Hamas structures in the Ghaza Strip in the weeks that follow |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Weltgeschichte, Discovery '97 |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Israel" wird erstmals um 1210 v. Chr. auf der Israelstele des Pharaos Merenptah erwähnt. Das bezog sich damals auf die Stämme der Hebräer die in Kanaan lebten. Für den Namen Israel hat man sich 1948 bei der Gründung des Staates entschieden. Andere Vorschläge waren: Zion, Judäa, Neu-Judäa. | The name "Israel" is mentioned for the first time around 1210 B.C. on the Israel-Pillar of Pharaoh Merneptah. This then referred to the tribes of the Hebrews who lived in Canaan. The name Israel was chosen in 1948 on the occasion of the establishing of the state. Other proposals were: Zion, Judea, New Judea. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |