|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since Dec. 2024, National-, Staats, Handels- und Marineflagge – national, state, merchant and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE)   |
andere Flaggen – other Flags: |
|
 |
2025, Flagge des Militärrats zur Befreiung Syriens – flag of Military Council for the Liberation of Syria, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Volker Preuß   |
 |
seit/since 17.03.2016, Rojava, Flagge der Kurdenregion Rojava in Nordsyrien – flag of the Kurdish region of Rojava in Northern Syria, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
Flagge der Chaldäer (Christen der Chaldäisch-katholische Kirche) – flag of the Chaldeans (Christians of the Chaldean Catholic Church), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge der Aramäer – flag of the Arameans, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2 (2:3), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge der Assyrer – flag of the Assyrians, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 7:10, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge der Drusen – flag of Druze, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
bis/to 1918, Flagge des Osmanischen Reichs – flag of the Ottoman Empire, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1918–1920, Flagge des arabischen Aufstands – flag of the Arab Uprising, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen |
 |
1920 (März–Juli / March–July), Flagge des Königreichs Syrien – flag of the Kingdom of Syria, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
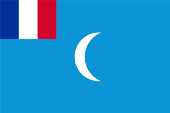 |
1920 (Juli–Aug. / July–Aug.), Syrien unter französischem Mandat – Syria under French Mandate, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1932, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1932–1958, 1961–1963, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3 (1:2), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1958–1961, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1963–1972, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1972–1980, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1980–2024, National-, Staats, Handels- und Marineflagge – national, state, merchant and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1980–2024, Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1980(?)–2024, Flagge der Streitkräfte – flag of the Armed Forces, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1980(?)–2024, Flagge des Heeres – flag of the Army, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1980(?)–2024, Flagge der Luftwaffe – flag of the Air Force, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1980(?)–2024, Flagge der Marine – flag of the Navy, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
2012–2024, Flagge der Nationalen Verteidigungskräfte – flag of the National Defence Force, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1966–2024, Flagge der Baath-Partei – flag of the Baath Party, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
Die heutige Flagge
Syriens wurde am 13.03.2025 im Rahmen der Annahme einer Übergansverfassung
offiziell festgelegt. Sie war faktisch schon seit dem 10.12.2024 mit der
Machtübernahme der der islamistischen Machthaber in Gebrauch genommen
worden, nachdem sie in den Jahren zuvor von der Opposition verwendet wurde.
Die Flagge zeigt – wie in den Jahren von 1932 bis 1958 und 1961 bis 1963 –
drei waagerechte Streifen in Grün, Weiß und Schwarz, sowie drei fünfzackige
rote Sterne in der Mitte des weißen Streifens. Die drei Sterne standen ursprünglich für die drei ehemaligen
osmanischen Provinzen Damaskus, Aleppo und Deir az-Zor, aus denen Syrien
nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg gebildet wurde. Die Flagge war bereits 1932
eingeführt und bis 1958 beibehalten worden, als sich das Land 1958 der
Vereinigten Arabischen Republik (VAR) anschloss und dann die gemeinsame
Flagge in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz benutzt wurde. Sie noch einmal von 1961 bis
1963 in Gebrauch. Die Farben der Flagge sind die Panarabischen Farben (siehe
unten) und beziehen sich auf die Flagge des Arabischen Aufstandes, die 1918
von den Haschemiten aus Hedschas eingeführt wurden war. Den Farben wird
heute auch folgende Bedeutung gegeben: Rot steht für das Blut, das für die
Erlangung der Ziele im Kampf vergossen wurde, Weiß symbolisiert die
strahlende Zukunft, Schwarz steht für die Jahre der Unterdrückung und Grün
ist die Farbe des Propheten Mohammed und des Islams. Die vorher verwendete
Flagge Syriens war am 29.03.1980 eingeführt worden, nachdem sie schon einmal
zwischen 1958 und 1961 in Verwendung war. Sie zeigte drei waagerechte
Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz, sowie zwei fünfzackige grüne Sterne in
der Mitte des weißen Streifens. Der Farbendreiklang von Rot, Weiß und
Schwarz wird auch hier manchmal als Panarabische Farben bezeichnet. Das ist
so nicht ganz richtig. Die drei Farben gehen zurück auf Gamal Abd el-Nasser,
ägyptischer Offizier, Politiker sowie späterer Staats- und Ministerpräsident
(1918–1970), wichtigster Vertreter des arabischen Nationalismus und
Panarabismus. Nach der nationalen Revolution des Jahre 1952 wurde in Ägypten
die Arabische Befreiungsflagge eingeführt, welche eben diese Ideale
repräsentierte. Sie wurde, zumindest in der Auswahl und Anordnung Vorbild
für viele andere arabische Staaten und Staatenbündnisse. Die Farben stehen
immer für die Revolution (Rot), die Zukunft (Weiß) und die Vergangenheit
(Schwarz). Die Farben Rot, Weiß und Schwarz gehen trotzdem auf die Flagge
des Arabischen Aufstandes im Ersten Weltkrieg zurück. Zu den Farben des
Arabischen Aufstandes (Arabische Bewegung) gehört allerdings noch Grün. Die
erste Flagge Syriens geht auf das Jahr 1920 zurück, als es kurzeitig ein
Königreich Syrien gab. Dessen Flagge war die Flagge des Arabischen
Aufstandes, jedoch zeigte das rote Dreieck am Mast noch zusätzlich einen
weißen, siebenzackigen Stern. Danach kam das heutige Syrien und auch der
Libanon unter französische Mandatsverwaltung des Völkerbundes. Für das
Gebiet wurde 1920 eine hellblaue Flagge mit einem Halbmond und der
französischen Trikolore in der Oberecke eingeführt. Aber schon nach wenigen
Monaten wurde das Mandatsgebiet ethnisch-religiös in verschiedene Gebiete
aufgeteilt, die alle ihre eigenen, verschiedenen Flaggen hatten, jedoch meist
mit der französischen Trikolore in der Oberecke. Das waren: 1)
Alawiten-Staat von Latakia (1920–1936), 2) Staat von Aleppo (1920–1924), 3)
Staat von Damaskus (1920–1922), 4) Staat Großlibanon (1920–1943), 5)
Drusen-Staat von Souaida (1921–1932). Diese Gebiete wurden nach und nach
wieder unter eine gemeinsame Verwaltung gestellt, die 1922 gegründete
Syrische Föderation. Deren Flagge zeigte drei horizontale Streifen in Grün,
Weiß und Grün und die französische Trikolore in der Oberecke. Aus dieser
Föderation ging 1925 der Staat Syrien hervor, der die grün-weiß-grüne Flagge
wahrscheinlich bis 1932 beibehielt. Am 01.01.1932 wurde eine neue Flagge
eingeführt. Sie zeigte drei waagerechte Streifen in Grün, Weiß und Schwarz,
sowie drei fünfzackige rote Sterne in der Mitte des weißen Streifens. Die
Farben dieser Flagge sind die Panarabischen Farben (siehe unten) und
beziehen sich auf die Flagge des Arabischen Aufstandes, die 1918 von den
Haschemiten aus Hedschas eingeführt wurden war. Die drei Sterne standen für
die drei ehemaligen osmanischen Provinzen Damaskus, Aleppo und Deir az-Zor,
aus denen Syrien nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg gebildet wurde. Die Flagge blieb
in Syrien in Gebrauch, bis sich das Land 1958 der Vereinigten Arabischen
Republik (VAR) anschloss und die gemeinsame Flagge benutzt wurde. Diese
zeigte drei waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz, sowie zwei
fünfzackige grüne Sterne (Syrien und Ägypten) in der Mitte des weißen
Streifens. Nach dem Austritt Syriens aus der VAR im Jahre 1961 wurde wieder
die vorherige Flagge eingeführt. Am 08.03.1963 wurde eine neue Flagge
eingeführt, die der Flagge der VAR ähnelte. Sie zeigte drei waagerechte
Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz, sowie drei fünfzackige grüne Sterne in
der Mitte des weißen Streifens. Die drei Sterne auf dieser Flagge
symbolisierten eine geplante Union mit Ägypten und dem Irak. Im Irak wurde
diese Flagge auch eingeführt, und im Prinzip bis 2008 beibehalten. Im Jahre
1971 kam in Syrien Präsident Hafiz al Assad an die Macht und 1972 wurde wieder eine
neue Flagge eingeführt. Die drei Sterne wurden entfernt und durch eine
goldene Version des Staatswappens ersetzt. Am 29.03.1980 wurde wieder die
Flagge der VAR eingeführt und bis heute beibehalten. Die zwei Sterne stehen
nun für die Hoffnung, mit Ägypten einst wieder ein starkes Bündnis zu
schließen. Die Panarabischen Farben: Der Farbenvierklang von Grün, Weiß, Schwarz und Rot ist ein speziell arabisches Farbsymbol, die Panarabischen Farben. Diese Farben wurden während des 1. Weltkriegs, bei der Loslösung des Königreichs Hedschas vom Osmanischen Reich, durch den Scherifen Hussein von Mekka – aus dem Geschlecht der Haschemiden – als Farben der Arabischen Bewegung offiziell eingeführt. Als Vorlage diente die Flagge des Hedschas. Die Farben haben folgende Bedeutung: Rot ist die Farbe von Omar, dem zweiten Kalifen; Weiß steht für die Omajiaden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den fünften Kalifen Moawija I. zurückgeht; Grün steht für die Fatimiden, eine ismailitisch-schiitische Kalifendynastie, die auf den vierten Kalifen Ali zurückgeht; und Schwarz steht für die Abbasiden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den Kalifen Abbas I. zurückgeht. Rot ist außerdem die Farbe der Haschemiden, eine arabische Herrscherdynastie, die wahrscheinlich auf Haschim ibn Abd al-Manaf, den Großvater Mohammeds, zurückgeht. |
The current flag of Syria
was officially adopted on 13th of March in 2025 as part of the adoption of a
transitional constitution. It had actually been in use since 10th of
December 2024, when the new Islamist rulers took power, after having been
used by the opposition in previous years. As in the years from 1932 to 1958 and 1961 to 1963, the flag features three horizontal stripes in green, white and black, as well as three five-pointed red stars in the centre of the white stripe. The three stars originally stood for the three former Ottoman provinces of Damascus, Aleppo and Deir az-Zor, from which Syria was formed after the First World War. The flag had already been introduced in 1932 and was retained until 1958, when the country joined the United Arab Republic (VAR) in 1958 and the common flag in red, white and black was then used. It was used again from 1961 to 1963. The colours of the flag are the Pan-Arab colours (see below) and refer to the flag of the Arab Revolt, which was introduced by the Hashemites from Hejaz in 1918. The colours are also given the following meaning today: Red stands for the blood spilled to achieve the goals in the struggle, white symbolises the bright future, black stands for the years of oppression and green is the colour of the Prophet Mohammed and Islam. The previously used flag of Syria was introduced on 29th of March in 1980, having already been in use between 1958 and 1961. It showed three horizontal stripes in red, white and black, as well as two five-pointed green stars in the centre of the white stripe. The colour triad of red, white and black is also sometimes referred to here as the Pan-Arabic colours. This is not entirely correct. The three colours go back to Gamal Abd el-Nasser, Egyptian officer, politician and later president and prime minister (1918-1970), the most important representative of Arab nationalism and pan-Arabism. After the national revolution of 1952, the Arab Liberation Flag was introduced in Egypt, representing these ideals. It became a model for many other Arab states and confederations, at least in its choice and arrangement. The colours always stand for the revolution (red), the future (white) and the past (black). Nevertheless, the colours red, white and black go back to the flag of the Arab Revolt during the First World War. However, the colours of the Arab Revolt (Arab Movement) also include green. The first flag of Syria dates back to 1920, when there was a brief Kingdom of Syria. Its flag was the flag of the Arab Uprising, but the red triangle on the mast also showed a white, seven-pointed star. Afterwards, what is now Syria and Lebanon came under the French mandate of the League of Nations. A light blue flag with a crescent and the French tricolor in the upper corner was adopted for the area in 1920. But after just a few months, the mandate was divided ethnically and religiously into different areas, each with their own different flags, but nearly all with the French tricolor in the top corner. These were: 1) Alawite State of Latakia (1920–1936), 2) State of Aleppo (1920–1924), 3) State of Damascus (1920–1922), 4) State of Greater Lebanon (1920–1943), 5) Druze State of Souaida (1921–1932). These areas were gradually brought back under common administration, the Syrian Federation, founded in 1922. Its flag featured three horizontal stripes of green, white and green and the French tricolor in the upper corner. The state of Syria emerged from this federation in 1925, which probably retained the green-white-green flag until 1932. A new flag was introduced on 1st of January in 1932. It featured three horizontal stripes of green, white and black, as well as three five-pointed red stars in the middle of the white stripe. The colors of this flag are the Pan-Arab Colors (see below) and refer to the flag of the Arab Uprising introduced by the Hashemites from Hejaz in 1918. The three stars stood for the three former Ottoman provinces of Damascus, Aleppo and Deir az-Zor, from which Syria was formed after the First World War. The flag remained in use in Syria until the country joined the United Arab Republic (UAR) in 1958 and the common flag was used. This flag showed three horizontal stripes of red, white and black, as well as two five-pointed green stars (Syria and Egypt) in the middle of the white stripe. After Syria left the UAR in 1961, the previous flag was reintroduced. On 8th of March in 1963, a new flag was introduced that was similar to the UAR flag. It featured three horizontal stripes of red, white and black, as well as three five-pointed green stars in the middle of the white stripe. The three stars on this flag symbolized a proposed union with Egypt and Iraq. This flag was also introduced in Iraq and has in principle been retained to 2008. In 1971, President Hafiz al Assad came to power in Syria and in 1972 a new flag was introduced once more. The three stars were removed and replaced with a golden version of the national coat of arms. The UAR flag was reintroduced on 29th of March in 1980 and has been retained to this day. The two stars now represent the hope of once again forming a strong alliance with Egypt. The Pan-Arabian Colors: The four colours of green, white, black and red are a special Arabic colour symbol, the Pan-Arabic colours. These colours were officially introduced as the colours of the Arab Movement during the First World War, when the Kingdom of Hejaz broke away from the Ottoman Empire, by Sheikh Hussein of Mecca – from the Hashemid dynasty. The flag of the Hejaz served as a model. The colours have the following meanings: red is the colour of Omar, the second caliph; white stands for the Umayyads, a dynasty of caliphs that goes back to the fifth caliph Moawiya I.; green stands for the Fatimids, an Ismaili-Shiite dynasty of caliphs that goes back to the fourth caliph Ali; and black stands for the Abbasids, a dynasty of caliphs that goes back to the caliph Abbas I. Red is also the colour of the Hashemids, an Arab ruling dynasty that probably goes back to Hashem ibn Abd al-Manaf, the grandfather of Muhammad. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since Jul. 2025, Wappen von Syrien – coat of arms of Syria, Quelle/Source: Suriye Arap Cumhuriyeti, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Dec.2024–Jul.2025, Wappen von Syrien – coat of arms of Syria, Quelle/Source: See page for author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1980–2024, Wappen von Syrien – coat of arms of Syria, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1972–1980, Wappen von Syrien – coat of arms of Syria, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das heutige Staatswappen Syriens wurde am 3. Juli 2025 eingeführt, ein Stilbruch zum vorherigen Wappen, das in seiner Grundform bereits 1932 als Wappen des Landes angenommen und seitdem – je nach politischem Kurs – immer wieder leicht abgewandelt worden war. Das Wappen zeigt damals wie heute einen goldenen Falken, jetzt nur noch als flächige Silhouette. Der goldene Falke ist das Emblem des Kuraisch-Stammes, dem der Prophet Mohammed entstammte. Der Falke verzichtet auf jegliches schmückendes Beiwerk, wenn man von den drei von der Flagge bekannten Sternen absieht, die oberhalb des Kopfes des Falken erscheinen. Sie wurden sicherlich von der Flagge übernommen, standen jedoch ursprünglich für die drei ehemaligen osmanischen Provinzen Damaskus, Aleppo und Deir az-Zor, aus denen Syrien nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg gebildet wurde. Bis zum Jahr 2025 zeigte der Falke auf der Brust einen Schild, meist entsprechend der jeweils gültigen Flagge gestaltet worden war. Das Schriftband darunter trug immer den Namen des Landes. Lediglich in der Zeit der Vereinigten Arabischen Republik (1958–1961) wurde ein anderes Wappen verwendet, das zwar ähnlich war, aber den Adler Saladins zeigte. |
The current national coat
of arms of Syria was introduced on 3rd of July in 2025, a break in style
from the previous coat of arms, which was adopted as the country's coat of
arms in its basic form already in 1932 and has been slightly modified ever
since, depending on the political course. Then as now, the coat of arms shows a golden falcon, now only as a two-dimensional silhouette. The golden falcon is the emblem of the Kuraish tribe from which the Prophet Mohammed descended. The falcon is devoid of any decorative accessories, apart from the three stars known from the flag, which appear above the falcon's head. They were certainly taken from the flag, but originally stood for the three former Ottoman provinces of Damascus, Aleppo and Deir az-Zor, from which Syria was formed after the First World War. Until 2025, the falcon displayed a shield on its chest, usually designed corresponding to the flag in force at the time. The ribbon below always bore the name of the country. Only during the period of the United Arab Republic (1958–1961) a different coat of arms was used, which was similar but showed the eagle of Saladin. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1972–2024, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1963–1972, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1948–1958, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Besiedlung durch Kanaaniter und Hurriter 2. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Besiedlung durch Aramäer Ende 2. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Teil Assyriens 539 v.Chr. · zu Persien 333 v.Chr. · zum Reich Alexanders des Großen 300 v.Chr. · Zentrum des Reiches der Seleukiden 63 v.Chr. · zum Römischen Reich 395 n.Chr. · zum Oströmischen Reich (Byzanz) 635–637 · Eroberung durch die Araber, Islamisierung ca. 945–1000 · zum Reich der Hamdaniden 1076 · Eroberung durch die Seldschuken, später an das Reich der Fatimiden (Ägypten) 1099–1291 · teilweise unter der Herrschaft der Kreuzfahrer (Fürstentum Antiochia, Grafschaft Tripolis, Königreich Jerusalem) 1303–1260 · Teil des Mongolenreiches 1260 · Eroberung durch die Mamluken (Ägypten) 1516–1918 · Teil des Osmanischen Reiches (Türkei) 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg, Eroberung durch britische und arabische Truppen im Jahre 1918 1919 · Abzug der britischen Truppen, Besetzung durch französische Truppen 1920 · Proklamation des Haschemitischen Königreiches Syrien durch Faisal I., Niederwerfung durch französische Truppen, Syrien wird französisches Völkerbundsmandat 1926 · Ausgliederung des Libanon als eigene Republik 1936 · geplante Unabhängigkeit wird nicht gewährt 1939 · Abtretung von Alexandrette (Iskenderun) an die Türkei 1939–1945 · Zweiter Weltkrieg, britische und "freie" französische Truppen besetzen das Land im Jahre 1941 1941 · formelle Unabhängigkeit 17.04.1946 · Abzug der französischen Truppen, volle Unabhängigkeit von Frankreich 1958 · Zusammenschluss mit Ägypten zur Vereinigten Arabischen Republik (VAR) 1961 · Militärputsch, Ende der Vereinigten Arabischen Republik 1963 · Wahlen, die Baath-Partei kommt an die Macht 1967 · Sechstagekrieg gegen Israel, Israel besetzt die syrischen Golanhöhen 1970 · Machtübernahme durch General Hafiz al-Assad 1973 · neue Verfassung, demokratischer, sozialistischer, souveräner Volksstaat Oktober 1973 · Angriff Syriens und Ägyptens auf Israel, israelische Truppen dringen in Syrien ein 1976 · Einmischung Syriens in den libanesischen Bürgerkrieg, syrische Truppen besetzen große Teile des Libanon 1991 · 2. Golfkrieg, Syrien unterstützt die USA 10.06.2000 · Tod von Hafiz al-Assad 10.07.2000 · Baschar al-Assad, Sohn von Hafiz al-Assad, wird zum Präsidenten gewählt 2005 · die syrischen Truppen verlassen den Libanon seit 2011 · Bürgerkrieg (zunächst 2011 radikal-islamische Proteste, ab 2012 Invasion des Islamischen Staats, ab 2014 Rückeroberungen durch die Syrische Regierung und Kurden, dabei Kurdische Expansion, ab 2015 Invasion der Türkei im Norden, die Syrische Regierung bittet Russland um Hilfe, der Islamische Staat wird zerschlagen, die Kurden halten die eroberten Gebiete besetzt oder verwalten sie gemeinsam mit der Syrischen Regierung, die radikal-islamischen Kräfte werden im Nordwesten isoliert (Idlib), die Türkei hält Gebiete im Norden besetzt) 17.03.2016 · die Kurden proklamieren im Norden Syriens die Autonome Region "Rojava" (Syrisch-Kurdistan, Westkurdistan) November/Dezember 2024 · radikal-islamistische syrische Rebellen unter Ahmed al-Sharaa beginnen aus der Region Idlib heraus eine Großoffensive und besetzen binnen weniger Tage nahezu das ganze Land, am 07.12.2024 verließ Präsident Assad zur vor der Einnahme von Damaskus Syrien in Richtung Russland März 2025 · Formierung des bewaffneten Widerstands im Raum Latakia unter dem "Militärischen Rat zur Befreiung Syriens" gegen die radikal-islamistische Führung des Landes |
|
|
4th millenary B.C. · settlement by Kanaanitans and Hurrits 2nd millenary B.C. · settlement by Arameans end of 2nd millenary B.C. · part of Assyria 539 B.C. · to Persia 333 B.C. · to the Empire of Alexander the Great 300 B.C. · center of the Empire of the Seleukids 63 B.C. · to the Roman Empire 395 A.D. · to the East Roman Empire (Byzantium) 635–637 · conquest by the Arabs, Islamization ca. 945–1000 · to the Empire of the Hamdanids 1076 · conquest by the Selchuks, later to the Empire of the Fatimids (Egypt) 1099–1291 · partial under the rule of the crusaders (Principality of Antiochia, County Tripolis, Kingdom of Yerusalem) 1303–1260 · part of the Empire of the Mongols 1260 · conquest by the Mamluks (Egypt) 1516–1918 · part of the Ottoman Empire (Turkey) 1914–1918 · First World War, conquest by British and Arabian troops in the year 1918 1919 · withdrawal of the British troops, occupation by French troops 1920 · proclamation of the Hashemit Kingdom of Syria by Faisal I., subjection by French troops, Syria becomes a French mandate territory of the League of Nations 1926 · excorporation of Libanon as an own republic 1936 · planed independence is not granted 1939 · ceding of Alexandrette (Iskenderun) to the Turkey 1939–1945 · Second World War, British and "free" French troops occupy the country in 1941 1941 · formal independence 17th of April 1946 · withdrawal of the French troops, full independence from France 1958 · union with Egypt to the United Arabian Republic (UAR) 1961 · military coup d’état, end of the United Arabian Republic 1963 · elections, the Baath Party comes to the power 1967 · Six Days War against Israel, Israel occupies the Syrian Golan Heights 1970 · takeover by General Hafiz al-Assad 1973 · new constitution, democratic, socialistic, sovereign people's state October 1973 · attack of Syria and Egypt against Israel, Israeli troops invade Syria partially 1976 · intervention of Syria in the Lebanese civil war, Syrian troops occupy large parts of Lebanon 1991 · 2nd Gulf War, Syria supports the USA 10th of June 2000 · death of Hafiz al-Assad 10th of July 2000 · Bashar al-Assad, the son von Hafiz al-Assad, becomes elected to president 2005 · the Syrian troops leave Lebanon since 2011 · civil war (initially in 2011 radical Islamic protests, from 2012 invasion of the Islamic State, from 2014 recaptures by the Syrian government and Kurds, including Kurdish expansion, from 2015 invasion by Turkey in the north, the Syrian government asks Russia for help, the Islamic State is destroyed, the Kurds occupy the conquered areas or administer them together with the Syrian government, the radical Islamic forces are isolated in the northwest (Idlib), Turkey occupies areas in the north) 17th of March in 2016 · the Kurds proclaim in Northern Syria the Autonomous Region of "Rojava" (Syrian Kurdistan, West Kurdistan) November/December 2024 · radical islamist Syrian rebels under Ahmed al-Sharaa launch a major offensive from the Idlib region and occupy almost the entire country within a few days, on 7th of December in 2024, President Assad leaves Syria for Russia before the capture of Damascus March 2025 · formation of the armed resistance in the Latakia region under the "Military Council for the Liberation of Syria" against the country's radical Islamist leadership |
|
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte, Volker Preuß | |
Präsident Assad und seine Frau – President Assad and his wife |
Machthaber Sharaa und seine Frau – Ruler Sharaa and his wife |
| Der Name "Syrien" geht auf die Griechen zurück, als das Gebiet des heutigen Syrien zu Assyrien (Staat von Assur) gehörte. Assyrien heißt auf assyrisch "Aschschur", eventuell ein Hinweis auf die arabische Bezeichnung dieser geographischen Region "Bilad Asch-Scham". | The name "Syria" has old Greek roots, as the area of the today’s Syria belonged to Assyria (State of Assur). Assyria is in Assyrian language "Ashshur", possibly a hint to the Arabian name of that geographic region "Bilad Ash-Sham". |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |