Irak |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Irak |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
Flagge des Heeres – flag of the Army, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: By MrPenguin20 [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe – flag of the Air Force, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: By MrPenguin20 (Own work. Based on flag visible here.) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge der Marine – flag of the Navy, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: By MrPenguin20 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1917–1921, Nationalflagge – national flag, Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen |
 |
1921–1958, Nationalflagge – national flag, Quelle/Source: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild |
 |
1921–1958, Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild |
 |
1959–1963, |
 |
1943–2003, |
 |
1963–1991,   |
 |
1991–2004,   |
 |
2004–2008,   |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge des Irak wurde am 22.01.2008 eingeführt. Sie zeigt drei horizontale Streifen in den Farben Rot, Weiß und Schwarz und im weißen Mittelstreifen in grüner stilisierter arabischer Schrift die Worte "Allahu Akbar" (Allah ist groß). | Today's flag of Iraq was introduced on 22nd of January in 2008. It shows three horizontal strips in the colors red, white and black and in the white center stripe in green stylized Arabic letters the words "Allahu Akbar " (Allah is Great). |
| Die Flagge ist die letzte ihrer Art, welche die schrittweise Abschaffung der Flagge von 1963 verkörpert. Diese Flagge zeigte im weißen Mittelstreifen drei grüne Sterne. | The flag is the last of its kind, which embodies the gradual abolition of the flag of 1963. This flag showed three green stars in the white center stripe. |
| In Folge eines gescheiterten Staatsstreichs im Jahre 1963 kam eine neue Regierung an die Macht, welche eine Vereinigung mit Syrien und Ägypten anstrebte. Daher wurde (ebenso wie in Ägypten und Syrien) am 31.07.1963 eine neue Flagge angenommen, die sich am Vorbild der aus Ägypten stammenden Arabischen Befreiungsflagge orientierte: waagerecht Rot, Weiß und Schwarz gestreift, mit drei grünen Sternen im weißen Mittelstreifen. Die drei Sterne stehen für Irak, Ägypten und Syrien, die sich 1963 zur Vereinigten Arabischen Republik (VAR) zusammenschließen wollten. Die Sterne wurden auch nach dem Ende des VAR-Projektes in der irakischen Flagge beibehalten. | In result
of a failed coup d'état in the year 1963 came a new government into might,
which aimed for an unification with Syria and Egypt. That's why was adoped (just as in Egypt and Syria) a new flag on the 31st of July in 1963 which was orientated in the model of the from Egypt descending Arabian Liberation Flag: horizontally red, white and black striped with three green stars in the white middle stripe. The three stars stand for Iraq, Egypt and Syria, which wanted in 1963 to join to the United Arabic Republic (UAR). The stars got maintained in the Iraqi flag even after the end of the UAR project. |
| Am 14.01.1991, kurz vor dem Zweiten Golfkrieg, wurden auf Veranlassung von Präsident Saddam Hussein zwischen die drei grünen Sterne im weißen Mittelstreifen in kufischer Schrift die Worte "Allahu Akbar" (Allah ist groß) eingefügt. | On 14th of January in 1991 – directly before the Second Gulf War – were added by order of President Saddam Hussein the words "Allahu Akbar" (Allah is great) between the three green stars in the white middle stripe in green kufic letters. |
| Saddam Hussein wurde 2003 durch eine Militärintervention der USA und ihrer Verbündeten gestürzt. Die Flagge mit den drei Sternen und dem "Allahu Akbar" in kufischer Schrift blieb bis 2004 gültig. Am 28.06.2004 wurde die Flagge dann ein wenig abgeändert, in dem die kufische Schrift der Worte "Allahu Akbar" in eine stilisierte Schrift umgewandelt wurde. Am 22.01.2008 wurde dann durch entfernen der Sterne die heutige Flagge eingeführt. |
Saddam Hussein was overthrown in 2003 by a military intervention of the United States and its allies. The flag with the three stars and the "Allahu Akbar" in
kufic script remained valid until 2004. On 28th of June in 2004, the flag was changed a little bit, by altering of the in kufic script written words "Allahu Akbar" into a more stylized typeface. The current flag was introduced on 22nd of January in 2008 by removing the stars. |
| Der Farbendreiklang von Rot, Weiß und Schwarz wird manchmal als Panarabische Farben bezeichnet. Das ist so nicht ganz richtig. Die drei Farben gehen zurück auf Gamal Abd el-Nasser, ägyptischer Offizier, Politiker sowie späterer Staats- und Ministerpräsident (1918–1970), wichtigster Vertreter des arabischen Nationalismus und Panarabismus. Nach der nationalen Revolution des Jahre 1952 wurde in Ägypten die Arabische Befreiungsflagge eingeführt, welche eben diese Ideale repräsentierte. Sie wurde, zumindest in der Auswahl und Anordnung Vorbild für viele andere arabische Staaten und Staatenbündnisse. Die Farben stehen immer für die Revolution (Rot), die Zukunft (Weiß) und die Vergangenheit (Schwarz). Die Farben Rot, Weiß und Schwarz gehen auf die Flagge des Arabischen Aufstandes im Ersten Weltkrieg zurück. Zu den Farben des Arabischen Aufstandes (Arabische Bewegung) gehört allerdings noch Grün. | The
colour triad of red, white and black is referred as Panarabian colours.
This is not entirely correct. The three colours go back to the late Gamal
Abd el-Nasser (1918–1970), Egyptian military officer, politician as well as
later the state's president and prime minister, and most important
representative of the Arabian nationalism and panarabism. After the national revolution of 1952 the Arabian Liberation Flag was introduced in Egypt, which represented those ideals. It was, at least in choice and arrangement a model for many
other Arabian states and state alliances. The colours stand always for the
revolution (red), the future (white) and the past (black). The colours have
their roots in the flag of the Arabian Revolt during the First World War.
Yet the colours of the Arabian Revolt (Arabian Movement) include even green. |
| Der Farbenvierklang von Grün, Weiß, Schwarz und Rot ist ein speziell arabisches Farbsymbol, die Panarabischen Farben. Die (pan)arabischen Farben wurden während des 1. Weltkriegs, bei der Loslösung des Königreichs Hedschas vom Osmanischen Reich, durch den Scherifen Hussein von Mekka – aus dem Geschlecht der Haschemiden – als Farben der Arabischen Bewegung offiziell eingeführt. Als Vorlage diente die Flagge des Hedschas. Die Farben haben folgende Bedeutung: Rot ist die Farbe von Omar, dem zweiten Kalifen; Weiß steht für die Omajiaden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den fünften Kalifen Moawija I. zurückgeht; Grün steht für die Fatimiden, eine ismailitisch-schiitische Kalifendynastie, die auf den vierten Kalifen Ali zurückgeht; und Schwarz steht für die Abbasiden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den Kalifen Abbas I. zurückgeht. Rot ist außerdem die Farbe der Haschemiden, eine arabische Herrscherdynastie, die wahrscheinlich auf Haschim ibn Abd al-Manaf, den Großvater Mohammeds, zurückgeht. Grün ist außerdem die Farbe des Islam im Allgemeinen, und bezieht sich somit nicht nur auf die arabischen Länder. | The
colour quartet of four, green, white, black and red is a special Arabian
colours symbol, the Panarabian colours. The (Pan)Arabian colours were
officially introduced by the Sheriff Hussein of Mekka – of the lineage of
the Hashemides – as colours of the Arabian Movement during the First World
War at the secession of the Kingdom of Hedjas from the Ottoman Empire. The
flag of Hedjas served as pattern. The colours have the following meaning: Red is the colour of Omar, the second calif; white stands for the Omajiades, a calif-dynasty, which goes back to the fifth calif Moawija I.; green stands for the Fatimides, a ismailitic-shiit calif-dynasty, which goes back to the fourth calif Ali; and black stands for the Abbasides, a calif-dynasty, which goes back to the calif Abbas I. Red is also the colour of the Hashemides, an Arabian sovereign-dynasty, which probably goes back to Hashim ibn Abd al-Manaf, the grandfather of Mohammed. Green is in addition generally the colour of Islam, and does not refer only to the Arabian countries. |
| Die erste Flagge Flagge des Irak war eine inoffizielle Flagge, und wurde von den gegen das Osmanische Reich kämpfenden Arabern verwendet. Sie geht direkt auf die Flagge des Landes Hedschas zurück, dass sich an die Spitze des Arabischen Aufstandes gestellt hatte. | The first
flag of the Iraq was an unofficial flag, and was used from the against the
Ottoman Empire fighting Arabs. It goes directly back to the flag of the State of Hedjas, which placed itself on the top of the Arabian rebellion. |
| Im Jahre 1921 kam der Irak unter britische Kontrolle, da Großbritannien dieses ehemalige Osmanische Staatsgebiet als Völkerbundsmandat übertragen bekam. Die Briten gründeten das Königreich Irak, und setzten einen Haschemiten, einen Angehörigen des Herrscherhauses von Hedschas auf den Thron. Die Flagge des Königreiches zeigte ebenfalls die Farben des Arabischen Aufstandes, jedoch in einer anderen Reihenfolge. Die zum Mast hingewandte Seite der Schwarz, Weiß und Rot längsgestreiften Flagge zeigte ein grünes Trapez mit zwei siebenzackigen weißen Sternen. Der siebenzackige Stern geht auf die Haschemiten zurück. Er soll für die sieben Suren des Koran stehen, aber auch für die sieben Provinzen des von den Haschemiten beanspruchten Landes (Irak, Syrien, Libanon, Palästina, Jordanien, Hedschas und Asir). | In the
1921 the Iraq came under British control, because United Kingdom got assigned
those former Ottoman territory as a mandate of the League of Nations. The British established the Kingdom of Irak, and deployed an Hashemite on the throne, a member of the ruling dynasty of Hedjas. The flag of the kingdom showed likewise the colours of the Arabian Revolt, however in an other sequence. The to the pole pointing side of the black, white and red lengthwise striped flag showed a green trapezoid with two seven-jagged white stars. The seven jagged star goes back to the Hashemites. It should stand for the seven suras of the Koran but for the seven provinces of the from the Hashemites demanded land, too (Iraq, Syria , Lebanon , Palestina, Jordan , Hedjas and Asir). |
| Im Jahre 1958 wurde die Monarchie durch einen Militärputsch gestürzt, und die Republik ausgerufen. Es wurde daher im Jahre 1959 eine neue Flagge angenommen. Sie war nun Schwarz, Weiß und Grün senkrecht gestreift mit einem achtzackigen roten Stern im weißen Feld, mit einer goldenen Scheibe in der Mitte. | In the year 1958 the monarchy was unseated by a military coup d'état and the republic was proclaimed. Because of this was adoped a new flag in the year 1959. It was now black, white and green vertical striped with an eight-jagged red star in the white field with a golden disk in the middle. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind heute wie folgt definiert: Rot = HEX: #cd1125, RGB 205|17|37, CMYK 0|92|82|20, Pantone 186; Grün = HEX: #017b3d, RGB 1|123|61, CMYK 99|0|50|52, Pantone 348. | The colors of the flag are today defined as follows: red = HEX: #cd1125, RGB 205|17|37, CMYK 0|92|82|20, Pantone 186; green = HEX: #017b3d, RGB 1|123|61, CMYK 99|0|50|52, Pantone 348. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE), Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
1965–1991, Wappen des Irak – coat of arms of Iraq, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
 |
1991–2008, Wappen des Irak – coat of arms of Iraq, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
 |
seit/since 2008, Wappen des Irak – coat of arms of Iraq, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das heutige Staatswappen wurde im Jahre 1965 eingeführt. Es zeigt den Adler Saladins mit einem Wappenschild, das die Farben des Landes wie in der Flagge wiedergibt. Die Inschrift unterhalb des Adlers zeigt den Staatsnamen in kufischer Schrift. Das Wappen wurde in Folge der Änderung der Flagge in den Jahren 1991, 2004 und 2008 geändert. | The coat of arms of the state was introduced in 1965. It shows the eagle of Saladin with a blazon, that carries the colours of the land, and with this the colours of the failed UAR. The inscription in kufian font reproduces the name of the state. The coat of arms was changed in result of the change of the flag in the years 1991, 2004 and 2008. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Volker Preuß | |
andere Flaggen – other Flags: |
|
| Kurden/Kurds: | |
 |
Flagge der Autonomen Region Kurdistan – flag of Autonomous Iraqi Kurdistan Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Jesiden/Yazidis: | |
 |
Flagge der Jesiden – flag of the Yazidis, Variante / variant, nicht offiziell - not official |
| Turkomanen/Turcomans: | |
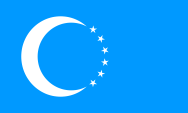 |
Flagge der Turkomanen – flag of the Turcomans, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Christen/Christians: | |
 |
Flagge der Chaldäer (Christen der Chaldäisch-katholische Kirche) – flag of the Chaldeans (Christians of the Chaldean Catholic Church) original Seitenverhältnis – original ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: chaldeanwiki.com |
 |
Flagge der Aramäer – flag of the Arameans |
 |
Flagge der Assyrer – flag of the Assyrians Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 7:10, Quelle/Source: UNPO |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1931–2004, seit/since 2019, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: Slady, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
2004-2019, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: vectored by FOX 52, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4.
Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Reich der Sumerer 3. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Reich der Akkader 1800–600 v.Chr. · Assyrisches Reich 1700–1530 v.Chr. · Babylonisches Reich 539 v.Chr. · persische Eroberung Babyloniens 331–323 v.Chr. · zum Reich Alexanders des Großen 312–140 v.Chr. · zum Reich der Seleukiden 141 v.Chr. bis 224 n.Chr. · Teil des Partherreichs 224–651 · Teil des Sassanidenreichs seit 636 · arabische Eroberung, Eindringen des Islam 762 · Bagdad wird Hauptstadt des Arabischen Kalifats 1258 · mongolische Eroberung 1534 · die Türken erobern Bagdad 1638 · das gesamte Gebiet des heutigen Irak kommt an das Osmanische Reich 1914–1915 · britische Eroberung 1921 · Großbritannien erhält Irak (die osmanischen Provinzen Mossul, Bagdad und Basra) als Mandat des Völkerbunds übertragen, Gründung des Königreichs Irak, Inthronisation des Haschemiten Faisal 30.06.1930 · nominelle Unabhängigkeit, Irak bleibt britische Einflusssphäre 1933 · Ghasi I. (Sohn von Faisal I.) übernimmt den Thron 1939 · Faisal II. (Sohn von Ghasi I.) übernimmt den Thron 24.02.1955 · Irak tritt dem Bagdadpakt bei und erhält die volle Souveränität, Großbritannien darf jedoch weiter Militärbasen in Irak unterhalten 14.07.1958 · Militärputsch unter Oberst Kassem, Sturz der Monarchie, Ermordung des Königs und des Premierministers, Proklamation der Republik 1959 · Austritt aus dem Bagdad-Pakt (neuer Name: CENTO), Großbritannien muss seine Stützpunkte räumen 1959 · Putschversuch der Baath-Partei 1961 · Kuweit-Konflikt, Kurden-Konflikt 1963 · Putschversuch der Baath-Partei, Ermordung von Kassem 1968 · Machtübernahme durch die Baath-Partei 1979 · Saddam Hussein wird Präsident 1980 · Ausbruch des 1. Golfkrieges (Irak gegen Iran) 20.08.1988 · Waffenstillstand zwischen Irak und Iran 1989/1990 · Spannungen mit Kuweit wegen des Öls, die USA lassen durch April Glaspie (Botschafterin der USA im Irak) erklären: "Die USA werden zu der Auseinandersetzung zwischen dem Irak und Kuweit keine Stellung beziehen" 02.08.1990 · der Irak besetzt Kuweit 15.01.1991 · die USA erklären Irak den Krieg 17.01.1991 · Ausbruch des 2. Golfkriegs (USA gegen Irak) 28.02.1991 · Kapitulation des Irak 1994 · Anerkennung der Souveränität Kuweits durch den Irak 1996 · Parlamentswahlen, Sieg für die regierende Baath-Partei 1996 · Kurdenaufstand 2003 · Ausbruch des 3. Golfkriegs (USA gegen Irak), der Irak wird widerrechtlich von USA, Großbritannien und Polen angegriffen und besetzt, der Irak wird US-amerikanisches Protektorat 2004 · Saddam Hussein wird gefangen genommen 28.06.2004 · Gewährung nomineller Selbstverwaltung (Übergangsverfassung) Oktober 2005 · neue Verfassung 30.12.2006 · Saddam Hussein wird nach einem Schauprozess von einem Tribunal zum Tode verurteilt und unter äußerst fragwürdigen Bedingungen hingerichtet 2008 · Abzug der polnischen und britischen Truppen 2009–2010 · Abzug der US-amerikanischen Kampftruppen, 50.000 Ausbilder und Militärberater bleiben im Land 2014–2017 · der Islamische Staat erobert Gebiete im Nordosten, anschließend Befreiungskrieg 2020 · das irakische Parlament beschließt den vollständigen Abzug aller US-amerikanischen Truppen 2021 · Abzug der US-amerikanischen Truppen, Militärberater bleiben jedoch im Land |
| 4th
millenary B.C. · Sumerian Empire 3rd millenary B.C. · Akkad Empire 1800–600 B.C. · Assyrian Empire 1700–1530 B.C. · Babylonian Empire 539 B.C. · Persian conquest of Babylonia 331–323 B.C. · to the Empire of Alexander the Great 312–140 B.C. · to the Empire of the Seleukides 141 B.C.–224 A.D. · part of the Parthian Empire 224–651 · part of the Empire of Sassanides since 636 · Arabian conquest, penetration of the Islam 762 · Bagdad becomes capital of the Arabian Califate 1258 · Mongolian conquest 1534 · the Turk conquest Bagdad 1638 · the whole area of the today's Iraq comes to the Ottoman Empire 1914–1915 · British conquest 1921 · United Kingdom gets Iraq (the Ottoman provinces of Mossul, Bagdad and Basra) assigned as a mandate of the League of Nations, foundation of the Kingdom of Iraq, enthronement of Faisal I. (Hashemite Dynasty) 30th June 1930 · nominal independence, Iraq remains a British zone of influence 1933 · Ghasi I. (son of Faisal) takes the throne 1939 · Faisal II. (son of Ghasi) takes the throne 24th of February 1955 · Iraq joines the Bagdad Pact and gets the full sovereignty, however United Kingdom is allowed to keep military bases in Iraq 14th of July in 1958 · military coup d'état under colonel Kassem, overthrow of the monarchy, assassination of the king and the premier, proclamation of the republic 1959 · withdrawal from the Bagdad Pact (new name: CENTO), United Kingdom has to evacuate it's bases 1959 · attempted coup d'état by the Baath Party 1961 · Kuwait conflict, Kurd conflict 1963 · attempted coup d'état by the Baath Party, assassination of Kassem 1968 · the Baath Party comes into power 1979 · Saddam Hussein becomes president 1980 · outbreak of the 1st Gulf War (Iraq against Iran) 20th of August in 1988 · cease fire between Iraq and Iran 1989/1990 · tensions with Kuwait because of the Oil, the USA declare by April Glaspie (ambassadress of the USA in Iraq): "The USA will not take position about the quarrels between the Iraq and Kuwait" 2nd of Aug. 1990 · Iraq occupies Kuwait 15th of January 1991 · the USA declare the war against Iraq 17th of January in 1991 · outbreak of the 2nd Gulf War (USA against Iraq) 28th of Febr. 1991 · surrender of the Iraq 1994 · recognition of Kuwait's sovereignty by the Iraq 1996 · parliament's elections, victory for the governing Baath party 1996 · Kurd revolt 2003 · outbreak of the 3rd Gulf War (USA against Irak), the Iraq gets illegally attacked and occupied by USA, United Kingdom and Poland, the Iraq becomes an US-American protectorate 2004 · Saddam Hussein is captured 28th of June in 2004 · granting of nominal self administration (provisional constitution) October 2005 · new constitution 30th of December in 2006 · Saddam Hussein becomes condemned to death after a show trial and executed under very questionable conditions 2008 · withdrawal of the Polish and British troops 2009–2010 · withdrawal of the US-American combat troops, 50.000 trainers and military advisers remain in the country 2014–2017 · the Islamic State conquers areas in the north-east, followed by a war of liberation 2020 · the Iraqi parliament decides to withdraw all US-American troops 2021 · withdraw of all US-American troops, military advisers remain in the country |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte, hintergrund.de |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name des Landes geht auf das babylonische Wort für "Ursprung" zurück. Er wurde offenbar gewählt, um auf die Wiege der Zivilisation hinzuweisen, deren alte Städte wie z.B. Ur hier im Zweistromland zu finden sind. | The name of the country goes back to the Babylonian word for 'origin'. It was apparently chosen to point to the cradle of civilization, whose ancient cities, such as Ur, are found here in Mesopotamia. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |