Ghana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Ghana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
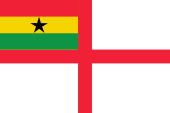
National- und Handelsflagge, Gösch und Präsidentenstandarte – national and merchant flag, jack and standard of the president, |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, |
 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe |
 |
Flagge der Zivilluftfahrt |
|
|
|
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
bis/to 1957, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1964–1966, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1963–2003, |
 |
bis/to 2003(?) |
|
|
|
| Die heutige Flagge Ghanas wurde am 06.03.1957 anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit eingeführt und am 28.02.1966 wiederhergestellt. Sie zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Gelb und Grün mit einem schwarzen fünfstrahligen Stern im gelben Mittelstreifen. | The today's flag of Ghana was introduced on 6th of March in 1957 in occasion to the independence day and reestablished on 28th of February in 1966. It shows three horizontal stripes in red, yellow and green with a black five-jagged star in the yellow middle stripe. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind auch als die "Panafrikanischen Farben" bekannt: Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische und auch amerikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen, steht für die politische Einheit Afrikas, ja aller Schwarzen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. | The
colors of the flag are even known as the "Panafrican colors": Perhaps in
1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize
the commons of all people with black skin. The colour-triad
green-yellow-red, wich used many african and even american countries in
their flags after the independence, stands for the political unity of
Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the
origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent
state in Africa.
|
| Rot steht in der Flagge Ghanas für das Blut, das im Kampf für Freiheit und Unabhängigkeit vergossen wurde, Gelb für die Reichtümer des Landes (Gold, früherer Landesname "Goldküste"), Grün für Wälder und Landwirtschaft. Der Stern ist der "Leitstern der afrikanischen Freiheit". | Red stands in the flag of Ghana for the blood, given in the fight for freedom and independence, yellow for the wealth of the land (gold, former name of the country "Gold Coast"), green for forests and agriculture. The star is the "lead-star of the african freedom". |
| Ghana orientiert sich teilweise am britschen Ensign-System. Das weißt auf die Verbindungen zu Großbritannien hin. | Ghana is partially orientated in the British Ensign-System. This points to the connexions to United Kingdom. |
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Handelsschiffe und seefahrende Privatpersonen aus Kolonien dürfen nur dann einen Red Ensign mit Badge führen, wenn von der britischen Admiralität eine entsprechende Erlaubnis für die Kolonie erteilt wurde. |
Great
Britain introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. |
| Bis zur Unabhängigkeit wurde in der Goldküste die blaue, britische Dienstflagge (Blue Ensign) mit dem 1889 eingeführten Emblem (Badge) benutzt. Es zeigte einen Elefanten mit drohender Gebärde vor einer Palme inmitten einer afrikanischen Landschaft. Unten auf dem Badge waren die Buchstaben "G.C." in Rot zu sehen. | Until the independence was used in the Gold Coast the blue, British official flag (Blue Ensign) with the in 1889 introduced emblem (badge). It showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge were to see the letters "G.C." in red. |
| Im Jahre 1964 führte der Präsident Kwane Nkrumah ein Ein-Partei-System in Ghana ein. Die Flagge Ghanas wurde daraufhin so verändert, dass sie der Flagge der herrschenden Partei (Convention People's Party) glich. Dazu wurde der gelbe Mittelstreifen weiß umgefärbt. Nach einem Militärputsch im Jahre 1966 wurde die alte Flagge wieder eingeführt. Die Farben sind, außer Schwarz, wie folgt definiert: Rot = Pantone 032, Gelb = Pantone 109, Grün = Pantone 355. | In the year 1964 the president Kwane Nkrumah introduced a one-party-system in Ghana. The flag of Ghana was because of that changed in this way, that it equaled the flag of the governing party (Convention People's Party). For it was colored the yellow middle stripe into white. After a military revolt in the year 1966 was re-introduced the old flag again. With the exception of black, the colors are defined as follows: red = Pantone 032, yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World | |
| Wappen – Coat of arms: | |
 |
Wappen von Ghana – coat of arms of Ghana, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen wurde am 04.03.1957 von Königin Elisabeth II. verliehen. Das Wappenschild ist durch ein goldgerändertes grünes Kreuz mit goldenem Leoparden geviert: Das erste Feld zeigt gekreuzt einen Stab und ein Schwert, das zweite Feld ein Schloss, das dritte Feld einen Kakaobaum und das vierte Feld eine Goldmine. In der Mitte des grünen Kreuzes befindet sich ein goldener Leopard. Er steht für die frühere Kolonialmacht Großbritannien. Über dem Schild ein Wulst mit schwarzem Stern und zwei goldene Adler als Schildhalter. Auf dem Rand das Motto "Freedom and Justice" → "Freiheit und Gerechtigkeit". | The coat
of arms of the state Ghana get awarded by queen Elisabeth II. on 4th of
march in 1957. The blazon is squared by a golden bordered green cross with a
golden leopard: the first field dhowes crossed a baton and a sword, the second field a castle, the third field a cacao tree and the fourth a gold mine. In the middle of the green cross is positioned a golden leopard. He stands for the former colonial power, United Kingdom. Over the shield a torus with a black star and two golden eagles as shield-holders. On the border the motto "Freedom and Justice" |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
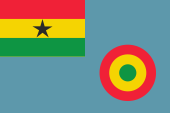
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ca. 1200 · Einwanderung der Akan-Stämme 1471 · Entdeckung der Goldküste durch die Portugiesen 1482 · Gründung des portugiesischen Forts Elmina ca.1500–ca.1870 · Gründung und Verwaltung zahlreicher Forts und Handelsposten durch europäische Mächte (Niederlande, Brandenburg, Frankreich, England, Dänemark, Schweden), jedoch seit dem 18. Jhd. wachsende britische Dominanz 1683 · Gründung des brandenburgisch-preußischen Forts Großfriedrichsburg (bis 1720, heute Prince's Town) 1685 · Gründung des brandenburgisch-preußischen Forts Dorothea (bis 1709) 1694 · Gründung des brandenburgisch-preußischen Forts Takrama (bis 1708, heute Nsama) 1719 · Gründung des Ashanti-Reiches der Akan (Hauptstadt = Kumasi) 1750 · nur die Küste wird noch durch die Niederlande, Großbritannien und Dänemark kontrolliert 1807 · das Ashanti-Reich erreicht seine größte Ausdehnung 1821 · Gründung der britischen Kronkolonie Goldküste 1872 · Großbritannien bringt die gesamte Küste unter seine Kontrolle 1826–1874 · Unterwerfung des Ashanti-Reiches durch Großbritannien, Errichtung des britischen Protektorats über Ashantiland 1874–1901 · Unterwerfung des Hinterlandes der Goldküste (Nordterritorium) durch Großbritannien, Errichtung des britischen Protektorats über das Nordterritorium, jedoch setzt sich der Name Goldküste für das gesamte britische Gebiet durch (offiziell seit 1874) 1922 · West-Togo (bis 1918 deutsche Kolonie) wird als Mandat des Völkerbundes and die Goldküste angegliedert 1949 · Gründung der Convention People's Party (CPP) durch Kwame Nkrumah 1951 · Wahlen, Sieg der CPP, Gewährung der inneren Selbstverwaltung für die Goldküste 1956 · Volksabstimmung in West-Togo für den Anschluss an die Goldküste 06.03.1957 · Unabhängigkeit als Dominion Ghana innerhalb des Commonwealth 01.07.1960 · Ghana wird Republik 1964 · Errichtung eines Ein-Parteien-Systems 1966 · Militärputsch, Verbot der CPP, in Folge Militärregierungen, außer 1969–1972 und 1979–1981 1981 · Parteienverbot 1992 · Aufhebung des Parteienverbotes |
| ca. 1200 · immigration of the Akan tribes 1471 · discovering of the Gold Coast by the Portugese 1482 · foundation of the Portugese Fort Elmina ca.1500–ca.1870 · foundation and management of many Forts and trade stations by european powers (Netherlands, Brandenburg, France, England, Denmark, Sweden), however since the 18th cent. growing British dominance 1683 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Großfriedrichsburg (until 1720, today called Prince's Town) 1685 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Dorothea (until 1709) 1694 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Takrama (until 1708, today Nsama) 1719 · foundation of the Ashanti Empire of the Akan people (capital = Kumasi) 1750 · only the coast is still controlled by the Netherlands, United Kingdom and Denmark 1807 · the Ashanti Empire achieve his largest expanse 1821 · foundation of the British crown colony Gold Coast 1872 · United Kingdom controles the whole coast 1826–1874 · subjection of the Ashanti Empire by United Kingdom, establishment of the British protectorate over Ashanti-Land 1874–1901 · subjugation of the outback of the Gold Coast (Northern Territory) by United Kingdom, establishment of the British protectorate over the Northern Territory, however triumphs the name Gold Coast for the whole British territory (official since 1874) 1922 · Western Togo (until 1918 German colony) gets incorporated to the Gold Coast as a mandate of the League of Nations 1949 · foundation of the Convention People's Party (CPP) by Kwame Nkrumah 1951 · elections, victory of the CPP, granting of inner self administration for the Gold Coast 1956 · plebiscite in West Togo for the annexion by the Gold Coast 6th of March in 1957 · independence as Dominion of Ghana within the Commonwealth 1st of July in 1960 · Ghana becomes a republic 1964 · establishment of a one-party-system 1966 · military coup d'état, interdiction of the CPP, in consequence military governments, except 1969–1972 and 1979–1981 1981 · party ban 1992 · repeal of the party ban |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Wikipedia (D) |
| Der Name "Ghana" lautet übersetzt "König" und geht auf den traditionellen Titel der Stammeshäuptlinge zurück. | The name "Ghana" means translated "king" and goes back to the traditional title of the tribal chiefs. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |
| Landkarte der historischen Regionen – Map of the historical Regions: |
|
| Quelle/Source: Weltgeschichte |
|
Zahlenschlüssel für die Forts und Handelsstützpunkte der Europäer 1482 bis
1872 – number's cey for the forts and trade stations of the europeans: |
|||
| 1 | Apollonia (Beyin) | 1750 brit., 1867 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 2 | Elise Carthago | 1640–1680 nied. | |
| 3 | Duma | 1623–1636 port. | |
| 4 | Ruyghaver | 1640–1680 nied. | |
| 5 | St. Anthony (Axim) | 1515 port., 1642 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 6 | Großfriedrichsburg | 1683 brand., 1720–1725 nied. | |
| 7 | Takrama | 1694–1708 brand. | |
| 8 | Dorothea | 1685–1709 brand. | |
| 9 | Metal Cross (Dixcove) | 1691 brit., 1867 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 10 | Batenstein | 1598 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 11 | Witzen (Takoradi) | 1652 schwed., 1657 dän., 1659 nied., 1664 brit., 1665-1693 nied. | |
| 12 | Sekondi | 1680 brit., 1779 frz., 1867 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 13 | Orange | 1670 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 14 | St. Sebastian (Shama) | 1520 port., 1640 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 15 | Fanzösisches Fort | 1680–1688 | |
| 16 | Commenda | 1670 brit., 1695 nied., 1867 brit. | |
| 17 | Vredenburg | 1688 nied., 1782 brit. | |
| 18 | São Jorge de Minha (Elmina) | 1482 port., 1637 nied., 1872 brit. | |
| 19 | Cape Coast Castle | 1652
schwed., 1659 dän., 1661 nied., 1662 brit., 1663 nied., 1664 brit. |
|
| 20 | Royal | 1658 dän., 1685 brit. | |
| 21 | Portugiesisches Fort | 1650–1662 | |
| 22 | Nassau | 1598 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit. | |
| 23 | Britisches Fort | 1660 brit., 1663 nied., 1664 brit. | |
| 24 | Anashan (Anamabu) | 1683–1690 port. | |
| 25 | William | 1657 schwed., 1659 dän., 1674 brit. | |
| 26 | Egya | 1663 brit. | |
| 27 | Amsterdam (Saltpond) | 1631 brit., 1665 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit. | |
| 28 | Tantamkweri | 1725 brit. | |
| 29 | Leydsamheid (Apam) | 1697 nied., 1782 brit., 1785–1811 nied. | |
| 30 | Winneba | 1687 brit. | |
| 31 | Beraku | 1667 nied., 1782 brit., | |
| 32 | Shido | 1690 brit. | |
| 33 | Fort James | 1673 brit. | |
| 34 | Crèvecoeur | 1650 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit. | |
| 35 | Christiansborg (Accra) | 1578
port., 1657 schwed., 1659 dän., 1679 port., 1694 dän., 1850 brit. |
|
| 36 | Portugiesisches Fort | 1530–1578 | |
| 37 | Augustenborg | 1787 dän., 1850 brit. | |
| 38 | Friedensborg | 1784 dän., 1850 brit. | |
| 39 | Vernon (Tema) | 1787 brit. | |
| 40 | Konigstein (Ada) | 1784 dän., 1850 brit. | |
| 41 | Prinzenstein (Keta) | 1784 dän., 1850 brit. | |
|
brand. = brit. = dän. = frz. = nied. = port. = schwed. = |
brandenburgisch/Brandenburg (← hier klicken ) britisch/British dänisch/Danish französisch/French niederländisch/Dutch portugiesisch/Portugese schwedisch/Swedish |
||