Iran |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Iran |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source: See File history below for details., Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1576–1665 Flagge unter den Safawiden – flag under the Safavid dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1665–1722 Flagge unter den Safawiden – flag under the Safavid dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1737–1796 Flagge unter den Afschariden – flag under the Afsharid dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1750–1794 Flagge unter der Zand-Dynastie – flag under the Zand dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1797–1845 Flagge unter der Kadscharen-Dynastie – flag under the Qajar dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
ca.1845–ca.1848 Flagge unter der Kadscharen-Dynastie – flag under the Qajar dynasty, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
ca.1848–1896 Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
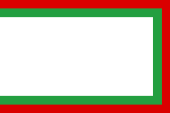
1896–1907 Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: www.worldstatesmen.org |
 |
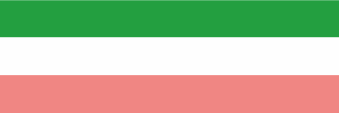
1907–1910 National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
1907–1910 Staats- und Marineflagge – state and naval flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
1910–1925 National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1910–1925 Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1925–1964 National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national state and merchant flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) 1964–1979 Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1964–1979 National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1964–1979 Marineflagge – naval flag, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1925–1979(?) Gösch – jack, Quelle/Source, nach by: Das Flaggenbuch |
 |
1964–1979 Lotsen(ruf)flagge und Unterscheidungsflagge für Lotsenfahrzeuge – pilot jack and differentiational flag for pilot's vessels, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1971(?) Flagge des Schah – flag of the Shah, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1971(?) Flagge des Kronprinzen – flag of the Crown Prince, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1971(?) Flagge der Prinzen – flag of the Princes, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1979 Flagge des Verteidigungsministers – flag the of Minister of Defense, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1979 Flagge für Minister – flag for Ministers, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1979 Standarte des Oberkommandierenden der Streitkräfte – standard of the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1979 Flagge für Admirale – flag for Admirals, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
bis/to 1979 Standarte des Kommandeurs eines Kriegshafens – standard of a Commander of a war harbour, Quelle/Source, nach by: Flags of the World |
 |
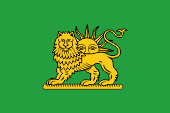
bis/to 1979 Flagge des Roten Löwen – flag of the Red Lion, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
|
|
|
| Die heutige Flagge wurde am 29.07.1980 eingeführt. Sie zeigt drei Querstreifen in Grün, Weiß und Rot. Der weiße Mittelstreifen wird durch schmale Streifen in stilisierter arabischer Schrift vom grünen und roten Streifen abgegrenzt. Das rote Staatswappen ist zentral im weißen Streifen angeordnet. Die Farben Grün, Weiß und Rot gehen auf das Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts zurück. Heute wird ihnen folgende Bedeutung zugesprochen: Grün ist die Farbe des Islam, Weiß die des Friedens und Rot die des Mutes und der Tapferkeit. Die arabischen Schriftzeichen in den Streifen bedeuten "Allah Akbar" (Allah ist groß), oben und unten je elf mal . Die somit insgesamt zweiundwanzig Schriftornamente verweisen auf das Datum 22. Bahman (11. Februar 1979 – Tag der Rückkehr von Ayatollah Khomeini nach Iran). | The
today's flag was introduced on 29th of July in 1980. It shows three
horizontal stripes in green, white and red. The white middle stripe is
separated by narrow stripes in stylized Arabian fonts from the green and the
red stripe. The red coat of arms is placed centrally in the white stripe. The colours green, white and red have their roots in the end of the 19th century. Today they have the following meaning: green is the colour of the Islam, white is the colour of peace and red red is the colour of courage and bravery. The Arabian fonts mean "Allah Akbar" (Allah is great) above and below ever eleven times. The with this altogether twentytwo fonts ornaments refer to the date of the 22nd Bahman (11th of Februaryin 1979 – day of the return of Ayatollah Khomeini to Iran). |
| Das alte Persien verwendete weiße Flaggen mit Abbildungen von Löwe und Sonne. Diese Symbole, und auch die Farbkombination Rot, Weiß und Grün, gehen auf das alte Volk der Meder zurück, die Vorfahren der Perser. Die Sonne hat ihren Ursprung im Mithras-Kult, der Religion der Meder auch der Perser. Nach anderen Quellen stand die Sonne für die später populäre Lehre des Zarathustra und die Reinheit der Gedanken, jedoch ist das Symbol viel älter. Der Löwe stand für Kraft und Mut. | The ancient Persia used white flags with pictures of the lion and sun. These symbols, and even the color combination of red, white and green, go back to the ancient people of the Medes, the ancestors of the Persians. The sun has its origins in the Mithraic cult, the religion of the Medes and the Persians. According to other sources, the sun stood for the later popular doctrine of Zoroaster and the purity of thought, but the symbol is much older. The lion stood for strength and courage. |
|
Mit den herrschenden Dynastien wechselten oft auch die Symbole und Flaggen. Manchmal auch innerhalb einer Dynastie. Erwähnenswert ist hier das 17. Jahrhundert unter den Safawiden, als die bisherigen einfarbigen grünen Flaggen mit Löwe und Sonne durch Streifenflaggen abgelöst wurden, in denen die Farben Rot, Blau und Weiß dominierten, manchmal um einen goldenen Streifen ergänzt. Eine Praxis, welche die Afschariden beibehalten haben.
Die zeitweise und lokal regierenden Zand-Fürsten kehrten zu einer einfarbigen Flagge zurück. Diese war weiß mit einem schmalen grünen Rand und zentral tauchten auf der Flagge wieder Löwe und Sonne auf. Unter den Kadscharen fiel dann der güne Außenrand weg. Von der Mitte bis zum Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts wurde erstmals eine Streifenflagge in Grün, Weiß und Rot mit Löwe und Sonne in der Mitte verwendet, um 1896 kurzzeitig wieder von einer weißen Flagge mit grünem Rand und Löwe und Sonne in der Mitte abgelöst. Nach der bürgerlichen Revolution wurde die weiße Flagge mit einem grün-roten Rand umgeben. |
The symbols and flags often changed with the ruling dynasties. Sometimes also within a dynasty. Worth mentioning
is here the 17th century under the Safavids, when the former monochrome green flags with lion and sun were replaced by striped flags, in which the colors red, blue and white dominated, sometimes
added by a golden stripe. A practice which the Afsharids have maintained.
The timely and locally-governing Zand-Princes returned to a single-colored flag. That was white with a narrow green border, and the lion and the sun reappeared on the flag. Then the green border fell away among the Qajar dynasty (Kadzars). From the middle to the end of the 18th century, a striped flag in green, white and red with a lion and a sun was used for the first time. In 1896 it was replaced by a white flag with a green border and lion and sun in the middle. After the bourgeois revolution, the white flag was surrounded by a green-red border. |
| Im Jahre 1910 wurde eine neue Flagge in waagerechter Anordnung der Farben Grün, Weiß und Rot eingeführt. Meist wurde die Flagge im Format 1:3 verwendet. Im Jahre 1925 hatte die Dynastie der Pahlewi den Thron übernommen. Es wurden zahlreiche Reformen eingeleitet und im Jahre 1933 auch das Aussehen der Flagge genau beschrieben, z.B. das exakte Aussehen der roten Farbe, die vorher eher als Rosa ("Apfelrot") dargestellt wurde. | In the
year 1910 was introduced a new flag
in horizontal arrangement of the colours green, white and red. This flag was mostly used in the
ratio of 1:3. In the year 1925 the dynasty of the Pahlewi tooked over the throne. There were initiated many reforms and in the year 1933 was even exactly described the view of the flag for instance the exact view of the red colour which was previously pictured as a pink ("apple red"). |
| Die Art und Weise der Darstellung von Löwe und Sonne wurde erst ab dem Beginn des 19. Jahrhunderts vereinheitlicht, da 1806 der "Orden des Löwen und der Sonne" gegründet worden war. Von diesem Orden wurde die Symbolik erneut auf die Flaggen des Landes übertragen. Etwa ab dem Jahre 1845 wurde der Löwe mit dem Schwert des Ali – Schwiegersohn des Propheten Mohammed und Begründer der Schia – dargestellt. Wahrscheinlich um die Verteidigungsbereitschaft der Schia gegen die Reformbestrebungen des Babismus zu verdeutlichen. | The type
and manner of the portrayal of lion and sun was standardized not until the
begin of the 19th century, as the "order of the lion and the sun" was
established in 1806. From this order was transfered again the symbolism to
the flags of the country. Perhaps since the year 1845 the lion was pictured with the sword of Ali – son-in-law of the prophet Mohammed and founder of the Shia, probably to clarify the readiness for defense of the Shia against the reform ambitions of the Babism. |
| Zeitweise wurde die Flagge Persiens von einem breiten grünen Saum umgeben. Grün ist die Farbe Fatimiden, einer ismailitisch-schiitischen Kalifendynastie, die auf den vierten Kalifen Ali zurückgeht; Grün ist außerdem die Farbe des Islam im Allgemeinen. | From time
to time the flag of Persia was surrounded by a broad green border. Green is the colour of the Fatimides, an ismailite-shiite dynasty of Califes, which goes back to the fourth Calif Ali; green is also in general the colour of the Islam. |
| In der Zeit zwischen der Proklamation der Islamischen Republik Iran am 01.04.1979 und dem Zeitpunkt der Annahme der heutigen Flagge am 29.07.1980 wurden grün-weiß-rote Flagge ohne das Löwe-und-Sonne-Symbol verwendet. | In the period between the proclamation of the Islamic Republic of Iran on 1st of April in 1979 and the date of the adoption of today's flag on 29th of July in 1980 were in use green-white-red flags without the lion-and-sun-symbol. |
| Mit der heutigen Flagge übernahm die Islamische Republik nur die Farben von der alten iranischen Flagge. Ansonsten wurde jede heraldische Erinnerung an die Zeit des Schahs ausgelöscht. | With the
today's flag the Islamic Republic maintained only the colours from the old
Iranian flags. Otherwise every heraldical memory to the shahs became erased. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind heute wie folgt definiert: Rot = HEX: #da0000, RGB 218|0|0, CMYK 0|100|100|15, Pantone 179; Grün = HEX: #239f40, RGB 35|159|64, CMYK 78|0|60|38, Pantone 355. | The colors of the flag are today defined as follows: red = HEX: #da0000, RGB 218|0|0, CMYK 0|100|100|15, Pantone 179; green = HEX: #239f40, RGB 35|159|64, CMYK 78|0|60|38, Pantone 355. |
| Die Flagge des Roten Löwen wurde nach dem Vorbild der Flagge des Roten Kreuzes gestaltet, und repräsentierte bis 1980 eine gleichartige, nur für Perser (Iraner) zuständige Organisation. | The flag of the Red Lion was created after the model of the flag of the Red Cross and represented until 1980 an analagous, only for Persians (Iranians) responsible organization. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß nach/by Die Welt der Flaggen, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Wikipedia (D) | |
Wappen – coat of arms: |
|
 |
Wappen (Emblem) von Persien/Iran – coat of arms (emblem) of Persia/Iran |
 |
Wappen (Emblem) Islamische Republik Iran – coat of arms (emblem) of the Islamic Republic of Iran Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
| Das Wappen des Kaiserreichs Iran (Keshvaré Shahanshahiyé Irân), bis 1935 Persien genannt, geht auf die Symbolik des "Ordens des Löwen und der Sonne" zurück. Beide Symbole sind aber wesentlich älter, und wurden von Persien bereits im Mittelalter verwendet. Am oberen Rand des Wappens ist die Krone der Pahlewis zu erkennen. | The coat of arms of the Empire of Iran (Keshvaré Shahanshahiyé Irân), until 1935 named Persia, has it's roots in the symbolism of the "order of the lion and the sun". But both symbols are essentially elder and they were in use by Persia already in the middle ages. On the upper side of the coat of arms is to distinguish the crown of the Pahlewi dynasty. |
| Das auf der heutigen Flagge in Rot geführte Emblem wird als Staatswappen in Grün dargestellt. Es besteht aus vier Halbmonden, die als Globus angeordnet sind. Zentral ein Schwert, verstärkt und betont durch ein arabisches Schriftzeichen an der Spitze. Das Schwert und die Halbmonde stehen für die fünf Grundprinzipien des islamischen Glaubens. Der Globus symbolisiert den weltweiten Kampf der unterdrückten Völker. | The in
the today's flag in red depicted emblem is as coat of arms of the state
coloured in green. It consists of four crescents, arranged like a globe. In
the center a sword amplifyed and accentuated by an Arabian letter on the
top. The sword and the crescents stand for the five fundamental principles
of the Islamic religion. The globe symbolizes the worldwide struggle of the oppressed nations. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß nach/by Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde Islamische Republik Iran – aircraft roundel of the Islamic Republic of Iran Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Jahrtausend v.Chr. · Staat Elam ca. 1000 v.Chr. · Einwanderung der Arischen Stämme 650 v.Chr. · der Stamm der Perser erobert die Landschaft Parsa, und erhält erst auf diese Weise seinen Namen 550 v.Chr. · Sieg über die Meder 547 v.Chr. · Sieg über die Lyder 539 v.Chr. · Sieg über Babylonien 525 v.Chr. · persische Eroberung Ägyptens 490 v.Chr. · Niederlage bei Marathon gegen die Griechen 331 v.Chr. · Schlacht von Gaugamela, Alexander der Große unterwirft Persien 323 v.Chr. · Tod des Alexander 312 v.Chr. · Alexanders Feldherr Seleukos wird Satrap (Diadoche) von Babylon, die Satrapie Babylon erstreckte sich anfänglich nur auf dem Gebiet des Südostzipfels des heutigen Irak, Seleukos gründed die Dynastie der Seleukiden (bis 160 v.Chr.), spätere Ausdehnung des Seleukidenreiches auf das Gebiet des heutigen Iran, Afghanistan, Irak, Syrien und Südliche Türkei 243 v.Chr. · erstmalig taucht in der Geschichtsschreibung der Name Iran (Eran - Land der Arier) auf 150 v.Chr.–224 n.Chr. · Herrschaft der parthischen Arsakiden-Dynastie über Persien 224–642 · Herrschaft der Sassaniden-Dynastie in Persien (zarathustrische Staatsreligion) 642 · Zusammenbruch des Perserreiches unter dem arabischen Ansturm, Eindringen des Islam, Persien wird Teil des Arabischen Kalifats ca. 850 · Persien ist nur noch nominell vom Kalifat abhängig 1040 · Eroberung durch die türkischen Seldschuken 1256–1258 · Mongoleneinfälle unter Hülägü (Enkel des Dschingis Khan), Errichtung der Herrschaft der Mongolischen Ilkhane (bis 1335) 1382–1393 · Eroberung durch den Mongolenführer Timur Lenk 1502 · Begründung der Dynastie der Safawiden, Gründung des Neupersischen Reichs, der schiitische Islam wird Staatsreligion 1747 · Abspaltung von Afghanistan 1786–1925 · Herrschaft der Kadscharen-Dynastie 1803–1823 · Persien verliert seine Kaukasischen Besitzungen an Russland 1905–1906 · bürgerliche Revolution 1907 · Aufteilung Persiens in russische und britischen Einflusssphären 1914–1915 · militärische Besetzung der Einflusssphären durch Russland und Großbritannien 1919 · Persien wird britisches Protektorat 1921 · Putsch unter Reza Schah Pahlewi 1925 · Absetzung des letzten Kadscharen-Schahs, Reza Pahlewi lässt sich selbst zum Schah ausrufen, Gründung der Dynastie der Pahlewi 1935 · Umbenennung Persiens in Iran 1941–1946 · Besetzung durch britische und sowjetische Truppen, Rücktritt von Reza Pahlewi, Inthronisation seines Sohnes Mohammed Reza Pahlewi 1946 · Beitritt zum Bagdad-Pakt (CENTO) 1963 · „Weiße Revolution“ (Modernisierung des Landes, Bodenreform, Frauenstimmrecht) 1964 · Ayatollah Ruhollah Musawi Chomeini geht ins Exil 1971 · Jubiläumsfeierlichkeiten - 2500 Jahre persische Monarchie 1978–1979 · Unruhen, der Schah verlässt den Iran 01.04.1979 · Proklamation der Islamischen Republik Iran durch Chomeini 27.07.1980 · Tod des Schah Mohammed Riza Pahlewi 1980–1988 · 1. Golfkrieg (Iran gegen Irak) 03.06.1989 · Tod des Schiitenführers Ayatollah Ruhollah Musawi Chomeini seit 2011 · Iran beteiligt sich am Bürgerkrieg in Syrien |
| 3rd millenary B.C. · State of Elam ca. 1000 B.C. · immigration of the Aryan tribes 650 B.C. · the tribe of the Persians captures the landscape of Parsa and gets in this wise it's name 550 B.C. · victory over the Medians 547 B.C. · victory over the Lydians 539 B.C. · victory over Babylonia 525 B.C. · Persian conquest of Egypt 490 B.C. · defeat near Marathon against the Greek 331 B.C. · battle near Gaugamela, Alexander the Great subjects Persia 323 B.C. · death of the Alexander 312 B.C. · Alexander's general Seleukos becomes Satrap (Diadoch) of Babylon, the Satrapy of Babylon extends initialy only on the area of the southeastern part of the today's Iraq, Seleukos establishes the dynasty of the Seleukides (until 160 B.C.), later expansion of the Seleukide's Empire over the territories of the today's Iran, Afghanistan, Iraq , Syria and southern Turkey 243 B.C. · for the first time in the history appears the name Iran (Eran - land of the Aryans) auf 150 B.C.–224 A.D. · reign of the parthian Arsakide's dynasty over Persia 224–642 · reign of the Sassanide's dynasty over Persia (Zarathustrian state religion) 642 · collapse of the Persian Empire because of the Arabian onslaught, penetration of the Islam, Persia gets a part of the Arabian Califate ca. 850 · Persia is only nominally dependent from the Califate 1040 · conquest by the Turkish Seljuqs 1256–1258 · Mongolians invade under Huelaegue (Dshingis Khan), establishment of the reign of the Mongolian Ilkhanes (until 1335) 1382–1393 · conquest by the Mongolian leader Timur Lenk 1502 · establishment of the Safavid dynasty, foundation of the New Persian Empire, the shiite Islam becomes state religion 1747 · separation of Afghanistan 1786–1925 · reign of the Qajar dynasty 1803–1823 · Persia loses it's Caucasian possessions to Russia 1905–1906 · civil revolution 1907 · division of Persia into Russian and British zones of influence 1914–1915 · military occupation of the zones of influence by Russia and United Kingdom 1919 · Persia becomes a British protectorate 1921 · coup d'état by Reza Schah Pahlewi 1925 · deposition of the last Qajar shah, Reza Pahlewi lets proclaim itself as shah, foundation of the Pahlewi dynasty 1935 · rename of Persia into Iran 1941–1946 · occupation by British and Soviet troops, resignation of Reza Pahlewi, enthronement of his son Mohammed Reza Pahlewi 1946 · joining to the Bagdad Pact (CENTO) 1963 · „White Revolution“ (modernization of the country, ground reform, women's suffrage) 1964 · Ayatollah Ruhollah Musawi Chomeini goes in exile 1971 · anniversary's ceremony - 2500 years Persian monarchy 1978–1979 · riots, the shah leaves Iran 1st of April in 1979 · proclamation of the Islamic Republic of Iran by Chomeini 27th of July in 1980 · death of the shah Mohammed Riza Pahlewi 1980–1988 · 1st Gulf War (Iran against Iraq) 3rd of June in 1989 · death of the Shiite leader Ayatollah Ruhollah Musawi Chomeini since 2011 · Iran is taking part in the civil war in Syria |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Discovery '97, Wikipedia (DE) |
| Das Wort "Iran" ist sehr alt und schon sehr lange als Landesnamen in Gebrauch, wenn er auch erst 1935 offiziell angenommen und für europäische Länder verbindlich wurde. Der Name geht auf das altpersische Wort "ariyan" zurück (später "Eran"), was "Land der Arier" heißt. | The word "Iran" is very old and has long been used as
the country's name, although it was only officially adopted in 1935 and
became binding for European countries. The name goes back to the ancient Persian word "ariyan" (later "Eran"), which means "Land of the Aryans". |
| Vor 1935 wurde allgemein die Bezeichnung "Persien" verwendet, eigentlich eine Region im Süden das Landes, Parsa oder Fars genannt, was "Land der Reinen" heißt, und letztendlich der hier und im gesamten Iran lebenden Ethnie ihren Namen gegeben hat: "Perser" | Before 1935 the term "Persia" was used, actually a region in the south of the country, called Parsa or Fars, which means "Land of the Pure", and finally gave its name to the ethnicity living here and throughout Iran: "Persians" |
| Der Nordwesten des Landes Iran war in der Antike als "Medien" bekannt. | The north-west of Iran was known in the ancient world as "Media". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |