Guyana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Guyana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
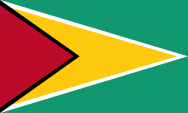 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (D) |
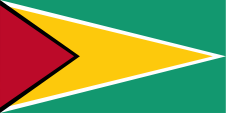 |
Handels- und Seedienstflagge
– merchant flag and official flag at sea, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (D) |
|
|
|
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1875–1906,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1906–1919,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1919–1954, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1954–1966, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1973–1980, Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1980–1985, Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Quelle/Source: By Prez001 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1985–1992, Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Quelle/Source: von Prez001 (Eigenes Werk) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1992–1997, Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Quelle/Source: By Prez001 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge Guyanas wurde am 26.05.1966 eingeführt. Sie zeigt auf grünem Grund zwei gleichschenklige Dreiecke mit der Basis an der Stangenseite, wobei innerhalb des größeren weißgeränderten gelben Dreiecks ein rotes schwarzgerändertes Dreieck liegt. Grün steht für die Wälder und die Landwirtschaft des Landes, Weiß für den Wasserreichtum, Gelb für die Bodenschätze, Schwarz die Ausdauer und Rot die Begeisterung und Opferbereitschaft des Volkes. | The today's flag of Guyana was introduced on 26th of may in 1966. It shows on green ground two isosceles triangles with the base on the pole site, wehere within the larger white-bordered yellow triangle lies a red black-bordered triangle. Green stands for the woods and the agriculture of the country, white for the water's riches, yellow the natural ressources, black for the endurance and red for the people's enthusiasm and willingness for sacrifice. |
| Die Flagge ist eigentlich ein Entwurf des Vexillologen Whitney Smith, und ist unter der Bezeichnung "Golden Arrow" ("Goldener Pfeil") bekannt. Jedoch hatte die ursprüngliche Ausführung ein rotes Feld ohne Umrandung. Das englische College of Arms hatte die Änderung vorgenommen. Whitney Smith wollte ursprünglich, obwohl nur 30 % der Bevölkerung afrikanischen Ursprungs sind, mit der Flagge die panafrikanischen Farben (Grün, Gelb und Rot) kombinieren. Nach den Änderungen sind diese zwar noch enthalten, doch ergibt sich eine weitere Eigentümlichkeit: In der Flagge erscheinen nun auch die Garvey-Farben (Rot, Schwarz und Grün). | The flag
is in principle designed by the vexillologist Whitney Smith and is known for
the denomination "Golden Arrow". But the original realisation has a red
field without a border. The english College of Arms made the changes.
Whitney Smith would with the flag initially combine the Pan-African colours
(green, yellow und red), although only 30% of the population are from
African origin. After the changes they are indeed contained, but now results
a further peculiarity: In the flag appear now even the Garvey-Colours (red,
black and green). |
| Die Farbkombination von Grün, Gelb und Rot in der heutigen Flagge sind die Panafrikanischen Farben: Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika - Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Für die politische Einheit Afrikas steht der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Äthiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. | The
combination of the colours green, yellow and red in the today's flag are the
Pan-African colours: Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the
Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with
black skin. For the political unity of Africa stands the colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african countries in their flags after the independence. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. |
| Die Farbenkomination aus Rot, Schwarz und Grün wird Garvey-Farben genannt. Es sind die Farben, die Markus Garvey 1917 für die Flagge der United Negro Improvement Association schuf und die in diesen Farben gestreift war. Er war ein Befürworter der "Zurück nach Afrika"-Bewegung und sah in diesen Farben diejenigen eines Staates für Schwarze, der in Afrika entstehen sollte. Die Farben wurden dann aber in den USA und der Karibik als diejenigen der Black-Power-Bewegung bekannt, fanden aber in Afrika nur wenig Zuspruch. Trotzem wird auch diese Farbenkombination manchmal als panafrikanische Farben bezeichnet. | The combination of the colours red, black and green is named Garvey-colours. They are those colours who created Markus Garvey in 1917 for the flag of the United Negro Improvement Association, which was striped in this colours. He was a supporter of the "Back-to-Africa"-Movement and saw in them the colours of a state of Blacks, which should be accomplished in Africa. But the colours get known in the USA and in the Caribic as the colours of the Black-Power-Movement, and get in Africa few persuasion. Nevertheless this colour-combination is sometimes named as Panafrican Colors. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind wie folgt definiert: Rot = Pantone 032, Gelb = Pantone 109, Grün = Pantone 355 und Schwarz. Andere Quellen nennen als Hex Code Scale: Rot #BE1E2D, Gelb #FFC20E, Grün #2A936A. | The colors of the flag are defined as follows: red = Pantone 032, yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355 and black. Other sources mention as Hex Code Scale: red #BE1E2D, yellow #FFC20E, green #2A936A. |
| Die erste Präsidentenstandarte wurde 1973 eingeführt. Es war eine Wappenflagge mit einem grünen Schild in der Mitte, der eine Federkrone zeigt. In den Folgejahren hatte jeder Präsident seine eigene Flagge. | The first flag of the president was introduced in 1973. It was a scutcheon-flag with a green shield in the middle, who shows a plume-crest. In the following years each President had his own flag. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flags of the World, Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen – coat of arms, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen wurde am 21.01.1966 von Königin Elisabeth II. verliehen. Es zeigt in einem weißen Schild eine Seerose, drei blaue Wellenlinien (sie stehen für den Wasserreichtum) und einen Canje-Fasan. Umgeben ist das Schild von einheimischen Symbolen: der Kopfputz (Federkrone) eines Häuptlings, zwei Diamanten und zwei Jaguare als Schildhalter, die Zuckerrohr und eine Hacke in den Krallen haben. Im Schriftband unter dem Schild das Staatsmotto: "Ein Volk, eine Nation, ein Schicksal". | The coat
of arms of the state was awarded on 21st of January in 1966 by queen
Elisabeth II. It shows in a white blazon a sea-rose, three blue waves
(standing for water-riches) and a Canje-Pheasant. The blaozon is surrounded
by native symbols: the headdress (plume-crest) of a indian chief, two diamonds and two jaguars as shield holders which have sugarcane and a hoe in their claws. In the saying-ribbon below the shield the state's motto: "One People, One Nation, One Destiny". |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
1499 · wahrscheinlich entdeckt Kolumbus die Küste Guyanas (eher
kommen aber Vespucci, Ojeda oder de la Cosa in Frage), auf Grund des
Vertrags von Tortesillas (1494) gilt Guyana offiziell als spanischer
Kolonialbesitz, wird jedoch nicht von
Spanien kolonisiert 1581 · niederländische Kolonisierung am Fluss Demerara 1595 · zusätzliche englische Kolonisierung (wahrscheinlich am Fluss Essequibo) 1595 · weitere niederländische Kolonisierung, Gründung von Stabroete (heute Georgetown) und Neu-Amsterdam, Bildung der niederländischen Kolonien Essequibo, Demerara und Berbice 1781 · britisch-niederländischer Krieg 1796 · in Folge des verlorenen britisch-niederländischen Kriegs müssen die Niederlande einen Teil ihrer Kolonien in Guyana an Großbritannien abtreten, Bildung von Britisch-Guyana 1814 · Vertrag von London, die Grenze zwischen Niederländisch- und Britisch-Guyana wird exakt festgelegt 1834 · Abschaffung der Sklaverei 1850–52 · starke Einwanderung aus Portugal 1928 · Gewährung teilweiser innerer Selbstverwaltung 1940 · in Folge des Beginns des zweiten Weltkriegs errichten die USA in Britisch-Guyana Militärbasen (Atkinson Field, Makouira) März 1953 · erste Verfassung, Gewährung innerer Autonomie, Wahlsieg der Progressive People's Party (PPP, von Indern dominiert), antibritische Unruhen 09.10.1953 · Großbritannien erklärt die Wahlen für ungültig, militärische Intervention der Briten, das Parlament wird aufgelöst 22.12.1953 · Verabschiedung der "provisorischen Verfassung" 1956 · teilweise Wiedereinführung der Verfassung vom März 1953 1957 · Wahlsieg der PPP März 1960 · erste Londoner Verfassungskonferenz 1961 · Wahlsieg der PPP 1962 · antibritische Unruhen 1964 · antibritische Unruhen, Verhängung des Ausnahmezustands, umstrittener Wahlsieg der PPP, jedoch stellt der People's National Congress (PNC, von Afroamerikanern dominiert) den Ministerpräsidenten November 1965 · zweite Londoner Verfassungskonferenz 26.05.1966 · Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen des Commonwealth of Nations 1970 · Loslösung von der britischen Krone, Guyana wird Republik, jedoch Verbleib im Commonwealth 1980 · neue Verfassung, Präsidialsystem 1982 · verschärfte Gebietsforderungen von Venezuela 1992 · erste unumstrittene freie und faire Wahlen, Wahlsieg der PPP 2001 · Wahlsieg der PPP 2015 · Wahlsieg der APNU (Machtwechsel) 2020 · Wahlsieg der PPP (Machtwechsel) |
History: |
|
1499 · Columbus probably discovers the coast of Guyana (but
likelyer this have been Vespucci, Ojeda or de la Cosa), because of the
Tortesillas Treaty (1494) is Guyana officially a Spanish colonial
possession, but becames not colonized by
Spain 1581 · Dutch colonization upon the river Demerara 1595 · additionally English colonization (probably upon the river Essequibo) 1595 · furthermore Dutch colonization, foundation of Stabroete (today Georgetown) and New Amsterdam, formation of the Dutch colonies Essequibo, Demerara and Berbice 1781 · British-Dutch war 1796 · in result of the losed British-Dutch war the Netherlands hade to cede a part of their colonies in Guyana to United Kingdom, formation of British Guyana 1814 · London Treaty, the border between Dutch and British Guyana gets exactly stated 1834 · abolition of the slavery 1850–52 · potent immigration from Portugal 1928 · granting of partial internal self government 1940 · as a result of the start of the Second World War the USA establish military bases in Britisch Guyana (Atkinson Field, Makouira) March 1953 · first constitution, granting of inner autonomy, electional victory of the Progressive People's Party (PPP, dominated by Indians), anti British agitations 9th of October in 1953 · United Kingdom declares the elections for unvalid, military intervention by the British, the parliament gets liquidated 22nd of December in 1953 · pass of the "provisional constitution" 1956 · partial re-introduction of the constitution from March 1953 1957 · electional victory of the PPP March 1960 · first Constitutional Conference in London 1961 · electional victory of the PPP 1962 · anti British agitations 1964 · anti British agitations, declaration of the state of emergency, disputed electional victory of the PPP, however the People's National Congress (PNC, dominated by of African descent) places the premier November 1965 · second Constitutional Conference in London 26th of May in 1966 · independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations 1970 · separation from the British crown, Guyana becomes a republic, but remains in the Commonwealth 1980 · new constitution, presidial system 1982 · aggravated claims for territory from Venezuela 1992 · first undisputed free and fair elections, electional victory of the PPP 2001 · PPP election victory 2015 · APNU election victory (change of power) 2020 · PPP election victory (change of power) |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97 |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Guyana" (auch Guayana) stammt wahrscheinlich aus den Indianischen Sprachen, und es gibt zwei Erklärungen: 1.) ehrenwert, 2.) viel Wasser. | The name "Guyana" (also Guyana, Guiana) comes probably from the Indian languages, and there exist two explanations: 1st) honorable, 2nd) lot of water. |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas der wahren Namen | |