Gambierinseln |
|||||||
| |||||||
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Gambierinseln |
|||||||
| |||||||
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
die Flagge
Frankreichs |
 |
seit /since 1984,    |
|
|
|
inoffizielle Flagge – unofficial Flag: |
|
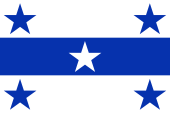 |
inoffizielle Flagge – unofficial flag, |
|
|
|
|
Die Gambierinseln – als Teil von Französisch-Polynesien
– haben offiziell keine eigene Flagge. Es muss die französische Trikolore
oder zusätzlich die Flagge von Französisch-Polynesien gehisst werden. Jedoch
gibt es for lokale Zwecke eine inoffzielle Flagge. Sie zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Weiß, Blau und Weiß (Verhältnis: 1:1:1), in jeder Ecke einen blauen fünfzackigen Stern, und in der Mitte des blauen Streifens einen weißen fünfzackigen Stern. Das Blau ist als Pantone 286c festgelegt. Im Jahr 1837 wollte ein Seemann namens Armand Mauruc unbedingt unter einer Flagge der Gambierinseln (Königreich Mangareva) Handel treiben, und er überzeugte König Maputeoa diese Flagge als Nationalflagge anzunehmen. Die vier blauen Sterne in den Ecken stehen für die Inseln Mangareva, Taravai, Aukena und Akamaru, und der weiße Stern in der Mitte steht für Temoe. Die Farbe Blau steht für das Meer und Weiß für das Christentum. |
The Gambier Islands – as a part of French Polynesia
– have officially no own flag. It must be hoisted the French tricolor or
additionally, the flag of French Polynesia. However, there exists for local
purposes an unofficial flag. It shows three horizontal stripes in white, blue and white (ratio: 1:3:1), in every corner one blue five-pointed star, and in the middle of the blue stipe one white five-pointed star. The colour blue is defined as Pantone 286c. In 1837, a sailor named Armand Mauruc wanted to trade necessarily under a flag of the Gambier Islands (Kingdom of Mangareva), and he convinced King Maputeoa to adopt this flag as national flag. The four blue stars in the corners represent the islands of Mangareva, Taravai, Aukena and Akamaru, and the white star in the center represents Temoe. The color blue stands for the sea and white stands for christianity. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World | |
|
|
|
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte von Französisch-Polynesien – Map of French Polynesia: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Gliederungen von Französisch-Polynesien – Subdivisions of French Polynesia: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |
|
|
|
|
ca. 1200 n.Chr. · beginnende polynesische Besiedlung 1797 · der britische Seefahrer John Wilson entdeckt die Inseln und nennt sie nach Kapitän James Gambier, einem Nachkommen Französischer Hugenotten, der seine Expedition unterstützt hatte 1825 · der britische Seefahrer Frederick William Beechey besucht die Gambierinseln 1834 · die Patres Honoré Laval und François d’Assise Caret beginnen mit der Christianisierung der Inseln und errichten eine Art christliche Theokratie, die erst im Jahre 1871 auf Weisung des Bischofs von Tahiti beendet wird 1836 · König Maputeoa lässt sich taufen (Gregorio I. Maputeoa) 1857 · Tod von König Gregorio I., Nachfolger wird sein ältester Sohn Gregorio II. Maputeoa 1868 · Tod von König Gregorio II., er hinterlässt keinen Erben, die Dynastie erlischt 1871 · Frankreich erklärt die Gambierinseln zum französischen Protektorat 1881 · Frankreich annektiert die Gambierinseln, sie werden französische Kolonie 1903 · Errichtung einer einheitlichen französischen Kolonialverwaltung für die Gesellschaftsinseln, Marquesas-Inseln, Tuamotuinseln, Gambier-Inseln und Austral-Inseln unter dem Namen "Französisch-Polynesien" |
|
|
|
ca. 1200 A.D. · beginning polynesian settlement 1797 · the British seafarer John Wilson discovers the islands and names them after Captain James Gambier, a descendant of French Huguenots who had supported his expedition 1825 · the British seafarer Frederick William Beechey visits the Gambier Islands 1834 · the Fathers Honoré Laval and François d'Assise Caret begin the Christianizing of the islands and establish a kind of Christian theocracy, which could only be terminated in 1871 by the direction of the Bishop of Tahiti 1836 · King Maputeoa is baptized (Gregorio I. Maputeoa) 1857 · death of King Gregorio I., succeeded by his eldest son Gregorio II. Maputeoa 1868 · death of King Gregorio II., he had no heir, the dynasty extinguishes 1871 · France declares the Gambier Islands to a French Protectorate 1881 · France annexes the Gambier Islands, they become a French colony 1903 · establishing of a unified French colonial administration for the Society Islands, Marquesas Islands, Tuamotu Islands, Gambier Islands and Austral Islands under the name "French Polynesia" |
| Quelle/Source Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World |
|
|
| Der britische Seefahrer John Wilson entdeckte die Inseln im Jahre 1797 und benannte sie nach Kapitän James Gambier, einem Nachkommen Französischer Hugenotten, der seine Expedition unterstützt hatte. | The British
seafarer John Wilson discovered the islands in 1797 and named them after Captain James Gambier, a descendant of French Huguenots, who had supported his expedition.| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia
(D) |
|
| ||