Helgoland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Helgoland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
ab/from 1890, Flagge von Helgoland – flag of Heligloand, Quelle/Source, nach by: Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein |
|
|
|
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
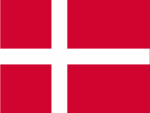 |
1773–1814, Helgoland gehört zu Dänemark – Heliogland belongs to Denmark, Quelle/Source, nach by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1814–1890, Flagge von Helgoland – flag of Heligloand, Quelle/Source, nach by: Wikipedia (D) |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge von Helgoland zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Grün Rot und Weiß. Die Farben gehen auf das Wappen der Insel zurück. | The flag of Heligoland shows three horizontal stripes in green red and white. The colours have their roots in the crest of the island. |
| Das Wappen von Helgoland zeigt einen zweifach geteilten Schild, in Grün, Rot und Silber (Weiß). Es wurde der Insel im Jahre 1696 vom Herzog von Schleswig verliehen, und soll auf eine Schiffsflagge zurückgehen. | The coat of arms of Heligoland shows a two-fold splited shield in green, red and silver (white). It was awarded to the island in 1696 by the Duke of Schleswig, and should go back to a ship's flag. |
| Zur Bedeutung der Farben hört man oft den Spruch: "Grün ist das Land, rot ist die Kant, weiß ist der Sand: Das sind die Farben von Helgoland." Jedoch stammt dieser Ausdruck aus dem 19. Jahrhundert, ist also jünger als die Farben selber, und wurde den Farben somit später als Bedeutung beigegeben. | About the meaning of the colours you often hear the saying: "Green is the land, red is the edge, white is the sand: these are the colors of Heligoland." However, this expression dates from the 19th Century, is thus younger than the colours themselves, so it was given to the colours as their meaning later. |
| Die Flagge, wenn sie denn verwendet wurde, galt ab 1773 nicht mehr, denn Helgoland wurde als ein Teil von Schleswig dänisches Hoheitsgebiet. Nach dem Frieden von Kiel wurde Helgoland offiziell von Dänemark an Großbritannien abgetreten, und es wurde eine Flagge in den Farben der Insel gehisst, die in der Oberecke den britischen Union Jack zeigte. | The flag, if it was used, was not longer allowed from 1773, because Heligoland, as a part of Schleswig, became Danish . After the Peace of Kiel, Heligoland was officially ceded by Denmark to the United Kingdom, and a flag in the colors of the island was hoisted, which showed the British Union Jack in the upper corner. |
| Im Jahre 1890 wurde Helgoland druch den Helgloland-Sansibar-Vertrag von Großbritannien an das Deutsche Reich abgetreten, und der Union Jack wurde von der Flagge entfernt, und die Flagge mit den drei Streifen in Grün,Rot und Weiß bis in die heutigen Tage beibehalten. | In the
year 1890, Heligoland was ceded from Great Britain to the German Empire by
the Helgloland-Zanzibar-Treaty, and the Union Jack was removed from the
flag, and they keeped the flag with the three stripes in green, red and
white to the present days. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Helgoland – coat of arms of Heligoland, Quelle/Source, nach by: Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen von Helgoland zeigt einen zweifach geteilten Schild, in Grün, Rot und Silber (Weiß). Es wurde der Insel im Jahre 1696 vom Herzog von Schleswig verliehen, und soll auf eine Schiffsflagge zurückgehen. | The coat of arms of Heligoland shows a two-fold splited shield in green, red and silver (white). It was awarded to the island in 1696 by the Duke of Schleswig, and should go back to a ship's flag. |
| Zur Bedeutung der Farben hört man oft den Spruch: "Grün ist das Land, rot ist die Kant, weiß ist der Sand: Das sind die Farben von Helgoland." Jedoch stammt dieser Ausdruck aus dem 19. Jahrhundert, ist also jünger als die Farben selber, und wurde den Farben somit später als Bedeutung beigegeben. | About the meaning of the colors you often hear the saying: "Green is the land, red is the edge, white is the sand: these are the colors of Heligoland." However, this expression dates from the 19th Century, is thus younger than the colours themselves, so it was given to the colours as their meaning later. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein | |
| Landkarte – Map: | |
|
|
| Die historische Landkarte zeigt die Lage Helgolands in der Deutschen Bucht, im Westen der preußischen Provinz Schleswig-Holstein. | The historical map shows the position of Heligoland in the German Sea, in the west of the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein. |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
Die Griechen kannten Helgoland wahrscheinlich als "Basileia", die Kelten als
"Abalus", und die Römer nannten sie wahrscheinlich "Glaesaria". Es war
offenbar Wohnstätte einer bedeutenden Kultur, und erhielt wohl wegen seiner
großangelegten Tempelanlagen den Namen Heiliges Land ("Helge Land"). Auf jeden Fall war Helgoland früher etwa zweihundertmal größer, und dicht besiedelt. Wahrscheinlich verlor die Insel im 9. Jahrhundert durch eine verheerende Sturmflut ca. 85% ihrer Landfläche, und im 12. Jahrhundert verlor sie noch einmal gut 80% ihres Landgebiets, wobei sie danach aus zwei Inseln bestand, nämlich Helgoland und Südstrand. Südstrand versank in der großen Sturmflut von 1362. Eine Landkarte des Husumer Karthographen Johannes Mejer von 1649 zeigt Details. Der bis dato bestehende Rest von Helgoland wurde Silvester 1720/1721 durch eine Sturmflut geteilt, und die Insel Düne trennte sich vom Festland ab. |
| Quelle/Source, nach by: www.eichner-dresden.de |
|
1721
· König Friedrich IV. von Dänemark zieht Schleswig
als ein verwirktes dänisches Lehen ein, das Herzogtum Schleswig geht an die
dänischen Könige zurück, die bis dato zu Holstein-Gottorf gehörende Insel
Helgoland kommt zum dänischen Herzogtum Schleswig 1773 · Vertragsregelung zwischen Dänemark und Russland: Schleswig und Holstein bleiben ungeteilt, das ältere Haus Holstein-Gottorf (inzwischen Zaren von Russland) verzichtet zugunsten der Könige von Dänemark auf Holstein, Dänemark tritt dafür Oldenburg und Delmenhorst an das jüngere Haus Holstein-Gottorf ab, Schleswig (und damit Helgoland) wird (mit Lauenburg und Holstein) Glied des dänisch-norwegischen Staates, wobei der dänische König als Herzog von Holstein auch deutscher Fürst ist, und Holstein somit Teil des Heiligen Römischen Reiches Deutscher Nation, Beginn einer Politik der Danisierung gegenüber den deutschen Einwohnern 1806 · Napoléon erzwingt die Gründung des Rheinbundes, ein Zusammenschluss von sechzehn süd- und südwestdeutschen Staaten unter französischem Protektorat, die aus dem Heiligen Römischen Reich Deutscher Nation austreten, daraufhin legt Kaiser Franz II. legt die Krone des Heiligen Römischen Reiches Deutscher Nation nieder, das Reich endet, Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg werden Dänemark angeschlossen 1807 · die Insel Helgoland wird von britischen Truppen besetzt 1814 · Frieden von Kiel, die Insel Helgoland wird Teil Großbritanniens 01.07.1890 · Helgoland-Sansibar-Vertrag, die Insel Helgoland kommt von Großbritannien an Preußen und wird so Teil des Deutschen Reiches, sie wird dem Kreis Süderdithmarschen in der preußischen Provinz Schleswig-Holstein angeschlossen 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg, Helgoland ist evakuiert 1922 · Helgoland wird ein eigener Kreis in der preußischen Provinz Schleswig-Holstein 1932 · Helgoland wird dem Kreis Pinneberg in der preußischen Provinz Schleswig-Holstein angeschlossen 1939–1945 · Zweiter Weltkrieg, Helgoland wird am 18. April 1945 von der Britischen Luftwaffe bombardiert, 1.000 Flugzeuge werfen mindestens 7.000 Bomben ab, die Insel war unbewohnbar geworden, die Bevölkerung wird vollständig evakuiert 18.04.1947 · die britische Armee versucht vergeblich mit Hilfe der bis heute größten nichtnuklearen Explosion der Weltgeschichte (mit 6700 Tonnen Sprengstoff) die komplette Insel wegzusprengen 1947–1952 · die britische Luftwaffe nutzt Helgoland als Übungsplatz für Bombenabwürfe 20.12.1950 · zwei Heidelberger Studenten und ein Dozent besetzen die Insel und hissen die deutsche Flagge, die Flagge der Europäischen Bewegung und die Flagge von Helgoland 03.01.1951 · britische Offiziere beenden die Besetzung, daraufhin fordert der Bundestag der BRD die Rückgabe der Insel 01.03.1952 · Helgoland wird von Großbritannien freigegeben, und an die BRD angegliedert |
History: |
| The Greeks called Heligoland probably "Basilea", the Celts "Abalus", and the Romans probably called it "Glaesaria". It was obviously a significant cultural home, and was known for its large-scaled temples, and got thats why the name Holy Land ("Helge Land"). In any case, Heligoland was formerly about two hundred times larger and densely populated. Probably in the 9th century Heligoland lost about 85% of its land area by a devastating storm surge, and the in the 12th century it lost again ca. 80% of its land area, and after than it consisted of two islands, namely Heligoland and Suedstrand (South Beach). Suedstrand sank in the great flood of 1362. A map of 1649 from the cartographer Johannes Mejer from Husum shows details. The hitherto existing remnant of Helgoland was divided in the New Year's Eve 1720/1721 by a storm surge, and the Island of Dune was separated from the mainland. |
| Quelle/Source, nach by: www.eichner-dresden.de |
|
1721
· King Frederick IV. of Denmark confiscates
Schleswig as a forfeited Danish fiefdom, the Duchy of Schleswig comes back
to the Danish kings, the to this date to Holstein-Gottorp belonging island
of Heligoland comes to the Danish Duchy of Schleswig 1773 · contractual arrangement between Denmark and Russia: Schleswig and Holstein remain undivided, the older house of Holstein-Gottorf (now Czars of Russia) cedes Holstein in favor of the kings of Denmark, Denmark cedes Oldenburg and Delmenhorst to the younger line of the house of Holstein-Gottorf, Schleswig (and in this way Heligoland too) becomes (with Holstein and Lauenburg) a member of the Danish-Norwegian state, the Danish king is - as Duke of Holstein - a German prince, and thus a part of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, Beginning of a policy of danization towards the German population 1806 · Napoleon forces the creation of the Rhine Confederation, an alliance of sixteen southern and southwestern German states under French protectorate, which declare themselves sovereign and resign from the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, hereupon Emperor Franz II. lays down the crown of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the empire ends, Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg become annexed to Denmark 1807 · the island of Helgoland is occupied by British troops 1814 · Peace of Kiel, Helgoland is part of Great Britain 1st of July in 1890 · Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty, Helgoland comes from Great Britain to Prussia and is thus a part of the German Empire, Heligoland becomes connected to the district of South Dithmar in the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein 1914-1918 · First World War, Heligoland is evacuated 1922 · Heligoland is a separate circle in the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein 1932 · Heligoland becomes connected to the district of Pinneberg in the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein 1939–1945 · Second World War; Heligoland is bombed on 18t of April 1945by the British Air Force, 1.000 planes drop at least 7.000 bombs, the island had become uninhabitable, the population becomes completely evacuated 18th of April in 1947 · the British army tries in vain to blast away the entire island by the largest ever non-nuclear Explosion in the history of the world, with 6.700 tons of explosives 1947–1952 · the British Air Force uses the island as a training ground for bombing 20th of Dezember in 1950 · two students and a lecturer from Heidelberg occupy the island and hoist the German flag, the flag of the European Movement and the flag of Helgoland 3rd of January in 1951 · British officers stop the occupation, then the parliament of the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) demands the island back 1st of March in 1952 · Heligoland is released by the United Kingdom, and affiliated to the FRG |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Herders Conversations-Lexikon |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Helgoland" soll auf den Begriff "Heiliges Land“ zurückgehen, und auf alten Landkarten wird es als "Helge Land" bezeichnet. Es wird aber auch vermutet dass der Wortstamm "Hallig" enthalten ist, und somit auf eine kleine Insel im Nordfriesischen Wattenmeer verweist. | The name
"Heligoland" should go back to the term "Holy Land", and on old maps the
island is called "Helge Land". However, it is also believed that the root
word "Hallig" is included, and thus refers to a small island in the North
Frisian Wadden Sea. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |