Benin |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Benin |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
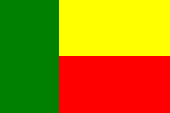 |
Nationalflagge –
national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
|
|
|
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
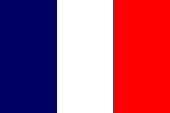 |
1894–1959, Flagge von Frankreich – flag of France, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1959–1975, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach by: Flags of the World |
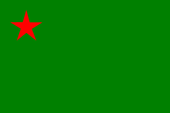 |
1975–1990, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach by: Flaggen und Wappen, Wikipedia (DE) |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
Vom November 1959 bis
30.11.1975 war die heutige Flagge bereits die Nationalflagge von Dahomey. Am 30.11.1975
wurde das Land in Benin umbenannt. Die an diesem Tag eingeführte, und bis zum 01.08.1990
beibehaltene grüne Flagge mit dem roten Stern, entsprach der farblichen Umkehrung der
roten Fahne der Revolutionären Volkspartei von Benin. Das Grün stand auf dieser Flagge
für die Landwirtschaft, das Rot für die Revolution und Sozialismus, und der rote Stern
selbst für die nationale Einheit. Die Flagge von Dahomey ist seit dem 01.08.1990 wieder
eingeführt. Sie besteht aus einem senkrechten grünen Streifen am Mast und zwei
waagerechte Streifen in Gelb und Rot im fliegenden Ende der Flagge.
|
From November 1959
until the 30th of November, 1975 the present day's flag was already the national flag of
Dahomey. On the 30th of November, 1975 the country was renamed to Benin. The green flag with the red star, introduced on this day and retained until the 1st of August, 1990, corresponds to the colour reversal of the Revolutionary People’s Party of Benin. The green on the flag stood for agriculture, the red for revolution and socialism, and the red star for national unity. The flag of Dahomey was reintroduced on the 1st of August, 1990. It consists of a vertical green stripe near the pole and two horizontal stripes of yellow and red in the flying end of the flag.
|
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1990, Wappen von Benin – coat of arms of Benin, Quelle/Source nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (D) |
historische Wappen – historical Coats of Arms: |
|
 |
1975–1990, Wappen von Benin – coat of arms of Benin, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
1964–1975, Wappen von Dahomey – coat of arms of Dahomey, Quelle/Source nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (D) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Der Schild des Wappens von Benin ist gevierteilt. Im ersten silbernen Feld sind typische Wohngebäude abgebildet, im zweiten silbernen Feld der höchste Orden des Landes, im dritten silbernen Feld eine Kokospalme, und im vierten silbernen Feld ein schwarzes dreimastiges Segelschiff auf blauen Meereswellen. Die Viertel des Wappens stehen somit für das Volk, ruhmreiche Vergangenheit, gewerbliche Produktion und Handel. In der Mitte des Schildes befindet sich eine kleine rote Raute. Schildhalter sind zwei goldene Panther. über dem Schild sind zwei schwarze Füllhörner zu sehen, aus denen Maiskolben hervorschauen. Auf einem silbernen Spruchband unterhalb des Wappens steht das Motto: "Fraternité, Justice, Travail" => "Brüderlichkeit, Gerechtigkeit, Arbeit". Das heutige Wappen wurde bereits im Jahre 1964 für Dahomey eingeführt und, wie die Flagge von Dahomey, am 01.08.1990 bestätigt. In den Jahren 1975–1990 zeigte das Wappen eine grüne Scheibe, umgeben von einem Kranz aus Maiskolben die mit einem roten Band verbunden waren. Im oberen Teil der grünen Scheibe befand sich ein roter fünfzackiger Stern und im unteren Teil, unmittelbar am Rand der Scheibe, das Blatt einer Kreissäge. | The shield of the coat
of arms of Benin is quartered. In the first silvery field are depicted typical homes, in
the second silvery one the supreme order of the land, in the third silvery one a coconut
palm, and in the fourth silvery one a black sailing ship with three masts on blue waves.
Thus the quarters of the coat of arms stand for the people, a glorious history, commercial
production and trade. In the centre of the shield a little red rhomb is positioned. Shield
holders are two golden panthers. Above the shield are two black cornucopias which contain
corncobs. On a silvery motto ribbon below the scutcheon appears the motto:
"Fraternité, Justice, Travail" => "Fraternity, Justice, Labor".
Today's coat of arms had already been introduced for Dahomey in 1964, and was, like the
flag of Dahomey, confirmed on the 1st of August, 1990. During the years 1975–1990 the
coat of arms showed a green disk, surrounded by a garland from corncobs, which were bound
with a red ribbon. In the upper part of the green disk was a red five-pointed star and in
the lower part, directly on the edge of the disk, the blade of a circular saw. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1975–1990, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1625
· Königreich Dahomey 1650 · Gründung des britischen Stützpunktes Fort William bei Ouidah (Whydah, Ajudá) 1671 · Gründung des französischen Stützpunktes Fort St. Louis bei Ouidah 1680 · Gründung des portugiesischen Stützpunktes Forte de São João Baptista de Ajudá bei Ouidah 1721 · das portugiesische Fort São João Baptista wird Brasilien unterstellt 1797 · Frankreich gibt den Stützpunkt Fort St. Louis auf 1807 · Großbritannien gibt den Stützpunkt Fort William auf 1844 · Das Fort São João Baptista wird verlassen 1865 · Portugal nimmt das Fort São João Baptista wieder in Besitz 1868–1893 · Frankreich errichtet Protektorate und Kolonien an der Küste (Cotonou, Porto-Novo, Ouidah) 22.06.1894 · Gründung der französischen Kolonie Dahomey 1899 · Dahomey wird Bestandteil der Kolonie Französisch-Westafrika 04.12.1958 · Frankreich gewährt der Republik Dahomey Autonomie 01.08.1960 · Frankreich gewährt der Republik Dahomey die Unabhängigkeit 1961 · Dahomey besetzt das Fort São João Baptista 1972 · Militärputsch unter Oberstleutnant Kérékou 1975 · Portugal erkennt die Inbesitznahme von Fort São João Baptista durch Dahomey an 30.11.1975 · Umbenennung in Volksrepublik Benin 1980 · Oberst Kérékou wird Präsident 1989–1990 · Unruhen 01.03.1990 · Rückbenennung in Republik Benin, Einleitung politischer Reformen |
History: |
| 1625
· Kingdom of Dahomey 1650 · foundation of the British base Fort William at Ouidah (Whydah, Ajuda) 1671 · foundation of the French base Fort St. Louis at Ouidah 1680 · foundation of the Portuguese base Forte de São João Baptista de Ajuda at Ouidah 1721 · the Portuguese fort of São João Baptista is assumed to Brazil 1797 · France leaves Fort St. Louis 1807 · the United Kingdom leaves Fort William 1844 · Fort São João Baptista is abandoned 1865 · Portugal re-appropriates Fort São João Baptista 1868–1893 · France establishes protectorates and colonies at the coast (Cotonou, Porto-Novo, Ouidah) 22nd of June in 1894 · founding the French colony of Dahomey 1899 · Dahomey becomes part of the colony of French West Africa 12th of April in 1958 · France grants autonomy to the Republic of Dahomey 1st of August in 1960 · France grants independence to the Republic of Dahomey 1961 · Dahomey occupies the Fort São João Baptista 1972 · military coup led by Lieutenant Colonel Kérékou 1975 · Portugal recognizes the seizure of Fort São João Baptista by Dahomey 30th of November in 1975 · renamed in People's Republic of Benin 1980 · Colonel Kérékou becomes president 1989–1990 · riots 3rd of January in 1990 · renaming in Republic of Benin, introduction of political reforms |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen, Länder der Erde |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name des Landes geht auf die langgestreckte Bucht von Benin und das alte Königreich Benin zurück. Dieses existierte zwischen dem 13. und dem 19. Jahrhundert, und lag allerdings größtenteils auf dem Gebiet des heutigen Nigeria. Der alte Name "Dahomey" (oder auch "Dahome"), geht auf das Königreich Dahome zurück, das ohne Zugang zur Küste zwischen den Königreichen Aschanti und Joruba im Gebiet des heutigen Benin lag. Es existierte zwischen dem 17. und dem 20. Jahrhundert, war extrem autoritär geführt und äußerst aggressiv. Vielleicht hat man deshalb im Jahre 1990 auf ein Rückbenennung in Dahomey verzichtet. | The name of the country
goes back to the elongated bay of Benin and to the old kingdom of Benin. It existed
between 13th and 19th century, but it was in the largely placed in the area of today's
Nigeria. The old name "Dahomey" (or "Dahome"), dates back to the Kingdom of Dahomey, which was placed without access to the coast between the Kingdoms of Ashantee and Joruba in the area of today's Benin. It existed between 17th and 20th century, was extremely authoritarian and extremely aggressive. Maybe that this was the reason to renounce a rename back in Dahomey in 1990. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Meyers Konversationslexikon via RetroBib Retrobibliothek, Volker Preuß | |