Wallonien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Wallonien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
Flagge von Wallonien – flag of Wallonia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Der Hahn ist der "Gallische Hahn". Dahinter verbirgt sich ein Wortspiel: Auf Latein heißt Hahn "Gallus". Das gleiche Wort wurde auch für die "Gallier" verwendet. Die französischsprachigen Romanen sehen sich als Nachfahren der Gallier an, und so bot sich der Hahn als Symbol an, und wurde als Nationalsymbol seit der Zeit der Rennaissance verwendet. Für Wallonien wurde der rote Hahn auf Gold im Jahre 1913 eingeführt, jedoch nicht offiziell. Erst im Jahre 1975 wurde er auch offziell verwendet, und am 15.07.1998 offiziell eingeführt. | The cock is the
"Gallic Rooster". Behind this is a pun: in Latin means cock "Gallus" .
The same word was also used for the "Gauls". The French speaking Romans see
themselves as descendants of the Gauls, and thus the cock presented itself as a symbol and
it became used as a national symbol since the time of the Renaissance. In Wallonia, the
red cock on gold was introduced in 1913, but not officially. Only in 1975, he was also
officially used, and officially adoped on 15th of July in 1998. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World | |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
in Belgien – Position in Belgium: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 58–51
v.Chr. · römische Eroberung 481–843 · zum Frankenreich 880 · im Herzogtum Lothringen zum Ostfrankenreich (Deutsches Reich), Flandern verbleibt beim Frankenreich 12. bis 14. Jhd. · als Kleinstaaten beim Deutschen Reich 1384 · durch Heirat an das Herzogtum Burgund und an das Deutsche Reich 1555 · Das Haus Habsburg erbt Burgund 1714 · die Habsburgischen Besitzungen kommen an die Österreichische Linie des Hauses Habsburg 1795 · Eroberung und Annexion durch Frankreich 1815–1830 · zu den Vereinigten Niederlanden 1830 · Gründung von Belgien mit dem Ziel ein französischprachiger Staat zu werden, Wallonien wird Belgien angeschlossen ca. 1840 · Gründung der „Flämischen Bewegung“ zum Erhalt der Flämischen Sprache und Kultur ca. 1880 · Gründung der „Wallonischen Bewegung“ als Widerpart 1898 · „Gleichheitsgesetz“, Belgien wird offiziell ein zweisprachiger Staat 1962–1963 · Festlegung der Sprachgrenze zwischen den Kulturgemeinschaften, Brüssel wird zweisprachig, Anerkennung der Deutschen Sprache als Regionalsprache in Ostbelgien 1970 · erste belgische Staatsreform, die Kulturgemeinschaften erhalten Verfassungsrang 1980 · zweite belgische Staatsreform, Schaffung der Wallonischen Region mit Autonomiestatus 1983 · Schaffung der Deutschsprachigen Gemeinschaft in Ostbelgien als Teil Walloniens 1988 · dritte belgische Staatsreform, Ausbau der Autonomie der Regionen, Schaffung der Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt 1994 · vierte belgische Staatsreform, Teilung der ehemaligen Provinz Brabant, weiterer Ausbau der Autonomie der Regionen, Belgien wird föderaler Bundesstaat 2001 · fünfte belgische Staatsreform, weiterer Ausbau der Autonomie der Regionen |
| 58–51 B.C.
· Roman conquest 481–843 · to the Frankonian Empire 880 · in the duchy Lorraine to the East Frankonian Empire (German Empire), Flandern remains at the Frankonian Empire 12th to 14th cent. · as small states within the German Empire 1384 · by marriage to the Duchy of Burgundy and in this way to the German Empire 1555 · the House of Habsburg inherits Burgundy 1714 · the Habsburg possessions come to the Austrian lineage of the House of Habsburg 1795 · conquest and annexation by France 1815–1830 · to the United Netherlands 1830 · creation of Belgium with the aim of a French speaking state to be, Wallonia becomes annexed to Belgium about 1840 · foundation of the "Flemish movement" to preserve the language and Flemish culture about 1880 · foundation of the "Walloon movement" as an adversary 1898 · "Equality Act", Belgium is officially a bilingual country 1962–1963 · definition of the linguistic border between the cultural communities, Brussels is bilingual, recognition of the German language as a regional language in Eastern Belgium 1970 · first Belgian state reform, the cultural communities become an constitutional rank 1980 · second Belgian state reform, creation of the Walloon Region with status of autonomy 1983 · establish of the German Community in Eastern Belgium as part of Wallonia 1988 · third Belgian state reform, expansion of regional autonomy, creation of the Region Brussels-Capital 1994 · fourth Belgian state reform, division of the former province of Brabant, further strengthening of the autonomy of regions, Belgium becomes a federal state 2001 · fifth Belgian state reform, further strengthening of the autonomy of the regions |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Wallonien", oder auch die Bezeichnung "Wallonen" für die französischsprachigen Belgier geht auf das germanische Wort "welsch" zurück, was "fremd" heißt. So wurde alles bezeichnet, was nicht-germanisch war. | The name
"Wallonia", or even the word "Walloon" for the French-speaking
Belgians go back to the Germanic word "welsch", what means
"foreign". So was called all that, what was not-Germanic. |
| Die Wallonen sprechen heute umgangssprachlich Wallonisch, was meist als französischer Dialekt angesehen wird, manchmal auch als eigenständige romanische Sprache. Amtssprache ist jedoch Französisch. | The Walloons speak Walloon colloquially today, which is usually regarded as a French dialect, but sometimes even as a separate Romanesque language. However, official language is French. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Wikipedia (D) | |
Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft – German-speaking Community: |
|
| mehr Info => hier klicken | more Info => click here |
 |
Flagge der
Deutschsprachigen Gemeinschaft in Belgien
– flag of the German-speaking Community in Belgium, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Mouvement Wallon pour le Retour à la France (Parti Rattachiste France): |
|
| Diese politische Bewegung bestrebt die Abspaltung Walloniens von Belgien und dessen Anschluss an Frankreich. | That political movement seeks the secession of Wallonia from Belgium and its annexation to France. |
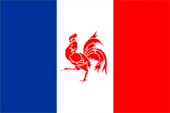 |
Flagge
der Bewegung – flag of the movement, |