|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
seit/since 1980, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE)   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|||
 |
1788–1914, | ||
 |
1864–1914, |
||
 |
1914–1980, Flagge von Australien – flag of Australia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   | ||
| Die Flagge wurde am 11.01.1980 angenommen. Sie zeigt drei senkrechte Streifen in Grün, Weiß und Grün im Verhältnis 7:9:7. Der Baum in der Mitte ist eine Norfolktanne, eine nur auf dieser Insel vorkommende Pflanzenart. Er erschien erstmals im Jahre 1856 auf dem Siegel der Insel. Das Grün in der Flagge scheint als Pantone 349 definiert zu sein. |
The flag was adopted on
11th of January in 1980. It shows three vertical stripes of green, white and green in the
ratio 7:9:7. The tree in the middle is a Norfolk fir, a plant species found
only on this island. It first appeared on the island's seal in 1856. The green
in the flag appears to be defined as Pantone 349. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Wikipedia (DE), Wikipedia (EN) | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
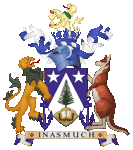 |
seit/since 1980, Wappen von Norfolk – coat of arms of Norfolk, Quelle/Source: Squiresy92 including elements from Sodacan, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
| Das Wappen von Norfolk wurde am 20.10.1980 von Elisabeth II. gewährt und eingeführt. Es zeigt ein blaues Wappenschild mit einer eingeschobenen weiße Spitze, darauf einem naturfarbenen Berg mit einer grünen Norfolk-Tanne und ein aufgeschlagenes Buch. Links und rechts neben der Spitze erscheinen zwei weiße fünfzackige Sterne. Über dem Schild erscheint ein Helm mit einer blauen Krone, mit einem weiß-blauem Wulst und blau-weißen Helmdecken. Oberhalb der Krone erscheint das Helmkleinod, ein goldener Löwe. Schildhalter sind ein Löwe und ein Känguru, beide jeweils auf einen blauen Anker stehend. Das Motto auf dem Spruchband lautet: "INASMUCH", das erste Wort in der Hymne der Insel. |
The arms of Norfolk were
granted and established by Elizabeth II. on 20th of October in 1980. It shows a blue escutcheon with an inset white peak, on which is a natural coloured mountain with a green Norfolk fir and an open book. Two white five-pointed stars appear to the left and right of the peak. Above the shield appears a helmet with a blue crown, with a white and blue torse and blue and white helmet covers. Above the crown appears the crest, a golden lion. Supprters are a lion and a kangaroo, each standing on a blue anchor. The motto on the banner reads: "INASMUCH", the first word in the island's anthem. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1774 ·
Entdeckung durch den britischen Seefahrer James Cook 1778 · Inbesitznmahme durch Großbritannien, Angliederung an die Kolonie Neusüdwales 1788–1814 · Britische Strafkolonie 1825–1855 · Britische Strafkolonie 1844 · Angliederung an die Kolonie Tasmanien 08.06.1856 · Übersiedlung von 190 Nachfahren der "Bounty-Meuterer" (nun "Islanders" genannt) von der Insel Pitcairn 01.11.1856 · Norfolk wird autonomes eigenständiges Territorium von Neusüdwales 1858 · 16 Pitcairner kehren von Norfolk auf ihre Insel zurück 1864 · vier weitere Pitcairner-Familien kehren von Norfolk auf ihre Insel zurück 1897 · Aufhebung der Autonomierechte 01.07.1914 · die Norfolk-Insel wird australisches Territorium 1976 · Versuche die Insel Norfolk Australien direkt anzugliedern scheitern am erbitterten Widerstand der Inselbewohner 10.08.1979 · Norfolk-Insel-Gesetz (Norfolk Island Act), erneute Garantie von Autonomierechten |
| 1774 ·
discovery by the British seafarer James Cook 1778 · appropriation by United Kingdom, affiliated to New South Wales 1788–1814 · British penal colony 1825–1855 · British penal colony 1844 · affiliated to Tasmania 8th of June 1856 · resettlement of 190 descendants of the "Bounty Mutineers" (now named "Islanders") from Pitcairn Island 1st of November 1856 · Norfolk becomes an autonomous independent territory of New South Wales 1858 · 16 Pitcairn-Islanders return from Norfolk to their island 1864 · four further families of Pitcairn-Islanders return from Norfolk to their island 1897 · abolition of the autonomy rights 1st of July 1914 · Norfolk Island becomes an Australian territory 1976 · attempts to annex Norfolk Island directly to Australia fail in the embittered resistance of the islands's residents 10th of August 1979 · Norfolk Island Act, again granting of autonomy rights |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN), World Statesmen |
| Der Name "Norfolk" wurde der Insel von James Cook einige Zeit nach ihrer Entdeckung gegeben. Er verlieh den Namen zu Ehren von Mary Howard, Herzogin von Norfolk. | The name "Norfolk" was given to the island by James Cook some times after the discovery. He awarded the name in honour of Mary Howard, Duchess of Norfolk. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |