Sint Maarten |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Sint Maarten |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
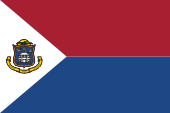 |
Flagge von St. Maarten |
| Die Flagge von St. Maarten wurde am 13.06.1985 angenommen. Sie zeigt in zwei waagrechten Streifen die Farben Rot und Blau, sowie in einem gleichschenkligen Dreieck an der Fahnenstange die Farbe Weiß und das Wappen des Landes. Es sind die Farben der Niederlande und auch der ehemaligen Niederländischen Antillen. Die Buntfarben der Flagge der Niederlande werden seit 1958 folgendermaßen definiert, hexadezimal: Rot ("Helles Zinnoberrot") = #A91F32 was Pantone 187 entsprechen würde, Blau ("Kobaltblau") = #1E4785 was Pantone 541 entsprechen würde. |
The flag of St. Maarten
was adopted on 13th of June in 1985. It shows the colours red and blue in
two horizontal stripes, as well as the colour white and the country's coat
of arms in an isosceles triangle on the flag pole. These are the colours of
the Netherlands and also of the former Netherlands Antilles. The colours of the flag of the Netherlands have been defined since 1958 as follows, hexadecimal: red ("bright vermilion") = #A91F32 which would correspond to Pantone 187, blue ("cobalt blue") = #1E4785 which would correspond to Pantone 541. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Sint Maarten – coat of arms of Sint Maarten, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Das Wappen von St. Maarten zeigt auf einem blauen, orangeumrandeten Schild ein Gerichtsgebäude, einen Gedenkstein und eine Salbeiblüte. Orange ist die Farbe des niederländischen Königshauses von Oranien-Nassau. Der Gedenkstein erinnert an die Teilung der Insel zwischen Frankreich und den Niederlanden im Jahre 1648, Salbei ist die Nationalpflanze. Oberhalb des Schildes ein fliegender Pelikan vor der Sonnenscheibe. In dem goldenen Spruchband unterhalb des Schildes das Motto der Insel: "SEMPER PROGREDIENS" → "Beständiger Fortschritt". | The coat
of arms of St. Maarten shows on a blue, orange surrounded shield a court
house, a memorial and a sage blossom. Orange is the colour of the Netherlands royal house of Oranien-Nassau. The memorial remembers the partition of the island among France and the Netherlands in the year 1648, sage is the national plant. Above the shield a flying pelican in front of the sunwheel. In the golden banner below the shield the motto of the island: "SEMPER PROGREDIENS" → "constant progress". |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |
| Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1493 · Christoph Kolumbus entdeckt die Insel am 11.
November, dem Tag des Heiligen Martin, und nennt sie "Isla de San Martín" 1625 · Gründung einer französischen Siedlung 1631-1633 · St. Martin ist Kolonie der Niederlande 1633 · St. Martin wird eine Kolonie von Spanien 1638 · Gründung einer spanischen Siedlung 1648 · Gründung einer französischen Siedlung 23.03.1648 · offizielle Teilung der Insel zwischen Frankreich und den Niederlanden 1651-1665 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist ein Lehen des Malteserordens 1672-1679 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von England besetzt 1679-1689 · die gesamte Insel ist von Frankreich besetzt 1689-1792 · der niederländische Teil von St. Martin untersteht der Verwaltung der Niederländischen Westindienkompanie 1690-1699 · die gesamte Insel ist von England besetzt 1699-1702 · die gesamte Insel ist von Frankreich besetzt 1702 · der offiziell französische Teil von St. Martin ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1703-1713 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von den Niederlanden besetzt 1744-1748 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1759-1763 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1779-1781 · die gesamte Insel ist von Frankreich besetzt 1781 · die gesamte Insel ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1781-1784 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1793-1794 · die gesamte Insel wird von den Niederlanden verwaltet 1794-1795 · der französische Teil von St. Martin ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1795-1801 · die gesamte Insel ist von Frankreich besetzt 1801-1802 · die gesamte Insel ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1810-1816 · die gesamte Insel ist von Großbritannien besetzt 1816 · offizielles Wiederherstellen der Teilung zwischen Frankreich und den Niederlanden 1828 · der niederländische Teil von St. Martin, Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, und Niederländisch-Guayana werden als Niederländisch-Westindien zusammengefasst und dem Gouverneur von Niederländisch-Guayana als Generalgouverneur unterstellt 1848 · der niederländische Teil von St. Martin, Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius werden als "Kolonie Curaçao en onderhorigheden" (Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies) zusammengefasst 1936 · der niederländische Teil von St. Martin nimmt offiziell als Landesnamen die niederländische Schreibweise "Sint Maarten" an 1948 · die "Kolonie Curaçao en onderhorigheden" wird in "Niederländische Antillen" umbenannt 1954 · die Niederländischen Antillen werden ein autonomer Teil der Niederlande 1994 · Volksabstimmung in Sint Maarten zugunsten des Verbleibs bei den Niederlanden 2000 · Volksabstimmung in Sint Maarten zugunsten eines separaten Status innerhalb der Niederlande 2006 · Sint Maarten und Curaçao erhalten einen separaten Status innerhalb der Niederlande 10.10.2010 · die Niederländischen Antillen werden aufgelöst, Sint Maarten wird ein autonomes Land der Niederlande |
|
1493 ·
Christopher Columbus discovers the island on 11th of November, the day of
St. Martin, and calls it "Isla de San Martín" 1625 · founding of a French settlement 1631-1633 · St. Martin's colony of the Netherlands 1633 · St. Martin is a colony of Spain 1638 · founding a Spanish settlement 1648 · founding of a French settlement 23rd of March in 1648 · official division of the island between France and the Netherlands 1651-1665 · the French part of St. Martin is a fief of the Order of Malta 1672-1679 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by England 1679-1689 · the entire island is occupied by France 1689-1792 · the Dutch part of St. Martin is under administration of the Dutch West India Company 1690-1699 · the entire island is occupied by England 1699-1702 · the entire island is occupied by France 1702 · the official French part of St. Martin is occupied by United Kingdom 1703-1713 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by the Netherlands 1744-1748 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by United Kingdom 1759-1763 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by United Kingdom 1779-1781 · the entire island is occupied by France 1781 · the entire island is occupied by United Kingdom 1781-1784 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by United Kingdom 1793-1794 · the entire island is owned by the Netherlands 1794-1795 · the French part of St. Martin is occupied by United Kingdom 1795-1801 · the entire island is occupied by France 1801-1802 · the entire island is occupied by United Kingdom 1810-1816 · the entire island is occupied by United Kingdom 1816 · official restore the division between France and the Netherlands 1828 · The Dutch part of St. Martin, Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, and Dutch Guiana become combined as Dutch West India and subordinated to the governor of Dutch Guiana as Governor General 1848 · The Dutch part of St. Martin, Aruba, Bonaire, Curacao, Saba, Sint Eustatius are called "colony Curaçao en onderhorigheden" (Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies) 1936 · the Dutch part of St. Martin officially takes over the Dutch spelling "Sint Maarten" as name of the country 1948 · the "colony Curaçao en onderhorigheden" is renamed to "Netherlands Antilles" 1954 · the Netherlands Antilles are an autonomous part of the Netherlands 1994 · referendum in Sint Maarten in favor of remaining in the Netherlands 2000 · referendum in Sint Maarten in favor of a separate status within the Netherlands 2006 · Sint Maarten and Curaçao receive a separate status within the Netherlands 10th of October in 2010 · the Netherlands Antilles are dissolved, Sint Maarten becomes an autonomous country of the Netherlands |
| Quelle/Source: World Statesmen, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97 |
| Am
Namenstag des Heiligen Martin, am 11. November 1493, entdeckt Christoph
Kolumbus die Insel, und nennt sie aus diesem Anlass "Isla de San Martín".
Die Insel wurde 1648 zwischen Frankreich und den Niederlanden aufgeteilt.
Allgemein gültig ist die Bezeichnung "St. Martin", jedoch wird der
französische Teil von St. Martin "Saint-Martin" genannt, der niederländische
Teil nennt sich "Sint Maarten". Der Heilige Martin lebte von 316 bis 397, war Bischof von Tours und teilte als Soldat seinen Mantel mit einem Bettler. |
On the name-day of St. Martin, on 11th of November in 1493, Christopher
Columbus discovered the island, and calls it on this occasion "Isla de San
Martín". The island became divided in 1648 between France and the Netherlands. Generally valid is the name "St. Martin", but the French part of St. Martin's is called "Saint-Martin", the Dutch part is called "Sint Maarten". Holy Martin lived from 316 to 397 A.D. was Bishop of Tours and divided as soldier his coat with a beggar. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Volker Preuß | |