|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 2004, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
seit/since 2004, |
 |
seit/since 1992, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
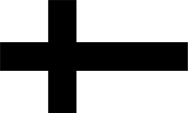 |
1384–1411, Flagge des Deutschen Ordens – Flag of the Teutonic Order (Teutonic Knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1411–1795, |
 |
1795–1858, Nationalflagge von Russland – National flag of Russia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1858–1915, Nationalflagge von Russland – National flag of Russia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
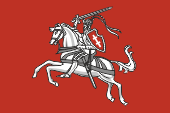
1918–1940, Nationalflagge – National flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1918–1940, Staatsflagge (Vorderseite) – State flag (averse), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
1918–1940, Staatsflagge (Rückseite) – State flag (reverse), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
ca. 1915, 1918, 1925, unbekannte Variante der Staatsflagge – unknown variant of state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: 1.) WEYER's Taschenbuch der Kriegsflotten, 1928, 2.) Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1918–1927, |
 |
1927–1940, |
 |
1927–1940, |
 |
1940–1953, |
 |
1953–1990, |
 |
1989–2004, Nationalflagge – National flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1992–2004(?), |
| Die Flagge Litauens wurde erstmals am 19.04.1918 offiziell gehisst, und am 20.03.1989 wieder eingeführt. | The flag of Lithuania was officially hoisted for the first time on 19th of April in 1918, and re-introduced on the 30th of March in 1989. |
Sie zeigt
drei waagerechte Streifen in Gelb, Grün und Rot. Über den Ursprung und die
Bedeutung der Farben gibt es drei Theorien, die sich sicherlich teilweise
überschneiden:
|
It shows
three horizontal stripes in yellow, green and red. About the origin and the
meaning of the colours there are three theories, which partially coincide
assuredly:
|
| Im Jahr 1940 und zwischen den Jahren 1944 und 1990 führte Litauen, als Teil der Sowjetunion, ein sowjetisches Modell. Bis 1953 eine einfache rote Flagge mit Hammer und Sichel in Gold, und unterhalb davon der Name der Sowjetrepublik "Lietuvos TSR", in goldenen lateinischen Lettern. Im Jahre 1953 wurde dann eine Sowjetflagge eingeführt, die drei waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Grün im Verhältnis 8:1:3 zeigte. In der Mitte des roten Feldes erschien, in Richtung Flaggenmast verschoben, Hammer, Sichel und Sowjetstern in Gold. Die Farben der Flagge von Litauen werden heute folgendermaßen angegeben: Gelb = Pantone 1235, Grün = Pantone 349 und Rot = Pantone 180. | In the
year 1940 and between the year 1944 and 1990 Lithuania used as part of the
Soviet Union a soviet model. Until 1953 a simple red flag with hammer and
sickle in gold and below of them the name of the Soviet Republic "Lietuvos
TSR", in golden Latin characters. In the year 1953 was introduced a Soviet Flagg, which showed three horizontal stripes in red, white and green in ratio 8:1:3. In the middle of the red field arised – moved in the direction of the flagstaff – hammer, sickle and Soviet star in gold. The colors of the flag of Lithuania today are indicated as follows: yellow = Pantone 1235, green = Pantone 349 and red = Pantone 180. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE) | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1991, Wappen Litauens – coat of arms of Lithuania, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Government of Lithuania, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Wappen – historical Coats of Arms: |
|
 |
1237–1561, Wappenschild des Deutschen Ordens – blazon of the Teutonic Order (teutonic knights), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1386–1569, Wappen Polen-Litauens – coat of arms of Poland-Lithuania, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
ca.1925–1940, 1990–1991, Wappen Litauens – coat of arms of Lithuania, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1942–1945, Ärmelabzeichen der Litauer in der Deutschen Wehrmacht – Sleeve insignia of the Lithuanians in the German Wehrmacht, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Avantgarde für Europa |
| Das Staatswappen von Litauen wurde in der heutigen Form im Jahre 1925 von Juzas Zikiris geschaffen. Es zeigt auf einem roten Schild einen silbernen Ritter mit erhobenem Schwert auf einem silbernen Pferd. Es soll an den legendären Ritter Vytis erinnern. Der Betrachter sieht den Ritter nach nach Links, in Richtung Westen ausgerichtet, um auf die Richtung hinzuweisen aus der in der Vergangenheit Gefahr für Litauen drohte. Das waren zum ersten der Deutsche Ritterorden, und zum zweiten der polnische Staat. Dieses Wappenbild war bereits seit dem 14. Jahrhundert in Verwendung. | The coat
of arms of Lithuania in the today's form was created in the year 1925 by
Juzas Zikiris. It shows on a red shield a silvery knight with outpulled
sword on a einem silvery horse. It should remember the legendary Knight Vytis. The viewer sees the knight orientated to the left – in western direction – to hint to the direction from where came menace for Lithuania in the past. These were for the first the Teutonic Order, and to the second the Polish state. This device was already in use since the 14th century. |
| Für die litauische Heraldik waren und sind seit dem 14. Jahrhundert die sogenannten Säulen des Gediminas von Bedeutung. Sie waren das Wappenbild der Dynastie der Gediminiden und das Symbol des Großfürstentums Litauen, eine weiße, stilisierte Burg auf rotem Grund. | For Lithuanian heraldry, the so-called Pillars of Gediminas have been important since the 14th century. They were the heraldic image of the Gediminid dynasty and the symbol of the Grand Pricipality of Lithuania, a white, stylised castle on a red background. |
| In der Zeit, in der Litauen zur Sowjetunion gehörte, war ein sowjetisches Modell in Verwendung, welches dem Wappen der Sowjetunion ähnelte. Am 11.03.1990 wurde wieder das Wappen von 1925 gültig, jedoch wurde 1991 eine kleine Änderung vorgenommen. Der ehemals rote Schild des Reiters ist nun blau, und das Doppelkreuz darin ist nicht mehr weiß sondern golden. | In the
times where Lithuania belonged to the Soviet Union was in use a soviet
model, which equals the coat of arms of the Soviet Union. On 11th of March 1990 they re-introduced the coat of arms of 1925, but there were made some changes in 1991. The formerly red shield of the horseman is blue now and the double-cross in it is no more white, but golden now. |
| Während
des Zweiten Weltkriegs, in der Zeit der deutschen Besetzung zwischen 1941
und 1944 hatte Litauen offiziell keine eigenen Hoheitszeichen. Es gehörte zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, in dem die Staaten den Baltikums und Teile des heutigen Nordwestens von Weißrussland zusammengefasst waren. |
During the Second World War – in the time of the German occupation between 1941 and 1944 – Lithuania had officially no own national emblems. It belonged to the Empire's Commissionership of Ostland, in which have been summarized the countries of the Balticum and parts of the today's northwest of White Russia (Belarus). |
| Die Litauische Legion, die im Zweiten Weltkrieg in Regimentsstärke freiwillig in den Reihen der Deutschen Wehrmacht gegen die Sowjetunion kämpfte trug als Ärmelabzeichen einen dreifach diagonalgestreiften Schild in den Landesfarben Gelb, Grün und Rot. | The Latvian Legion, which in the Second World War fought voluntary in potency of a regiment in the ranks of the German War Might against the Soviet Union used as sleeve-insignia a threefold diagonally striped shield in the country`s colours yellow, green and red. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE), Avantgarde für Europa | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Landkarte des Baltikums – Map of the Balticum: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 11.–12.
Jhd. · Besiedelung des heutigen Litauens durch die Litauer Mitte des 14. Jhd. · Einigung des litauischen Staates unter den Großfürsten Witens, Gedymin, Olgerd und Kejstut, es gelingt die Gebiete des heutigen Weißrusslands und Podoliens (in der heutigen Ukraine) zu erobern und so ein Gebiet von der Ostsee bis zum Schwarzen Meer unter einer Krone zu vereinigen 1384 · der Deutsche Orden erobert Samogitien 1386 · Jagiello, der Sohn des Fürsten Olgerd, seit 1377 Großfürst von Litauen, heiratet die polnische Königin Hedwig (Jadwiga) und wird als Wladyslaw II. zum König von Polen gekrönt, seither: Königreich Polen -Litauen 1410 · Wladyslaw II., König von Polen und Litauen, und Vytautas (Witold) Großfürst von Litauen schlagen den Deutschen Orden bei Tannenberg 1411 · 1. Frieden von Thorn, der Deutsche Orden muss Samogitien an Litauen abtreten 1569 · Polnisch-Litauischer Ausgleich (Union von Lublin), die beiden Landesteile bewahren sich jedoch innere Autonomie, Litauen tritt seine Territorien in der heutigen Ukraine an Polen ab 1772, 1793 und 1795 · Polnische Teilungen, Preußen, Russland und Habsburg teilen Polen-Litauen in drei Etappen vollständig unter sich auf, Litauen wird russisch, Aufteilung in die Gouvernements Wilna (russisch: Wiljnus, litauisch: Vilnius), Sudauen (russisch: Suwalki) and Kauen (russisch: Kowno, litauisch: Kaunas) ab Mitte des 19. Jhd. · Erstarken des litauischen Nationalismus 1905 · Konstituierung eines litauischen Landtags im Gouvernement Kowno (Kauen) 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg: 1915 das Deutsche Reich erobert Litauen 07.11.1917 · bolschewistische Revolution in Russland, Machtergreifung durch die Sowjets 03.03.1918 · Russland kapituliert gegenüber dem Deutschen Reich, Friedensvertrag von Brest-Litovsk, Herausbildung eines litauischen Staates (einschließlich Kauen und Teilen der Gouvernemente Wilna und Sudauen) 19.04.1918 · Litauen erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit von Russland, Proklamation der Republik Litauen 18.03.1921 · Friede von Riga, Sowjetrussland und Polen erkennen die Unabhängigkeit Litauens an, jedoch muss Litauen das Gebiet Vilnius (Wilna) an Polen abtreten, Litauen erhebt Anspruch auf das deutsche Memelgebiet 10.01.1923 · das Ergebnis einer Volksabstimmung ignorierend besetzt Litauen das deutsche Memelgebiet 1926 · Errichtung der Präsidialdiktatur durch die Nationalpartei 22.03.1939 · Litauen tritt das Memelgebiet wieder an das Deutsche Reich ab 23.08.1939 · deutsch-sowjetischer Nichtangriffspakt, Litauen wird sowjetische Interessensphäre und von der Sowjetunion besetzt 21.07.1940 · Proklamation der Litauischen Sozialistischen Sowjetrepublik (LSSR) 05.08.1940 · Aufnahme der LSSR in die Sowjetunion, Deportation von Tausenden von Einwohnern nach Sibirien 1939–1945 · Zweiter Weltkrieg: Juni/Juli 1941 Eroberung Litauens durch deutsche Truppen, Litauen kommt zum Reichskommissariat Ostland, etwa 3.000 Litauer kämpfen freiwillig in der Deutschen Wehrmacht gegen die Sowjetunion, Dezember 1944 Eroberung Litauens durch sowjetische Truppen, Litauen wird wieder LSSR und wird der Sowjetunion wieder angegeliedert, erhält jedoch das ehemals polnische Wilna-Gebiet zurück, erneut Deportation von Tausenden von Litauern nach Sibirien, teilweise Russifizierung 1988 · Erstarken der litauischen Demokratie- und Nationalbewegung "Sajudis" 18.05.1989 · Unabhängigkeitserklärung 11.03.1990 · Proklamation der Republik Litauen 06.09.1991 · die Sowjetunion erkennt die Unabhängigkeit Litauens an 1993 · Abzug der russischen Truppen 2004 · Litauen wird Mitglied der Europäischen Union und der NATO |
| 11th–12th
cent. · settlement of the today's Lithuania by the Lithuanians Middle of the 14th cent. · unification of the Lithuanian state under the Grande Princes Witens, Gedymin, Olgerd and Kejstut, they achieve to conquer the areas of the today's White Russia (Belarus) and of Podolia (in the today's Ukraine) and to unite in this way a territory from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea under one crown 1384 · the Order of the Teutonic Knights conquers Samogitia 1386 · Jagiello, the son of Prince Olgerd, since 1377 Grande Prince of Lithuania marrys the Polish Queen Hedwig (Jadwiga) and gets crowned as Wladyslaw II. to the King of Poland, thereafter: Kingdom of Poland-Lithuania 1410 · Wladyslaw II., King of Poland and Lithuania, and Vytautas (Witold) Grande Prince of Lithuania overcome the Order of the Teutonic Knights near Tannenberg 1411 · 1st Peace of Thorn, the Order of the Teutonic Knights has to cede Samogitia to Lithuania 1569 · Polish-Lithuanian Conciliation (Union of Lublin), the both countrysides preserve themselves interior autonomy, Lithuania cedes its territories in the today's Ukraine to Poland 1772, 1793 and 1795 · Polish Partitions, Prussia, Russia and Habsburg partition Poland-Lithuania fully among themselves in the phases, Lithuania becomes Russian, division in the Gouvernements of Wilna (Russian: Wiljnus, Lithuanian: Vilnius), Sudauen (Russian: Suwalki) and Kauen (Russian: Kowno, Lithuanian: Kaunas) from the middle of the 19th cent. · grow strong of the Lithuanian nationalism 1905 · constitution of a Lithuanian parliament in the Gouvernement of Kauen 1914–1918 · First World War: 1915 the German Empire conquers Lithuania 7th of November 1917 · bolshevistic revolution in Russia, seizure of power by the Soviets 3rd of March 1918 · Russia capitulates towards the German Empire, Peace Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, development of an Lithuanian state (including Kauen and parts of the Gouvernements of Wilna and Sudauen) 19th of April 1918 · Lithuania declares its independence from Russia, proclamation of the Republic of Lithuania 18th of March in 1921 · Peace of Riga, Soviet Russia and Poland recognize the independence of Lithuania, but Lithuania has to cede the area of Wilna to Poland, Lithuania claims the German Memel Area 10th of January 1923 · under disregard of the result of a plebiscite Lithuania occupies the German Memel Area 1926 · establishment of the presidial dictatorship by the National Party 22nd of March 1939 · Lithuania cedes the Memel Area back to the German Empire 23rd of August in 1939 · German-Soviet non aggression pact, Lithuania becomes a soviet sphere of interest and gets occupied by the Soviet Union 21st of July 1940 · proclamation of the Lithuanian Socialistic Soviet Republic (LSSR) 5th of August 1940 · inclusion of the LSSR into the Soviet Union, deportation of thousands of inhabitants to Sibiria 1939–1945 · Second World War: June/July 1941 conquest of Lithuania by German troops, Lithuania comes to the empire`s commissionership of Ostland, ca 3.000 Lithuanians fight voluntary in the German War Might against the Soviet Union, December 1944 conquest of Lithuania by soviet troops, Lithuania becomes once more LSSR and incorporated into the Soviet Union again, but gets back the formerly Polish Wilna Area, once more deportations of thousands of Lithuanians to Sibiria, partial russification 1988 · grow strong of the Lithuanian democracy and national movement "Sajudis" 18th of May 1989 · declaration of independence 11th of March 1990 · proclamation of the Republic of Lithuania 6th of September 1991 · the Soviet Union recognizes the independence of Lithuania 1993 · withdrawal of the Russian troops 2004 · Lithuania becomes a member in European Union and NATO |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Avantgarde für Europa |
| Der Name "Litauen" bzw. "Litauer" geht vermutlich auf das lateinische Wort "litus" zurück, was "Küste" heißt. | The name "Lithuania" resp. "Lithuanian" has probably its roots in the Latin word "litus", what means "coast". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |
| Landkarten zur Geschichte des Baltikums – historical Maps of the Balticum: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|