Lesotho |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Lesotho |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, |
 |
Flagge des Königs – flag of the king, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia.de |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
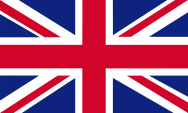 |
1868–1966, |
 |
1907–1931, |
 |
1931–1968, |
 |
1951–1966, |
 |
1951–1966, |
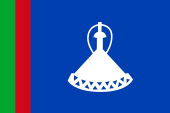 |
1966–1987, |
 |
1987–2006, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia.de   |
 |
1987–2006, Flagge des Königs – flag of the king, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia.de |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge von Lesotho wurde – nach Informationen von Wikipedia.de – anlässlich des 40. Jahrestages der Unabhängigkeit am 04.10.2006 angenommen. Die Flagge zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen im Verhältnis 3:4:3 in Blau, Weiß und Grün, wobei der weiße Mittelstreifen ein wenig verbreitert ist. In seiner Mitte ist ein schwarzer Basuto-Hut platziert. Die drei Farben der Flagge beziehen sich (wie in der 1987–2006 verwendeten Flagge) auf den nationalen Wahlspruch ("Frieden, Regen, Wohlstand"), Weiß steht für Frieden, Blau für den Regen und Grün für die Fruchtbarkeit des Landes und den Wohlstand. | The
today’s flag of Lesotho was – by informations of Wikipedia.de – adoped on
the occasion of the 40th anniversary of the independence on the 4th of
October in 2006. The flag shows three horizontal stripes in the ratio 3:4:3 in blue, white and green, however the white middle stripe is widen a little bit. In its middle is placed a black Basuto hat. The three colours of the flag refer (like in the 1987–2006 used flag) to the national motto ("peace, rain, prosperity "), white stands for peace, blue for rain and green for the fruitfulness of the country and the prosperity. |
| Die Farben der Flagge von Lesotho werden heute neben Schwarz und Weiß folgendermaßen angegeben: Blau = hexadezimal #00209F, was Pantone Reflex Blue entsprechen würde, Grün = hexadezimal #009543, was Pantone 355 entsprechen würde. | The colours of the flag of Lesotho are now given as follows, in addition to black and white: Blue = hexadecimal #00209F, which would correspond to Pantone Reflex Blue, Green = hexadecimal #009543, which would correspond to Pantone 355. |
| Als britisches Protektorat hatte Basutoland, wie Lesotho damals hieß, eigentlich keine eigene Flagge. Es musste der britische Union Jack verwendet werden. Angeblich wurde aber ab 1951 inoffiziell ein Blue Ensign als Nationalflagge verwendet. Er soll das Badge des Landes – einen grünen Schild mit einem goldenen Wollfließ, zwei goldenen Getreidegarben und einem Krokodil darauf – in der Mitte einer weißen Scheibe im fliegenden Ende der Flagge gezeigt haben. | As a
British protectorate Basuto Land – how Lesotho was named at that time –
really never had an own flag. There was to use the British Union Jack. Pretended there was already unofficially in use since 1951 a Blue Ensign as national flag. It should have shown the badge of the country – a green shield with a golden wool-wad, two golden wheat sheafs and a crocodile on it – in the middle of a white disk in the flying end of that flag. |
| Der britische Hohe Kommissar hatte seit 1907 seine eigene Flagge. Es handelte sich um die für Hohe Kommissare übliche Flagge, den Britischen Union Jack mit dem Abzeichen des Hohen Kommissars in der Mitte, eine von einem Kranz umgebene Abkürzung mit der britischen Krone darüber. Bis 1931 war der Britische Hohe Kommissar für Südafrika (Abkürzung: S.A.H.C.) für Basutoland zuständig. Nach dem Westminsterstatut wurde Südafrika 1931 unabhängig, und der Hohe Kommissar war nur noch für Betschuanaland, Basutoland und Swasiland zuständig (Abkürzung: H.C.). Im Jahre 1953 änderte sich nur die Form der Krone. | The
British High Commissioner had his own flag since 1907. It was the for the
High Commissioners usual flag, the British Union Jack with the badge of the
High Commissioner in the middle, an abbreviation with the British Crown
above, surrounded by a garland. Until 1931 the British High Commissioner in
and for South Africa (abbreviation: S.A.H.C.) was responsible for Basuto
Land. After the Statute of Westminster South Africa in 1931 became independent, and the High Commissioner was responsible only for Bechuanaland, Basutoland and Swaziland (abbreviation H.C). In 1953 was only changed the shape of the crown. |
| Die im Zusammenhang mit der Unabhängigkeit am 04.10.1966 angenommene und bis 1987 gültige Flagge zeigte die vier Farben der damals herrschenden Nationalpartei (BNP): Blau, Rot und Grün, mit einem weißen Basuto-Hut im blauen Feld. | The in
context with the independence on the 4th of October in 1966 adoped and until
1987 valid flag showed the four colours of the at that time governing
National Party (BNP): Blue, red and green with a white Basuto cap in the blue field. |
| Die zwischen dem 19.01.1987 und dem 04.10.2006 verwendete Flagge war diagonal gestreift. Sie zeigte ein weißes Feld oben links, und ein grünes Feld unten rechts, getrennt von einem blauen Streifen entlang der Diagonalen. Im weißen Feld befand sich ein brauner Schild mit Waffen, das Landeswappen in stilisierter Form. Die drei Farben der Flagge bezogen sich (wie in der heutigen Flagge) auf den nationalen Wahlspruch ("Frieden, Regen, Wohlstand"), Weiß steht für Frieden, Blau für den Regen und Grün für die Fruchtbarkeit des Landes und den Wohlstand. Der Schild im Obereck der Flagge symbolisierte, wie im Wappen, die Verteidigungsbereitschaft des Landes. Diese Flagge wurde am 19.01.1987 erstmals gehisst. | The
between the 19th of January 1987 and the 4th of October 2006 used flag was
diagonally striped. It showed a white field to the left above and a green
field on the right below, separated by a blue stripe along the diagonal. In the white field was positioned a brown shield with arms, the coat of arms in a stylized form. The three colours of the flag refered (like in the today's flag) to the national motto ("peace, rain, wealth"), white stands for peace, blue for the rain and green for the fruitfulness of the country and the wealth. The shield in the upper staff quadrant of the flag symbolizes – like in the coat of arms – the readiness for defence of the country. This flag was hoisted for the first time on 19th of January in 1987. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia.de, Wikipedia.en, World Statesmen, Die Welt der Flaggen, | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 2006, Wappen Lesothos – coat of arms of Lesotho, Quelle, nach: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1966–2006, Wappen Lesothos – coat of arms of Lesotho, Quelle, nach: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1951–1966, Wappen von Basutoland – coat of arms of Basutoland, Quelle, nach: Flags of the World |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen wurde anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit am 04.10.1966 eingeführt, und – wahrscheinlich im Jahre 2006 – farblich ein wenig abgeändert. Es zeigt auf einem Basuto-Schild ein Krokodil, das Symbol der Dynastie und des wichtigsten Stammes von Lesotho. Hinter dem Schild zwei gekreuzte Waffen des 19. Jahrhunderts. Die Schildhalter sind zwei Basuto-Pferde. Das Postament des Wappens ist der Berggipfel des "Nationalberges" Thababosiu. Im Vordergrund, auf einem Band der Wahlspruch der Monarchie in der Sprache Sesotho und in roten Buchstaben: "Khotso, Pula, Nala" → "Frieden, Regen, Wohlstand". | The coat
of arms was adoped on the occasion of the independence on 4th of October on
1966, and it was possibliy in 2006 changed a little bit in the colours. It
shows on a Basuto Shield a crocodile, the symbol of the dynasty and of the
primary tribe of Lesotho. Behind the shield two crossed arms of the 19th
century. The shield holders are two Basuto horses. The cantilever of the coat of arms is the peak of the "national mountain" Thababosiu. In the foreground om a banner the motto of the monarchy in Sesotho language and in red letters: "Khotso, Pula, Nala" → "Peace, Rain, Wealth". |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
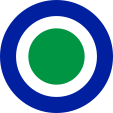 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1820 ·
der Zulu-König Tschaka erobert Südafrika, Flucht der Bantuvölker, Entstehung
des Basuto-Königreichs in den Bergen von Südafrika 1868 · das Basuto-Königreich bittet Großbritannien um Schutz vor den sich ausbreitenden Buren (die weißen Buren siedelten seit 1652 in Südafrika, und waren seit 1806 in langen Zügen auf der Flucht vor dem sich ununterbrochen ausbreitenden Britischen Kolonialsystem → Burenrepubliken), Großbritannien errichet das Protektorat Basutoland 1871 · Basutoland wird der Britischen Kapkolonie angeschlossen 1884 · nach Aufständen wird Basutoland wieder aus der Britischen Kapkolonie ausgegliedert, und direkt der Verwaltung des Britischen Kolonialamts unterstellt 1958 · Verfassung 1960 · erste Parlamentswahlen 1964 · Südafrika erhebt Anspruch auf Basutoland für die Zeit nach dessen bevorstehender Unabhängigkeit 15.05.1964 · neue Verfassung, innere Selbstverwaltung 1965 · Parlamentswahlen 04.10.1966 · Unabhängigkeit als Königreich Lesotho 1967 · Verfassungsreform, die Rechte des Königs werden eingeschränkt 1970 · Verfassung außer Kraft, Parteienverbot, Errichtung einer Präsidialdiktatur 1974 · Aufstand 1980 · militärische Aktionen Südafrikas in Lesotho gegen den ANC 1986 · Militärputsch 1991 · Parteienverbot aufgehoben 1993 · Ende der Militärdiktatur, Parlamentswahlen, neue Verfassung 1998 · Parlamentswahlen, Massendemonstrationen, Putschversuch des Militärs, Einmarsch von Truppen aus Botswana und Südafrika 2001 · die Truppen aus Botswana und Südafrika ziehen wieder ab 2014 · Putschversuch des Militärs |
History: |
| 1820 ·
the Zulu-King Tshaka conquers South Africa, escape of the Bantu nations,
nascence of the Basuto-Kingdom in the mountains of South Africa 1868 · the Basuto-Kingdom begs United Kingdom for protection against the unfurling Boers (the white Boers settle since 1652 in South Africa, and have been in escape since 1806 in long trails from the continuous extending of the British colonial system → Boer Republics), United Kingdom establishs the Protectorate of Basuto Land 1871 · Basuto Land becomes incorporated to the British Cape Colony 1884 · after riotings Basuto Land becomes excorporated out of the British Cape Colony, and subordinated directly under the administration of the British Colonial Office 1958 · constitution 1960 · initial elections of parliament 1964 · South Africa claimes Basuto Land for the time after its upcoming independence 15th of may 1964 · new constitution, internal self government 1965 · elections of parliament 4th of October 1966 · independence as Kingdom of Lesotho 1967 · reform of constitution, the rights of the King become restricted 1970 · constitution out of force, interdiction of parties, establishment of a presidial dictatorship 1974 · uprising 1980 · military campaigns of South Africa in Lesotho against the ANC 1986 · military coup d'état 1991 · stop of the interdiction of parties 1993 · end of the military dictatorship, elections of parliament, new constitution 1998 · elections of parliament, mass demonstrations, attempt to putsch by the armed forces, invasion of troops from Botsuana and South Africa 2001 · withdrawal of the troops from Botswana and South Africa 2014 · military coup attempt |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97 |
|
Mit freundlicher Untersützung von: Kindly supported by: |
Werner Lein |