Honduras |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Honduras |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 2026, |
 |
seit/since 2022, |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
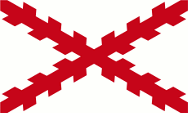 |
16. Jhd./cent. – 1785, zum spanischen Machtbereich – to the Spanish sphere of influence, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
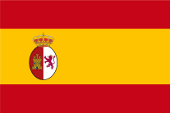 |
1785–1821, zum spanischen Machtbereich – to the Spanish sphere of influence, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1822–1823, Honduras gehört zu Mexiko – Honduras belongs to Mexico, Quelle/Source, nach/by: World Statesmen |
 |
1823–1824, Nationalflagge der Vereinigten Provinzen von Mittelamerika – national flag of the United Provinces of Central Amerika, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1824–1839, Nationalflagge der Zentralamerikanischen Konföderation – national flag of the Central American Confederation, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1839–1866, |
 |
1866–1949, |
 |
1949–2022, |
 |
2018, |
 |
2022–2026, |
 |
2022–2026, |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Honduras wurde 1823 Mitglied der Zentralamerikanischen Konföderation und übernahm deren blau-weiß-blau längsgestreifte Flagge. Auch nach dem Ende der Konföderation im Jahre 1838/1839 wurde in Honduras diese Flagge beibehalten. Erst im Jahre 1866 wurden fünf Sterne in der Mitte der Flagge angebracht, deren Spitzen auch schon mal nach unten zeigen konnten. Das Staatswappen auf der Marine- und Kriegsflagge wurde unterhalb durch fünf in einem Halbkreis angeordnete blaue Sterne ergänzt. Diese sollen, genau wie die Sterne in der im selben Jahr eingeführten Nationalflagge, an die fünf Staaten der Zentralamerikanischen Konföderation erinnern. Die Flagge in ihrer heutigen Form wurde am 18.01.1949 eingeführt, nachdem dass Format der Flagge in 2:1 geändert worden war. | Honduras became in the year 1823 a member of the Central American
Confederation and took over the blue-white-blue lengthwise striped flag.
Even after the end of the confederation in the year 1838/1839 this flag was
maintained in Honduras. In the year 1866 five stars were attached for the
first time in the middle of the flag, the tips of which could sometimes
point downwards. The coat of arms on the naval and war flag was added below by five in a semicircle arranged blue stars. Those should exactly like the stars in that in the same year introduced national flag remember the five states of the Central American Confederation. The flag in her today's form was introduced on the 18the of January in 1949, after the changing of the flag's ratio into 1:2. |
| Die Farbe der Flagge war nie exakt definiert, vorgegeben war ab 1866 "blau" (Gesetzesdekret Nr. 7 vom 16. Februar 1866) ab 1949 "türkis" (Gesetzesdekret Nr. 29 vom 26. Januar 1949). Das hat bis heute zur Folge, dass in der Praxis der blaue Farbton sehr unterschiedlich ausfallen kann, bis in zu Mittelblau und Dunkelblau. Das Dunkelblau wurde so auch offziell verwendet, besonders zwischen den 30er und 50er Jahren. Offenbar war der Blauton immer wieder Gegenstand von Diskussionen, gerade um dem Wortlaut des Gesetzes Nr. 29 gerecht zu werden. Im September 2018 wurde vorgeschlagen Maya-Blau zu verwenden (HEX: #73C2FB, RBG: 115|194|251, CMYK: 55|13|0|0, pt 2915 c). Die Nationale Autonome Universität von Honduras schlug im September 2020 ein Blau vor, HEX: #00BCE4 (RBG: 0|188|228, CMYK: 71|0|9|0, pt 306 c), was 2021 von der Regierung bestätigt wurde. Am 4. Januar 2022 führten die honduranischen Streitkräfte eine eigene Version des Blautons als "Gelbblau" (RBG: 85|180|176, CMYK: 66|4|35|1, pt 7472 c) ein, wohl wissend, dass damit dem Wortlaut des Gesetzes von 1949 als "Türkisblau" Genüge getan wird. |
The colour of the flag
was never exactly defined, but was specified as "blue" from 1866 (Decree-Law
No. 7 of 16th of February 1866) and "turquoise" from 1949 (Decree-Law No. 29
of 26th of January 1949). The consequence of this is that in practice the
shade of blue can be very different, up to medium blue and dark blue. Dark
blue was also used officially, especially between the 1930s and 1950s.
Apparently, the shade of blue has always been a subject of discussion,
precisely to comply with the wording of Decree-Law No. 29. In September 2018, it was proposed to use Maya blue (HEX: #73C2FB, RBG: 115|194|251, CMYK: 55|13|0|0, pt 2915 c). The National Autonomous University of Honduras proposed a blue in September 2020, HEX: #00BCE4 (RBG: 0|188|228, CMYK: 71|0|9|0, pt 306 c), which was confirmed by the government in 2021. On 4th January 2022, the Honduran Armed Forces introduced its own version of the shade of blue as "yellow blue" (RBG: 85|180|176, CMYK: 66|4|35|1, pt 7472 c), knowing that this would satisfy the wording of the 1949 law as "turquoise blue". |
| Vermutlich auf Grund der endlosen Diskussionen, Verwirrungen und Schwierigkeiten wurde unter einer neuen nationalkonservativen Regierung, die 2025 siegreich aus Wahlen hervorging, am ersten Tag ihrer Arbeit, dem 27. Januar 2026, die Nationalflagge wieder auf den Status des Jahres 2022 zurückgesetzt und auf Dunkelblau festgelegt. Ob das Militär, das die Flagge seit 2022 in Türkis verwendet, diesem Schritt gefolgt ist oder noch folgen wird, ist unbekannt. |
Presumably due to endless
discussions, confusion and difficulties, a new national conservative
government that emerged victorious from the 2025 elections restored the
national flag to its 2022 status on its first day in office, the 27th of
January in 2026, setting it back to dark blue. It is unknown whether the
military, which has been using the turquoise flag since 2022, has followed
or will follow this move. |
| Ebenso ist die Anordung der fünf Sterne nicht geregelt. Historisch überliefert ist seit 1866 die Anordung als Rechteck (nahezu Quadrat). Das Gesetzesdekret Nr. 29 vom 26. Januar 1949 sagt dazu aus: "Sie bilden mit vier von ihnen ein Rechteck parallel zu den Streifen, wobei der Rest in der Mitte desselben Vierecks platziert wird". Daraus wird jetzt aber abgeleitet, dass das Rechteck der Sterne die gleichen Seitenverhältnisse wie die Flagge haben soll, nämlich 1:2, was auf offziellen Darstellungen so übernommen wird. In der Praxis hat sich das nur teilweise durchgesetzt, es wird immer noch häufig die Form von 1866 verwendet. |
The arrangement of the
five stars is also not regulated. Historically, the arrangement as a
rectangle (almost square) has been handed down since 1866. The Decree-Law No. 29 of 26th of January 1949 states: "They form a rectangle with four of them parallel to the stripes, the rest being placed in the centre of the same quadrilateral". From this, however, it is now deduced that the rectangle of stars should have the same aspect ratios as the flag, namely 1:2, which is adopted as such on official depictions. In practice, this has only been partially implemented; the 1866 form is still frequently used. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Wikipedia (ES), Flags of the World, World Statesmen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
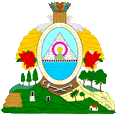 |
Wappen von Honduras – coat of arms of Honduras, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen, das nur sehr klein auf der Marineflagge zu sehen ist, zeigt eine dreieckige Pyramide in einem ovalen Schild. Sie soll Gleichheit und Freiheit symbolisieren. Zwei Türme links und rechts eines Vulkans stehen für Unabhängigkeit und Verteidigungsbereitschaft. Die Pfeile oberhalb des Schildes erinnern an die indianischen Bewohner des Landes. Die Füllhörner, die Minen und das Werkzeug stehen für die Naturreichtümer und die Bodenschätze des Landes. | The coat
of arms – which is only to see in a very small version on the
naval flag – showa a triangular pyramid in an oval shield. It should
symbolize equality and freedom. Two towers to the left and on the right of a
volcano stand for independence and readiness for defence. The arrows above
the shield remember the native Indian residents of the country. The
cornucopias, the mines and the tools stand for the natural wealth and the
mineral ressources of the country. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1502 ·
Kolumbus entdeckt die Küste von Honduras 1524 · Beginn der spanischen Eroberung und Kolonisierung durch Olid und Cortés 1535 · Errichtung des Vizekönigreiches Neuspanien, dem Mittelamerika (und damit auch das heutige Honduras) als "Generalkapitanat Guatemala" angeschlossen wird 15.09.1821 · Honduras erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit von Spanien 1822 · Honduras schließt sich dem Kaiserreich Mexiko an 1823 · nach dem Sturz des mexikanischen Kaisers wird die Verbindung zu Mexiko gelöst, und die Staaten des ehemaligen Generalkapitanats Guatemala verbinden sich zu den "Vereinigten Provinzen von Mittelamerika" (Zentralamerikanische Konföderation) 1838 · Honduras verlässt die Zentralamerikanische Konföderation 1838–1895 · Phase ständiger Putsche und Bürgerkriege 1860 · Der US-amerikanische Abenteurer und Pirat William Walker versucht in Honduras die Herrschaft an sich zu reißen, er wird von vereinten mittelamerikanischen Truppen gestellt und gefangen genommen und am 12.09.1860 in Trujillo hingerichtet 1895–1898 · Honduras bildet zusammen mit Nikaragua und El Salvador die Großrepublik Mittelamerika 1905 · USA-Militärintervention 1907 · Niederlage im Krieg gegen Nikaragua 1907 · USA-Militärintervention 1909–1911 · Bürgerkrieg 1911 · USA-Militärintervention 1913 · USA-Militärintervention 1924 · USA-Militärintervention, die USA besetzen die Swan-Inseln, die auch Islas del Cisne oder Islas Santanilla genannt werden, und errichten dort einen Militärstützpunkt 1963 · Militärputsch 1969 · 13 Tage dauernder „Fußballkrieg” zwischen Honduras und El Salvador 1971 · die USA treten die Swan-Inseln wieder an Honduras ab 1978 · Militärputsch 1980 · demokratische Reformen 1981 · erste Präsidentschaftswahlen, in der Folgezeit wechselnde Regierungen 1981 · Einrichtung des US-Militärstützpunkts Palmerola Air Base 2009 · Militärputsch, Wahlen, in der Folgezeit wechselnde Regierungen 2010 · Einrichtung des US-Marine-Militärstützpunkts Caratasca Lagune |
History: |
| 1502 ·
Columbus discovers the coast of Honduras 1524 · beginning of the Spanish capture and colonization by Olid and Cortés 1535 · establishment of the Vice Kingdom of New Spain, which Central America (and therewith even the today's Honduras) gets affiliated as "General Capitanate of Guatemala" 15th of September 1821 · Honduras declares its independence from Spain 1822 · Honduras joines the Empire of Mexico 1823 · after the overthrow of the Mexican emperor gets the connexion to Mexico untied, and the states of the former General Capitanate of Guatemala combine to the "United Provinces of Central America" (Central American Confederation) 1838 · Honduras leaves the Central American Confederation 1838–1895 · phase of permanent coups d'état and civil wars 1860 · the US-American adventurer and pirate William Walker trys to take over the rule in Honduras, he becomes stoped and arrested by united Central American troops, and executed on the 12th of September in 1860 in Trujillo 1895–1898 · Honduras constitutes together with Nicaragua and El Salvador the Great Republic of Central America 1905 · US-American military intervention 1907 · defeat in the war against Nicaragua 1907 · US-American military intervention 1909–1911 · civil war 1911 · US-American military intervention 1913 · US-American military intervention 1924 · US-American military intervention, the USA occupy the Swan Islands – also named Islas del Cisne or Islas Santanilla – and establish there a military base 1963 · military coup d'état 1969 · 13 days enduring „soccer war” between Honduras and El Salvador 1971 · the USA cede the Swan Islands back to Honduras 1978 · military coup d'état 1980 · democratic reforms 1981 · first presidency elections, changing governments in the period that followed 1981 · establishment of the US military base Palmerola Air Base 2009 · military coup, elections, changing governments in the period that followed 2010 · establishment of US military naval base Caratasca Lagoon |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Discovery '97, Wikipedia (D) |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name des Landes geht auf den spanischen Ausdruck "las honduras" zurück, was übersetzt "die Tiefen" bedeutet und sich auf das Tiefland im Nordosten des Landes bezieht. | The name of the country goes back to the Spanish term "Las Honduras", which translated means "the depths" what refers to the lowlands in the northeast of the country. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |