Schottland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Schottland |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, |
 |
seit/since 2017, |
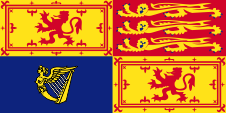 |
Flagge der britschen Königin für den Gebrauch in Schottland – Royal Standard for use in Scotland, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
 |
frühere Flagge des schottischen Königtums (Banner von Schottland), heute Flagge des Staatssekretärs für Schottland – former flag of the scottish kingdom (Banner of Scotland), today flag of the secretary of state for Scotland, Seitenverhältnis – ratio =
3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by: The Observers Book of Flags   |
| Die Nationalflagge Schottlands ist eine einfarbige blaue Flagge mit einem weißen Diagonalkreuz. Dies ist das Andreaskreuz. St. Andreas ist Schutzpatron und Nationalheiliger von Schottland. Die Flagge wird wird "Saltire" genannt. | The
national flag of Scotland is a single coloured blue flag with a white
diagonal cross. This is the St. Andrew's cross. St. Andrew (St. Andreas) is
the patron saint and national saint of Scotland. The flag is named
"Saltire". |
| Sie wurde zwischen 1286 und 1292 erstmals nachgewiesen, wobei sie wahrscheinlich noch viel älter ist. Es wird angenommen, dass die Flagge ursprünglich einmal in Schwarz und Weiß gehalten war, den keltischen Nationalfarben. | It is mentioned in records between 1286 and 1292, but is probably very much older. It is assumed that the flag’s colours were originally black and white, the Celtic national colors. |
| Der Farbton für das Blau der Schottischen Flagge ist nicht exakt definiert, nur soll das Blau heller sein als im Union Jack, wo das Blau mit Pantone 280 festgelegt ist. In der Praxis hat sich für das Blau in der Flagge Schottlans offenbar der Farbton Pantone 300 durchgesetzt. Das Verhältnis der Seiten ist ebenfalls nicht festgelegt, 3:5 hat sich aber bewährt. | The shade for the blue of the Scottish flag is not exactly defined, but the blue
has to be brighter than in the Union Jack, where the blue is fixed with Pantone 280. In practice, the shade Pantone 300 has apparently prevailed for the blue in the flag of Scotland. The ratio of the pages is also not fixed, 3: 5 has proven itself. |
| Eine weitere Flagge, die noch immer hoch im Ansehen steht, ist die rot-goldene Flagge des schottischen Königtums, die sich aus dem Wappen der schottischen Könige ableitet. Diese Flagge wird seit 1910 zweimal statt einmal in den Gevierten der Flagge der britischen Königin für den Gebrauch in Schottland verwendet. | Another flag, still highly regarded,
is the red-golden flag of the Scottish Kingdom, derived from the coat of
arms of the Scottish Kings. This flag is used twice
instead of once within the quarters of the flag of the Britisch Queen(King)
for use in Scotland since 1910. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen, Volker Preuß | |
| Wappen – Coat of arms: | |
 |
Wappen von Schottland – coat of arms of Scotland, Quelle/Source, nach/by: See page for author, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
|
|
|
| Das Wappenschild von Schottland ist einfarbig goldenen mit einem steigenden roten Löwen in der Mitte, innerhalb eines roten, liliengeschmückten Rahmens. Der Löwe geht auf Wilhelm der Löwe (1165-1214) zurück und der Lilienrand ist seit 1222 nachweisbar. Der liliengeschmückte Rahmen soll an die langjährige Allianz zwischen Schottland und Frankreich erinnern. |
The shield of Scotland is single coloured golden with a climbing red lion in the centre, within a red, lily-adorned frame. The lion has its roots in William the Lion (1143/1165–1214) and the lily-frame is mentioned in records since 1222. The lily-adorned frame reminds of the former long standing alliance between Scotland and France. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |
|
|
|
| Landkarte – Map: |
interaktive Landkarte – interactive Map: Quelle/Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ca. 400 v.Chr. · Einwanderung keltischer Stämme nach Schottland 85 · Britannien wird Provinz des Römischen Reiches 120–128 · Bau des römischen Hadrianswalls gegen Schottland 195 · der Hadrianswall wird überrannt ca. 420 · Besiedlung Schottlands durch die Scoten ca. 850 · Unterwerfung der bisher einheimischen Pikten durch die Scoten, Gründung des Königreichs Alba 9. Jhd. · Wikinger (Norweger) erobern den Norden Schottlands 1263 · Rückeroberung der norwegischen Gebiete (außer der Nordischen Inseln) in Schottland durch König Alexander III. 1296 · England besetzt große Teile Schottlands 1297 · Vertreibung der Engländer 1306 · Robert Bruce wird schottischer König 1314 · Schlacht von Bannockburn, Sieg der Schotten über die Engländer 1371 · Das Haus Stuart übernimmt das Königtum 1472 · die Nordischen Inseln kommen zu Schottland 1559–1568 · Reformation, Religionskrieg in Schottland 1568 · Flucht der katholischen schottischen Königin Maria Stuart in die Gefangenschaft nach England 1587 · Hinrichtung der Maria Stuart 1578 · James VI. (Jakob VI.) wird König von Schottland 1603 · James VI. (Jakob VI.) wird als James I. (Jakob I.) auch König von England 1707 · staatsrechtliche Vereinigung von England und Schottland zu Großbritannien 1745 · Prince Charles Edward Stuart (Bonnie Prince Charlie) landet aus Frankreich kommend in Schottland, Kämpfe gegen England 1746 · Schlacht von Culloden Moor, Charles flieht wieder nach Frankreich seit 1746 · teilweise rigorose Anglisierung Schottlands 1997 · Volksabstimmung über ein eigenes schottisches Regionalparlament 01.07.1999 · das Regionalparlament beginnt seine Arbeit 2014 · Referendum zum Austritt aus dem Vereinigten Königreich: 55 % Ablehnung |
|
ca. 400 B.C. · immigration of Celtic tribes toward Scotland 85 · Britain becomes a province of the Roman Empire 120–128 · construction of the Roman Hadrian's Wall against Scotland 195 · the Hadrian's Wall is overrun ca. 420 · colonization of Scotlands by the Scots ca. 850 · subjection of the native Pikts by the Scots, establishment of the Kingdom of Alba 9th century · Vikings (Norwegian) capture the north of Scotland 1263 · re-capture of the Norwegian territories (except the Nordic Islands) in Scotland by King Alexander III. 1296 · England occupies large parts of Scotland 1297 · expulsion of the English 1306 · Robert Bruce becomes King of Scotland 1314 · Battle of Bannockburn, victory of the Scots over the English 1371 · the House Stuart becomes rulers of the Scottish Kingdom 1472 · the Nordic Islands come to Scotland 1559–1568 · Reformation, religious war in Scotland 1568 · escape of the Catholic Scottish Queen Mary Stuart from Scotland and subsequent imprisonment in England 1587 · execution of the Mary Stuart 1578 · James VI. (Jacob VI.) becomes King of Scotland 1603 · James VI. (Jacob VI.) becomes also King of England as James I. (Jakob I.) 1707 · constitutional unification of England and Scotland into United Kingdom 1745 · Prince Charles Edward Stuart (Bonnie Prince Charlie) coming from France, lands in Scotland, battles against England 1746 · Battle of Culloden Moor, Charles escapes to France since 1746 · partially rigorous anglicizing of Scotland 1997 · successful plebiscite for an independent Scottish regional parliament 1st of July in 1999 · the regional parliament begins its work 2014 · referendum for an exit from the United Kingdom: 55% rejection |
| Translator of the English text: Joachim Nuthack |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Wikipedia (DE) |
| Der Landesname leitet sich von "Scoti", die lateinische Bezeichnung für die keltischen Gälen, was wahrscheinlich auf das griechische Wort "skotos" zurückgeht und "dunkel" heißt. Der Landesname "Scotia" wurde ursprünglich für die Insel Irland verwendet, ab dem 11. Jahrhundert wurde damit die Gegend nördlich des Flusses Forth bezeichnet. Gebräuchlich waren auch Alba, Albania oder Albany, die auf den gälischen Landesnamen zurückgehen. | The country's name derives from "Scoti", the Latin name for the Celtic Gaels, which probably goes back to the Greek word "skotos" meaning "dark".
The country name "Scotia" was originally used for the island of Ireland, from the 11th century it was used to describe the area north of the River Forth. Also in use were Alba, Albania or Albany, which go back to the Gaelic country's name. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |