Gambia |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Gambia |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag,    |
 |
seit/since 1970, |
 |
Flagge für Botschafter |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
| Britisch Westafrika, West Africa Settlements: | |
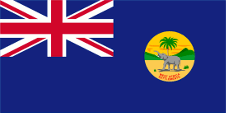 |
1869–1888, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Kolonie Gambia, The Colony of the Gambia: | |
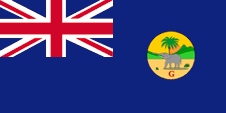 |
1888–1965, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE), Flags of the World |
| Als Gambia am 18.02.1965 unabhängig geworden ist, wurde die heutige Flagge Gambias erstmalig gehisst. Sie zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Blau und Grün. Diese werden durch schmale weiße Streifen voneinander getrennt. Das Verhältnis der Streifenbreite ist 6:1:4:1:6. Die Farbe Rot verkörpert die Sonne, Blau repräsentiert den Fluss Gambia, Grün symbolisiert die Landwirtschaft und den Reichtum des Landes, und das Weiß steht für den Frieden. |
As Gambia reached his independence on 18th of february in 1965, the today's
flag was hoisted up for the first time. It shows three horizontal stripes in
red, blue and green. Those are separated among themselves by narrow white
stripes. The stripe width ratio is 6:1:4:1:6. The color Red embodys the sun,
blue represents the river Gambia and green symbolizes the agriculture and
the richness of the land, and the white stands for the peace. |
| Vor der Unabhängigkeit wurde in Gambia die blaue, britische Dienstflagge (Blue Ensign) mit einem Emblem im wehenden Teil benutzt. | Previous to the independence in Gambia was in use the blue, British official flag (Blue Ensign) with an emblem in the flying part. |
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. |
Great
Britain introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag.The governments were asked to design appropriate badges. |
| Das 1869 eingeführte Emblem (Badge) zeigte einen Elefanten mit drohender Gebärde vor einer Palme inmitten einer afrikanischen Landschaft. Unten auf dem Badge war die Inschrift "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in Rot zu sehen. | The in 1889 introduced emblem (badge) showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge was to see the inscription "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in red. |
| Im Jahre 1888 wurde Gambia eine eigenständige britische Kronkolonie und es wurde ein neues Badge eingeführt. Dazu wurde legilich die Inschrift auf dem alten Badge abgeändert. Anstelle "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." erschien nun ein "G". Dieses Badge wurde bis zur Unabhängigkeit im Jahre 1965 verwendet. |
In 1888 The Gambia became
an own British Crown Colony and a new badge was introduced. For this purpose, only the inscription on the old badge was changed. Instead of "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." now a "G" appeared. This badge was used until independence in 1965. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen, Volker Preuß | |
| Wappen – Coat of arms: | |
 |
Das Wappen von Gambia – coat of arms of Gambia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1869–1888, Badge der West Africa Settlements – Badge of the West Africa Settlements, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
 |
1888–1965, Badge der Colony of the Gambia – Badge of the Colony of the Gambia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Das heutige Staatswappen wurde Gambia am 18.11.1964 von Königin Elisabeth II. verliehen. Damit trat anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit des Landes das im Jahre 1889 verliehene Badge außer Kaft. Das Wappen zeigt eine Axt und eine Hacke auf einem blauen, weiß und grün umrandeten Schild. Oberhalb des Schildes ein Helm mit blau-gelben Decken und einer Palmenpflanze. Als Schildhalter dienen zwei Löwen, jeweils mit Axt und Hacke. Sie stehen für Stolz und Würde. Unterhalb des Schildes ein Spruchband mit dem Staatsmotto: "Progress, Peace, Prosperity" → "Fortschritt, Frieden, Wohlstand". Axt, Hacke und Palme deuten auf die landwirtschaftlichen Strukturen in Gambia hin. Die beiden Löwen gehen auf die Kolonialmacht Großbritannien zurück. |
The today's coat of arms was awarded to Gambia on 18th of november in 1964
by the queen Elisabeth II. The badge awarded in 1889 was thus invalidated
on the occasion of the country's independence. The coat of arms shows an axe and a hoe on a blue, white and green bordered shield. Above the shield a helmet with blue-yellow blankets and a palm plant. As shield holders serve two lions, each with axe and hoe. They stand for pride and dignity. Below the shield a motto ribbon with the motto of the state: "Progress, Peace, Prosperity". Axe, hoe and palm tree refer to the agricultural structures in Gambia. The both lions remember United Kingdom, the colonial power. |
|
Seit 1865 durften Kolonialregierungen ein Badge (Abzeichen) verwenden. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. |
Colonial
governments have been allowed to use a badge since 1865. |
| Das 1869 eingeführte Emblem (Badge) zeigte einen Elefanten mit drohender Gebärde vor einer Palme inmitten einer afrikanischen Landschaft. Unten auf dem Badge war die Inschrift "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in Rot zu sehen. | The in 1889 introduced emblem (badge) showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge was to see the inscription "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in red. |
| Im Jahre 1888 wurde Gambia eine eigenständige britische Kronkolonie und es wurde ein neues Badge eingeführt. Dazu wurde legilich die Inschrift auf dem alten Badge abgeändert. Anstelle "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." erschien nun ein "G". Dieses Badge wurde bis zur Unabhängigkeit im Jahre 1965 verwendet. |
In 1888 The Gambia became
an own British Crown Colony and a new badge was introduced. For this purpose, only the inscription on the old badge was changed. Instead of "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." now a "G" appeared. This badge was used until independence in 1965. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE), Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen | |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
interaktive Landkarte der Region – interactive Map of the Region: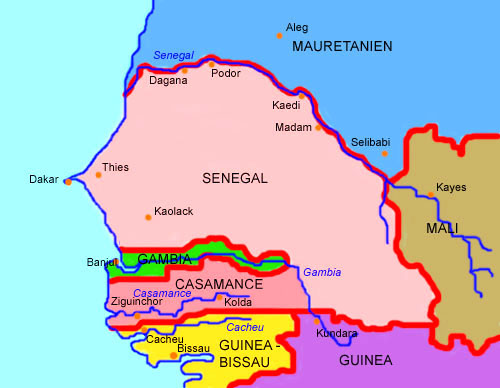 Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ca. 470
v.Chr. · der Seefahrer Hanno aus Karthago besucht die Region 1455 · Portugiesen entdecken die Mündung des Flusses Gambia, die Region selbst gehört zum Mali-Reich 1588 · Beginn der englischen Kolonisierung, in der Folge Konflikte mit Frankreich, welches das Gebiet beansprucht 1661 · England kauft James Island und errichtet den Handelsposten Fort James 1681 · Frankreich gründet den Handelsposten Albreda 1651–1658 · das Herzogtum Kurland betreibt auf der Jakobsinsel (James Island) einen Handelsposten 1783 · Pariser Frieden, Senegambien wird zwischen Frankreich und Großbritannien aufgeteilt, Frankreich erhält Senegal, Großbritannien erhält Gambia, das später Britisch-Westafrika angegliedert wird 1816 · Großbritannien kauft die Insel St. Mary’s Island gründet dort die Siedlung Bathurst (ab 1973 Banjul) 1857 · Frankreich tritt Albreda an Großbritannien ab 1888 · Gambia wird eine eigenständige britische Kronkolonie 1963 · Gewährung innerer Autonomie 18.02.1965 · Unabhängigkeit 24.04.1970 · Proklamation der Republik, Gambia bleibt jedoch im Commonwealth of Nations 1981 · Niederschlagung eines linken Armeeputsches, auch mit Hilfe senegalesischer Truppen 1982–1989 · Senegal und Gambia sind in der Konföderation Senegambia verbunden (gemeinsame Militär- Wirtschafts- und Finanzpolitik) 1994 · Putsch 2013 · Gambia erklärt den Austritt aus dem Commonwealth 2015 · Gambia wird zur "Islamischen Republik" deklariert 2017 · das Land wird wieder in "Republik Gambia" umbenannt 2018 · Gambia wird nach einem Beitrittsgesuch wieder in den Commonwealth aufgenommen |
| ca. 470 B.C. ·
the seafarer Hanno from Carthage visits the region 1455 · Portugese discover the mouth of the river Gambia, the region itself belongs to the Mali Empire 1588 · beginning of the English colonization, in result conflicts with France, which even claims the region 1661 · England acquires James Island and establishes Fort James trading post 1681 · France establishes the trading post of Albreda 1651–1658 · the Duchy of Courland operates a trading post on James Island 1783 · Paris Peace Treaty, Senegambia is divided between France and United Kingdom, France is given to Senegal, Gambia comes to United Kingdom and becomes later affiliated to British West Africa 1816 · United Kingdom acquires St. Mary’s Island and founds the settlement of Bathurst (from 1973 Banjul) 1857 · France cedes Albreda to United Kingdom 1888 · Gambia becomes a separate British crown colony 1963 · granting of inner autonomy 18th of February in 1965 · independence 24th of April in 1970 · proclamation of the republic, Gambia however stays in the Commonwealth of Nations 1981 · suppress of a left wingers army revolt, even with help by Senegalese troops 1982–1989 · Senegal and Gambia are connected in the Senegambia Confederation (joint military, economic and financial policy) 1994 · coup d'etat 2013 · The Gambia declares the withdrawal from the Commonwealth 2015 · Gambia is declared an "Islamic Republic" 2017 · the country is renamed back in "Republic of The Gambia" 2018 · The Gambia is admitted back to the Commonwealth after applying for membership |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Wikipedia (EN), Atlas zur Geschichte |
| Der Name des Landes wird mit dem Gambia-Fluss in Verbindung gebracht, jedoch ist die Herkunft dieses Namens umstritten. | The name of the country is associated with the Gambia River, but the origin of that name is controversial. |
| 1. These: Der Name geht auf die Sprache der Mandingo zurück und bedeutet: "Das Land ist der Fluss". |
Thesis 1: The name goes back to the Mandingo language and means "The land is the river". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |
| 2. These: Der Name geht auf die Sprache der Mandingo zurück und bedeutet: "Fluss Kaabu" oder "Land Kaabu". Kaabu war das Mandingo-Reich, das vom 16. bis zum 19. Jahrhundert existierte. | Thesis 2: The name goes back to the language of the Mandingo and means "Kaabu River" or "Kaabu Country". Kaabu was the Mandingo Empire, which existed from the 16th to the 19th century. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |
| 3. These: Der Name geht auf einen Übersetzungsfehler zurück, der im 16. Jahrhundert auf James Island gemacht wurde. Der Dolmetscher sagte auf eine Frage von Portugiesischen Seefahrern nicht den Namen des Landes, sondern seinen eigenen Namen: "Kambi". Und so wurde aus James Island "Kambi-yaa", was "Kambis Stelle" heißt, und sich auf den Fluss und das Land übertragen hat. | Thesis 3:
The name goes back to a translation error made in the 16th century on James
Island. The interpreter did not say the name of the country to a question
of Portuguese seafarers, but he told his own name: "Kambi". And so became
James Island "Kambi-yaa", what means "Kambis place", and that has been
transferred to the river and to the land. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |
| 4. These: Der Name geht auf das portugiesische Wort "câmbio" zurück, was "Austausch" oder auch "Handel" heißt. | Thesis 4: The name goes back to the Portuguese word "câmbio", what means "exchange" or "trade". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |