Dschibuti |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Dschibuti |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
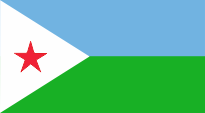 |
Nationalflagge –
national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 21:38, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since ca. 1620, Flagge Sultanat Tadjourah – flag of the Sultanate of Tadjourah, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen |
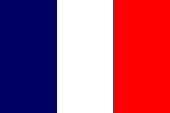 |
1862–1977, Flagge Frankreichs – flag of France, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1979, Flagge der LPAI – flag of LPAI party, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikimedia, By Jolle (Own work) [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
Flagge der Afar –
flag of the Afar, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (FR) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge von Dschibuti wurde am 27.06.1977 eingeführt. Sie zeigt zwei waagerechte Bahnen in Hellblau und Grün mit einem gleichschenkligem weißen Dreieck am Mast. In der Mitte des Dreiecks befindet sich ein fünfzackiger roter Stern. Blau ist die Farbe der ethnischen Gruppe der lssa und steht außerdem für Himmel und Meer. Grün symbolisiert die ethnischen Gruppe der Afar und den Islam. Weiß steht für den Frieden. Der rote Stern verkörpert den Kampf zur Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit aber auch die Einheit des Landes. Das weiße Dreieck mit den gleich langen Seiten repräsentiert das Landesmotto "Einheit, Gleichheit, Frieden". Die Flagge ist ihrem Ursprung nach die Flagge der LPAI-Partei. Als Farben für die Flagge von Djibouti werden angegeben: Blau = pt 292, Grün = pt 361, Rot = pt 032. | The flag of Djibouti
was introduced on 27th of June in 1977. It shows two horizontal stripes in pale blue and
green with an isosceles white triangle on the pole. In the middle of the triangle is
placed a five-pointed red star. Blue is the color of the ethnic group of lssa and stands moreover for heaven and sea. Green symbolizes the ethnic group of Afar and the Islam. White stands for the peace. The red star embodys the fight for the achievement of independence but the unity of the country too. The white triangle with the same long sides represents the motto of the land "unity, equality, peace". The flag is descends from the LPAI party-flag. The colours, are given for the flag of Djibouti: blue = pt 292, green = pt 361, red = pt 032. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Dschibuti – coat of arms of Djibouti Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
Wappen von Dschibuti – coat of arms of Djibouti Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Flaggen und Wappen |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen von Dschibuti wurde zeitgleich mit der Flagge eingeführt. Es zeigt zwei Arme (Afar und Issa) mit je einem Haumesser, zwischen ihnen eine Lanze und ein Rundschild (Verteidigungsbereitschaft). Darüber der rote Stern. Das Ganze ist umgeben von einem Kranz von Lorbeerblättern. Dieser steht für Einheit und Sieg Es gibt zwei Versionen des Wappens. Eine vollfarbige Variante und eine eher stilisierte Variante in Weiß und Gold. | The coat of arms of Djibouti was introduced at the time like the flag. It shows two arms (Afar and Issa) with ever one cutlass, between them a lance and a round shield. (defense readiness). Above that the red star. The whole is surrounded by a garland of laurel leafs. This stands for unity and victory. There are two versions of the coat of arms. A full coloured version and a more stylized version in white and gold. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Das Horn von Afrika, Stand Ende 2012, interaktive Landkarte |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 4.–10.
Jhd. · die Region des heutigen Dschibuti gehört zum christlichen Aksumitischen
Reich 10.–17. Jhd. · die Region des heutigen Dschibuti gehört zum islamischern Reich Adal 17.–19. Jhd. · Herrschaften lokaler arabischer Sultane (Sultanate Tadjourah, Gobat und Rahaita) 1862 · französische Erwerbung von Obock 1884 · Gründung des französischen "Protektorats von Obock, Tadjourah der Danakil und Somali" 1888 · Großbritannien erkennt das französische Protektorat an 1888 · Gründung von Dschibuti-Stadt durch die Franzosen 1892 · Dschibuti wird Hauptstadt 1896 · Bildung der Kolonie Französisch-Somaliland 1942 · im Zweiten Weltkrieg besetzen britische Truppen das Land (bis 1946) 1946 · Französisch-Somaliland wird zum Überseeterritorium erklärt 1956 · Frankreich gewährt eingeschränkte Autonomie 1958 · eine Volksabstimmung erwirkt den Verbleib bei Frankreich 1967 · Umbenennung in Französisches Territorium der Afar und Issa 1972 · Frankreich gewährt erweiterte Autonomie 27.06.1977 · Unabhängigkeit 1981 · Einführung des Einparteiensystems 1991–1994 · Kämpfe zwischen den Afar und Issa 1992 · Einführung des Mehrparteiensystems 2008 · Kämpfe mit Etritrea 2016 · China pachtet bei Dorale einen Stützpunkt als Marine-Außenposten |
History: |
| 4th to 10th
century · the region of today's Djibouti, belongs to the Christian Kingdom of
Aksum 10th to 17th century · the region of today's Djibouti belongs to the Islamic Kingdom of Adal 17th to 19th century · reign of local Arab sultans (Sultanates of Tadjourah, Gobat and Rahaita) 1862 · French acquisition of Obock 1884 · founding of the French "Protectorate of Obock, Tadjourah the Danakil and Somali" 1888 · United Kingdom recognizes the French protectorate 1888 · foundation of Djibouti City by the French 1892 · Djibouti becomes the capital 1896 · establish of the Colony of French Somaliland 1942 · during the Second World War, British troops occupy the country (until 1946) 1946 · French Somaliland is declared as overseas territory 1956 · France grants limited autonomy 1958 · a referendum soughts to remain with France 1967 · renamed in French Territory of the Afar and Issa 1972 · France grants extended autonomy 27th of June in 1977 · independence 1981 · introduction of one-party system 1991–1994 · struggles between the Afar and Issa 1992 · introduction of multiparty system 2008 · struggles with Etritrea 2016 · China leases a base at Dorale as a naval outpost |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Das Land hat seinen Namen von seiner im Jahre 1888 von den Franzosen gegründeten Hauptstadt. "Dschibuti" heißt übersetzt "heißer Topf". Die Bezeichnung bezieht sich auf die dortigen klimatischen Verhältnisse. | The country took its
name from its by the French in 1888 established capital. "Djibouti" means
"hot pot". The term points out to the local climatic conditions. |
| Quelle/Source: www.fdp-koeln.de, ca.2010, Wikipedia (D) | |