Deutsche Demokratische Republik |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Deutsche Demokratische Republik |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
1959–1989, Staatsflagge und Gösch – state flag and jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flaggen und Wappen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1959–1973, Handelsflagge – merchant flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Die Welt der Flaggen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1949–1959, 1989–1990, Staatsflagge – state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1960–1989, Standarte des Staatsratsvorsitzenden – standard of the Chairman of the State Counsel, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flaggen und Wappen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1989, Flagge des Vorsitzenden des nationalen Verteidigungsrates – flag of the Chairman of the National Defense Board, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1959–1989, Dienstflagge der Armee (Kriegsflagge) – official flag of the army (war flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1989, Dienstflagge der Marine (Marineflagge) – official flag of the navy (naval flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flaggen und Wappen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1989, Flagge der Hilfsschiffe – flag for aux ships, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flaggen und Wappen, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1989, Dienstflagge der Grenztruppen – official flag of the border patrol, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
bis/to 1989, Marineflagge der Grenztruppen – naval flag of the border patrol, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
seit/since 1934, Stadtflagge Groß-Berlins in Ost-Berlin nur bis 1956 verwendet – flag of Great Berlin in East Berlin used only until 1956 Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4, Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
 |
seit/since 1934, Dienstflagge Groß-Berlins, in Ost-Berlin ab 1956 Stadtflagge – official flag of Great Berlin, flag of East Berlin since 1956 Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
 |
1960–1968, Olympia-Flagge – Olympia flag, (Info ↑ klicken/click ↑) Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1955–1973, Postflagge – postal flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: nach/by: Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
|
|
|
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Postflaggen". |
 |
read here: Informations, history and facts about the theme "Postal flags". |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die spätere Flagge der DDR wurde in der Sowjetischen Besatzungszone bereits am 18.05.1948 angenommen. Sie zeigte damals nur drei horizontale Streifen in Schwarz, Rot und Gold, also ohne Wappen. Sie sollte für das ganze Deutschland stehen und eine Neuauflage der deutschen Flagge von 1848 und 1919 sein. | The later
flag of the GDR was already adoped in the Soviet Occupation Zone on 18th of
May in 1948. It showed then only three horizontal stripes in black, red and
gold, so without a coat of arms. It should stand for the whole Germany and be a renewal of the german flag from 1848 and 1919. |
| In der Verfassung der DDR vom 07.10.1949 heißt es dazu in Artikel 2: "Die Farben der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik sind Schwarz-Rot-Gold." | In the constitution of the GDR from the 7th of Oct. in 1949 is written about that in article 2: "The colors of the German Democratic Rep. are Black, Red, Gold." |
| In der Westlichen Besatzungszone wurde die gleiche Flagge am 23.05.1949 offiziell eingeführt. Auch sie sollte sollte für das ganze Deutschland stehen und eine Neuauflage der deutschen Flagge von 1848 und 1919 sein. Bei der Gründung der BRD wurde sie am 07.09.1949 als Flagge der BRD übernommen. | In the Western Occupation Zone the same flag was officially introduced on the 23rd of May in 1949. It should as well stand for the whole Germany and be a renewal of the german flag from 1848 and 1919. At the foundation of the FRG it became took over on the 7th of September in 1949 as flag of the FRG. |
| Nach der Gründung der DDR am 07.10.1949 wurde die in der Sowjetischen Besatzungszone am 18.05.1948 angenommene Flagge ebenfalls beibehalten, so dass die DDR in der Sowjetischen Besatzungszone die gleiche Flagge hatte wie die BRD in der Westlichen Besatzungszone. | After the foundation of the GDR on the 7th of October in 1949 was the in the Soviet Occupation Zone on 18th of May in 1948 adoped flag likewise maintained. In this way the GDR in the Soviet Occupation Zone had the same flag like the FRG in the Western Occupation Zone. |
| Mit der sich abzeichnenden endgültigen Trennung der beiden deutschen Staaten musste eine besser unterscheidbare Symbolik geschaffen werden. Darum wurde am 12.01.1950 ein Emblem für die DDR eingeführt. Per Gesetz vom 01.10.1959 wurde das Emblem in der Mitte der Flagge eingefügt. | With the looming ultimate separation of the both german states must have been created a better differentiatable symbolism. Because of this was introduced on 12th of January in 1950 an emblem of the GDR. Per law of the 1st of October in 1959 the emblem was placed in the middle of the flag. |
| Von 1959 bis 1973 hatte die DDR auch eine eigene Handelsflagge. Diese führte das Wappen in der Oberecke. Mehr als einmal war die Flagge aber "rein zufällig vom Seewind" mehrmals um die Flaggenleine gewickelt worden, das Emblem der DDR war nicht mehr zu erkennen, und die Flagge war nicht mehr von der der Bundesrepublik Deutschland zu unterscheiden. Das gefiel einigen Herren überhaupt nicht .... Die Flaggen der DDR wurden mit der Wiedervereinigung Deutschlands am 03.10.1990 abgeschafft. | From 1959 to 1973 the GDR had her own merchant flag. It had the coat of arms of the GDR in the upper canton. But more than once the flag was "only accidental by the Sea-Winds" several times swaddled around the flag-cord, the emblem of the GDR was not to recognize, and the flag was not to differentiate from the flag of the Federal Republic of Germany. Some Misters did not like this .... The flags of the GDR were abolished with the reunification of Germany on the 3rd of october in 1990. |
| Zwischen
1956 und 1964 hatten die DDR und die BRD eine gemeinsame Olympia-
Mannschaft, und zwischen 1960 und 1968 auch eine gemeinsame Olympia-Flagge.
In Sydney (1956) marschierte die gemeinsame Olympia-Mannschaft noch unter
der schwarz-rot-goldenen Flagge ein. In Rom (1960) und in Tokio (1964) wurde die schwarz-rot-goldenen Flagge mit weißen olympischen Ringen in der Mitte verwendet. In Mexiko-Stadt (1968) gab es dann schon zwei getrennte deutsche Mannschaften, die getrennt ins Olympia-Stadion einmarschierten, aber jeder der beiden Mannschaft marschierte unter der schwarz-rot-goldenen Flagge mit den weißen, olympischen Ringen in der Mitte in das Stadion ein. |
Between
1956 and 1964, the GDR and the FRG had a joint Olympic team, and between
1960 and 1968 even a joint Olympic flag. In Sydney (1956) the joint Olympic
team marched in, still under the black-red-golden flag. In Rome (1960) and Tokyo (1964), the black-red-golden flag was used with white Olympic rings in the middle. In Mexico City (1968)
there were already two separate German teams who marched separately into the
Olympic Stadium, but each of the two teams marched in under the
black-red-golden flag with the white Olympic rings in the middle. |
| Eine Sonderform der Flaggen sind die Banner, langestreckte Fahnen, die häufig an einem schmalen Querstab hängend aufgezogen oder befestigt werden. Informationen zu deutschen Bannern und Bannerflaggen <= hier klicken |
A special form of flags are the banners, long-stretched flags, which are
frequently fixed on a narrow crossbar. Informations about German banners and banner flags <= click here |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Jürgen Kaltschmitt | |
|
|
|
Standarte des Präsidenten – Standard of the president: |
|
 |
1949-1950, Standarte des Präsidenten – standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:8, Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1950-1951, Standarte des Präsidenten – standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:8, (Rekonstruktion – reconstruction) Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1951-1953, Standarte des Präsidenten – standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, (Rekonstruktion – reconstruction) Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1953-1955, Standarte des Präsidenten – standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, (Rekonstruktion – reconstruction) Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1955-1960, Standarte des Präsidenten – standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Standarte – Meaning/Origin of the Standard: |
|
| Die DDR hatte auch eine Standarte des Präsidenten. Zunächst, ab 1949, eine goldumrandete schwarz-rot-goldene Flagge mit den Inschriften "Präsident" und "DDR", deren Schriftart 1950 geändert wurde. Das Original der ersten Standarte befindet sich heute im Deutschen Historischen Museum in Berlin. 1951 wurde eine quadratische dreistreifige Flagge in schwarz-rot-gold eingeführt, die das Emblem der DDR in der Mitte zeigte. 1953 wurde das Emblem gewechselt. 1955 wurde eine einfarbig rote Standarte mit schwarz-rot-goldener Umrandung eingeführt, die bis zum Tode des Präsidenten Wilhelm Pieck im Jahre 1960 beibehalten wurde. Danach wurde das Amt des Präsidenten als Staatsoberhaupt abgeschafft, und durch das Amt des Vorsitzenden des Staatsrates ersetzt, der eine ähnliche Standarte verwendete. | The GDR
had a standard of the president, too. First, since 1949, it was a golden
bordered black-red-golden flag with the inscriptions "President" and "DDR"
whose font was changed in 1950. The original of the first standard is now to see in the German Historical Museum in Berlin. In 1951 was introduced a square flag with three stripes in black, red and gold, and in the middle was placed the emblem of the GDR. In 1953, the emblem was changed. In 1955 was introduced a single coloured red standard with a black, red and golded border, which was maintained until the death of president Wilhelm Pieck in 1960. Thereafter, the presidency as head of state was abolished, and became replaced by the chairman of the state council, who used a similar standard. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), Jürgen Kaltschmitt | |
|
|
|
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
erster Entwurf zum Wappen Wappen der DDR – first draft for the coat of arms of GDR, Quelle/Source: Iris Benner: Wettlauf um das Adlerwappen. In: museumsmagazin, H. 3/2008, Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
 |
1950-1953, Emblem der DDR – emblem of GDR, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia, Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
 |
1953-1955, Emblem der DDR – emblem of GDR, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia, Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1955-1990, Emblem der DDR – emblem of GDR, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia, Corel Draw 4 |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das erste
Emblem der DDR wurde am 12.01.1950 eingeführt. Es zeigte einen Hammer,
umgeben von Weizenähren. Noch 1951 wurde der vorläufige Charakter dieses
Symbols betont, der Begriff "Emblem" verwendet, und die Bezeichnung "Wappen"
vermieden. Es gab vorher Pläne der deutschen Tradition zu folgen, und einen Adler "der nach Osten blickt" als Staatssymbol einzuführen. Mit der Gründung der BRD entfiel dieser Vorschlag. |
The first
emblem of the GDR was introduced on 12th of January in 1950. It showed an
hammer, surrounded by wheat ears. Yet in 1951 the provisional nature of this
symbol was emphasized, designated as "emblem", and the term "coat of arms"
was officially avoided. In the times before, there were plans to follow the
German tradition and to introduce an eagle "looking to the east" as symbol
of the state. With the establishment of the FRG, this idea disappeared.
|
| Am 28.05.1953 wurde ein neues Emblem - bestehend aus Hammer, Zirkel und Ährenkranz - eingeführt. Die Symbolik stand für die Einheit derer, die in Industrie (Hammer), Wissenschaft (Zirkel) und Landwirtschaft (Ährenkranz) tätig sind. Am 26.09.1955 wurde noch ein roter Hintergrund ergänzt, und das Emblem in dieser Form bis zum Ende des Staates DDR beibehalten. Es wurde lediglich ab dem 31.05.1990 weitgehend aus der Öffentlichkeit verbannt. | On 28th
of May in 1953 was introduced a new emblem - consiting in hammer, circles
and ear wreath. The symbols stood for the unity of those who work in
industry (hammer), science (circles) and agriculture (ear wreath). On 26th
of September in 1955 a red background was added. The emblem was maintained
in this form until the end of the GDR. It has only been merely banished from
the public from the 31st of May in 1990. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen | |
|
|
|
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
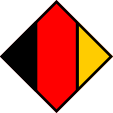 |
bis/to 1959, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Jürgen Kaltschmitt |
 |
1959–1990, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
|
|
|
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
08.05.1945
· Kapitulation der Deutschen Wehrmacht, russische Besetzung
Mitteldeutschlands, Ostdeutschland wird polnischer Verwaltung unterstellt 11.06.1945 · Kommunisten ergreifen unter sowjetischem Schutz die politische Initiative 1945–1949 · Einzelmaßnahmen zur Vorbereitung einer kommunistischen Machtergreifung 07.10.1949 · Gründung der DDR, kommunistische Machtergreifung auf sowjetische Initiative 06.07.1950 · DDR erkennt die dauerhafte polnische Besetzung Ostdeutschlands an 16.–17.06.1953 · Arbeiteraufstand gegen kommunistische Zwangsmaßnahmen 13.08.1961 · Bau der "Berliner Mauer" Sommer 1989 · Ausreise- und Fluchtwelle Herbst 1989 · Massendemonstrationen, zunächst für Demokratisierung, später für die Wiedervereinigung Deutschlands 09.11.1989 · Fall der "Berliner Mauer" 01.07.1990 · Währungs-, Wirtschafts- und Sozialunion mit der BRD 03.10.1990 · Anschluss der DDR an die BRD |
|
|
History: |
|
8th of May 1945
· capitulation of the German war-might, Russian occupation of middle
Germany, eastern Germany gets subordinated under Polish administration 11th of June 1945 · communists take the political initiative under Soviet protection 1945–1949 · single measures in preparation of a communist seizure of power 7th of October 1949 · foundation of the GDR, communist seizure of power in Soviet initiative 6th of July 1950 · GDR recognizes the enduring Polish occupation of eastern Germany 16th–17th of June 1953 · worker's revolt against communist forceed measures 13th of August 1961 · build of the "Berlin Wall" Summer 1989 · wave of exit and escape Autumn 1989 · mass demonstrations, initially for democratization, later for the reunification of Germany 9th of November 1989 · fall of the "Berlin Wall" 1st of July 1990 · currency-, economy - und social-union with the FRG 3rd of October 1990 · annexation of the GDR to FRG |
| Autor/author: Volker Preuß |
|
|
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Deutsche Demokratische Republik", war sehr widersprüchlich. Es wurde zwar Deutsch gesprochen, aber deutsch war dieser Staat nicht. Er war nicht souverän und stand unter der Kuratel der Sowjetunion. Demokratisch war dieser Staat auch nicht, denn es war eine Diktatur, so dass selbst die Bezeichung "Republik" nicht zutreffen kann. In der Praxis hat man das Wortungetüm gerne zu "DDR" verkürzt, auch "Mitteldeutschland, oder "Ostdeutschland", oder "Sowjetzone" waren gebräuchlich. | The name
"German Democratic Republic", was very contradictory. Here was indeed spoken
German, but that state was not German. It was not sovereign and existed
under the tutelage of the Soviet Union. This state was also not democratic,
because it was a dictatorship, so that even the designation "republic" does
not apply. In practice the word monster became oftenly shortened to "GDR"
("DDR"), further had been common "Central Germany, or" East Germany ", or
"Soviet Zone". |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |
|
|
|