Burma |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Burma |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 2010, National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national, state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World |
 |
seit/since 2010 (?), Flagge der Streitkräfte – flag of the armed forces, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
seit/since 2010 (?), Flagge der Streitkräfte – flag of the armed forces, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
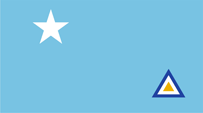
seit/since 2010, Seekriegsflagge – naval war flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
seit/since 2010, Flagge der Luftwaffe – flag of the Air Force Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
seit/since 2010, Flagge des Heeres – flag of the army Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
ca.1700–1886, Nationalflagge – national flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1886–1942, 1945–1948, Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1886–1942, 1945–1948, |
 |
1939–1941, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
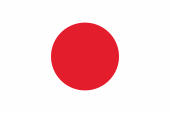
1941–1942, Flagge von Britisch-Burma – flag of British Burma, (provisorisch – provisional) Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1942–1945, Burma ist von Japan besetzt – Burma is occupied by Japan, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1942–1945, Flagge von Japanisch-Burma - inoffiziell – flag of Japanese Burma - unofficial, (Synyethe-Wunthann) Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1943–1945, Flagge von Japanisch-Burma - offiziell – flag of Japanese Burma - official, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
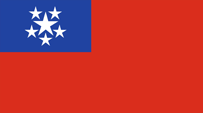
1945–1948, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
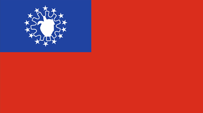
1948–1974, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen |
 |
1974–2010, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
 |
1974–2010, Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:9, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
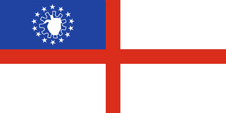 |
1974–2010, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge von Burma wurde am 21.10.2010 angenommen. Sie zeigt drei horizontale Streifen in Gelb, Grün und Rot und in der Mitte einen großen fünfzackigen, weißen Stern. Damit kehrt man zum Design der Jahre des Zweiten Weltkriegs unter der Besatzung der Japaner zurück, jedoch ist der weiße Stern der "Freiheitsliga" zu sehen. Die "Freiheitsliga" war der bewaffnete anti-japanische Widerstand. | The
today's flag of Burma was adopted on 21st of October in 2010. It shows three
horizontal stripes in yellow, green and red and in the middle a big
five-pointed white star. In this way they return to the design of the years of the Second World War under japanese occupation, but there arises the white star of the "Freedom League". The "Freedom League" was the armed anti-japanese resitance. |
| Die Flagge des von China abhängigen Königreiches Burma war ursprünglich einfarbig weiß, mit der Abbildung eines Pfaus in der Mitte. Sie wurde bis zur britischen Annexion im Jahre 1886 verwendet. Im Jahre 1939 wurde für das 1937 von Britisch-Indien getrennte Burma ein britischer Blue Ensign, eingeführt. | The flag of the from China dependent Kingdom of Burma was initialy single colour white, with the depiction of a peacock in the middle. It was in use until the British annexation in the year 1886. In the year 1939 was introduced for the in 1937 from British-India separated Burma a British Blue Ensign. |
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Handelsschiffe und seefahrende Privatpersonen aus Kolonien dürfen nur dann einen Red Ensign mit Badge führen, wenn von der britischen Admiralität eine entsprechende Erlaubnis für die Kolonie erteilt wurde. |
United
Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. |
| Burma, seit 1937 mit eigener Verwaltung, hat sich als Badge wieder den Pfau gewählt. 1942 wurde Burma von japanischen Truppen besetzt. Die Macht lag daraufhin innenpolitisch bei der 1942 Synyethe-Wunthann Partei und es wurde deren Flagge verwendet, faktisch bis 1945. 1943 wurde Burma als japanischer Satellitenstaat in die Unabhängigkeit entlassen. Die Flagge dieses Staates zeigte drei horizontale Streifen in Gelb, Grün und Rot, mit dem Pfau auf einer weißen Scheibe in der Mitte. 1945 wurde Burma von britischen Truppen besetzt, wieder dem britischen Kolonialreich eingegliedert, und es wurde wieder der Blue Ensign eingeführt. Am 04.01.1948 wurde Burma erneut in die Unabhänigkeit entlassen. Die in diesem Zusammenhang eingeführte Flagge war rot mit einer blauen Oberecke, darin ein weißer fünfzackiger Stern, umgeben von fünf kleineren Sternen. Ihren Ursprung hat diese Flagge in der Flagge der antijapanischen "Freiheitsliga", einer roten Flagge mit einem weißen Stern in der Oberecke. Die fünf kleineren Sterne in der neuen Flagge standen für die fünf größten Volksgruppen im Lande. Im Zusammenhang mit der Einführung einer neuen Verfassung wurde am 03.01.1974 auch eine neue Flagge eingeführt. Sie entspricht dem vorherigen Muster, jedoch zeigt sie anstelle der Sterne ein Zahnrad mit einer Reispflanze, von vierzehn Sternen kreisförmig umgeben. Das Zahnrad steht für die Industrie, die Reispflanze für die Landwirtschaft, und die vierzehn Sterne stellen die sieben Staaten und sieben Provinzen des Landes dar. Der Pfau wird nur noch in der Flagge des Präsidenten verwendet. Alle anderen Flaggen Burmas orientierten sich in ihrer Gestaltung bis zur Einführung der Flagge von 2010 noch immer am britischen Ensign-System. Als Farben für die Flaggen werden heute angegeben: Gelb = pt 166, Grün = pt 361, Rot = pt 1788 und Weiß. | Burma,
since 1937 with his own government, choiced as badge the peacock again. In
1942 Burma was occupyed by Japanese troops. Since 1942 the domestically
power lay with the Synyethe-Wunthann party and its flag was used, in fact
until 1945. In 1943 Burma gets independent as Japanese satellite state. The flag of this state showed three horizontal stripes in yellow, green and red, with the peacock on a white disk in the middle. In 1945 Burma was occupyed by British squads, re-incorporated the British colonial empire, and the Blue Ensign was introduced again. On 4th of January in 1948 Burma gets independent once more. The in this context introduced flag was red with a blue upper canton, in it a white five-jagged star, surrounded by five smaller stars. Her origin has this flag in the flag of the anti-japanese "freedom league", a red flag with a white star in the upper canton. The five smaller stars in the new flag stood for the five largest ethnic groups in the land. In context with the
introduction of a new constitution was introduced a new flag on 3rd of
January in 1974, too. It corresponds to the previous pattern, however it
shows instead of the stars a sprocket with a rice plant, circular surrounded
by fourteen stars. The sprocket stands for the industry, the rice plant for
the agriculture, and the fourteen stars represent the seven states and seven
provinces of the land. The peacock is only still in use in the flag of the
president. All other flags of Burma were orientated in their styling in the
British ensign system, until the introduction of the flag of 2010. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World, Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
1948-1974, Wappen von Burma – coat of arms of Burma, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (EN), Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
1974-2010, Wappen von Burma – coat of arms of Burma, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (EN), Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
seit/since 2010, Wappen von Burma – coat of arms of Burma, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (EN), Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das im Jahre 1948 eingeführte Wappen von Burma zeigte in der Mitte ein Siegel, mit einer Landkarte des Landes. Um die Landkarte lief ein golden gesäumter roter Ring mit dem Spruch: "Die Einheit führt zu Glück und Wohlstand". Unterhalb befand sich ein rosa Spruchband mit dem Landesnamen. Das Siegel wurde von drei blauen Löwen bewacht. Sie stehen für Mut, Kraft und Sauberkeit, die Zahl Drei ist eine Glückszahl. Die Elemente des Wappens wurden von üppigen goldenen Bändern, Decken und Verzierungen zusammengehalten. |
The In 1948 introduced coat of arms of Burma showed a seal in the middle,
with a map of the country. Around the map was placed a golded lined red ring with the motto: "The unity leads to happiness and prosperity". Below was placed a pink banner with the name of the country. The seal was guarded by three blue lions. They stand for courage, strength and cleanliness, the number three is a lucky number. The elements of the crest were bond with lush golden belts, blankets and ornaments. |
| Im Jahre 1974 wurde die Verfassung geändert. Das Land hieß jetzt "Sozialistische Republik der Union von Burma". Auch das Wappen wurde abgeändert. Einer der Löwen wurde entfernt und durch den weißen Stern der Freiheitsliga ersetzt. Das zentrale Siegel wurde jetzt von einem goldenen Kranz gesäumt. In der Mitte erschien ein silbernes Zahnrad auf blauem Grund, eine rote Silhouette des Landes wurde darübergelegt. | In 1974 the constitution was amended. The country was now called "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma". Also, the coat of arms was modified. One of the lions was removed and bevame replaced with the white star of the Freedom League. The central seal was now surrounded with a golden wreath. In the middle of it appeared a silver gear on blue background, a red silhouette of the country was laid over it. |
| Im Jahre 2010 wurde die Verfassung erneut geändert. Das Land heißt jetzt "Republik der Union von Myanmar". Auch das Wappen wurde wieder abgeändert. Es erscheint jetzt vollständig in Gold auf rotem Hintergrund. Das zentrale Siegel ist ganz verschwunden, die Landkarte/Silhouette des Landes erscheint an zentraler Stelle, umbeben von einem Kranz von zwei stilisierten Zweigen. |
In 2010 the constitution was amended again. The country is now called
"Republic of the Union of Myanmar". The coat of arms became also changed
again. It now appears completely in gold on a red background. The main seal
is completely gone, a map / silhouette of the country appears in central
position, surrounded by a wrath of two stylized branches. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Wikipedia (D) | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde (-Markierung) – aircraft roundel (marking) Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
Markierung am Seitenleitwerk – Fin Flash, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
840–1287
· Staat Pagan 1287 · mongolische Eroberung 1364 · Gründung des Königreiches Awa, Erstes Reich 1559 · Awa zerfällt in mehrere Kleinstaaten 1752 · Neu-Gründung des Königreiches Awa, Zweites Reich 1769 · Awa wird China tributpflichtig 1784 · Arakan wird von Awa annektiert 1824–1826 · Krieg gegen Großbritanien, Rangun, Arakan, Tenasserim, Manipur, Assam und die Küste werden von Britisch-Indien annektiert 1852–1853 · Krieg gegen Großbritanien, Pegu wird von Britisch-Indien annektiert 1862 · Arakan, Tenasserim und Pegu werden innerhalb von Britisch-Indien als Unterburma administrativ zusammengefasst 1885–1886 · Krieg gegen Großbritanien, das Königreich Awa wird als Oberburma von Britisch-Indien annektiert und einen Monat später mit Unterburma zu "Burma" vereinigt 01.04.1937 · Burma wird von Britisch-Indien abgetrennt, innere Selbstverwaltung 1942–1945 · Besetzung durch Japan im Zweiten Weltkrieg 1943–1945 · Shanland ist von Thailand annektiert 1943–1945 · Republik Burma unter Japanischer Oberhoheit 04.01.1948 · Großbritannien gewährt Unabhängigkeit 02.03.1962 · Ne Win Putsch 04.01.1974 · neue Verfassung, Umbenennung in Sozialistische Republik der Union von Burma 1988 · Militärputsch, Umbenennung in Union von Burma 1989 · Umbenennung in Union von Myanmar 1990 · Unruhen 2005–2007 · Umzug der Hauptstadt nach Naypyidaw 2007 · Unruhen 2007 · Regierungsprogramm "zur Zerstörung der christlichen Religion in Myanmar" 21.10.2010 · neue Verfassung, Umbenennung in Republik der Union von Myanmar |
History: |
|
840–1287
· State of Pagan 1287 · Mongol conquest 1364 · Establishing of the Kingdom of Awa, First Empire 1559 · Awa desintegrates into some smaller states 1752 · re-establishing of the Kingdom of Awa, Second Empire 1769 · Awa becomes tributary of the Chinese Empire 1784 · Arakan annexed by Awa 1824–1826 · war against United Kingdom, Rangoon, Arakan, Tenasserim, Manipur, Assam and the coast are annexed to British India 1852–1853 · war against United Kingdom, Pegu is annexed to British India 1862 · Arakan, Tenasserim and Pegu become united administratively as Lower Burma within British India 1885–1886 · war against United Kingdom, the Kingdom of Awa becomes annexed to British India as Upper Burma, and after one month united with Lower Burma to "Burma" 1st of April in 1937 · Burma gets separated from British-India, internal self government 1942–1945 · occupation by Japan in Second World War 1943–1945 · Shanland is annexed by Thailand 1943–1945 · Republik of Burma under Japanese supremacy 4th of January 1948 · United Kingdom grants independence 2nd of March 1962 · Ne Win revolt 4th of January in 1974 · new constitution, rename in Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma 1988 · military coup d’état, rename in Union of Burma 1989 · rename in Union of Myanmar 1990 · riots 2005–2007 · move of the capital to Naypyidaw 2007 · riots 2007 · governmental program "to destroy the Christian religion in Myanmar" 21st of October in 2010 · new constitution, rename in Republic of the Union of Myanmar |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Burma" geht auf das Volk der Burmesen zurück, die sich selbst als "Bamar" bezeichnen. Das gleiche Volk nennt sich aber auch "Myanma", was "die Starken" bedeutet. Die Burmesen stellen 70% der Bevölkerung. | The name "Burma"derives from the people of the Burmese, who call themselves "Bamar". The same people also called themselves "Myanma", meaning "the strong". The Burmese represent 70% of the population. |
| In der BRD wird häufig der Name "Birma" benutzt, was eine Eindeutschung der englischen Aussprache des Wortes "Burma" ist. In der Schweiz, in Österreich und auch in der ehemaligen DDR wird jedoch "Burma" verwendet. | In Germany is often used the name "Birma", what is a germanization of the english pronunciation of the word "Burma". However, in Switzerland, Austria and also in the former GDR (Eastern Germany), "Burma" is used. |
| Die Umbenennung des Landes in "Myanmar" erfolgte im Jahre 1989 einseitig seitens des Militärregierung. Die UNO hat die Änderung übernommen, während die USA und auch Australien sie offiziell ignorieren. Die burmesische Opposition plädiert ebenfalls für die Beibehaltung von "Burma". | The
renaming of the country to "Myanmar" occured in 1989 unilaterally by the
military government. The UN has accepted the change, while the USA and
Australia ignore it officially. Burma's opposition supports also the
maintenance of "Burma". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |