Bulgarien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Bulgarien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 1990, |
 |
1991 (?), |
 |
seit/since 1991, |
 |
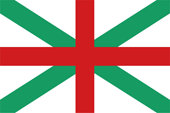
seit/since 1998, Kriegsflagge – war flag, in Wirklichkeit Truppenfahne – actually troop flag (?), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Scroch, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
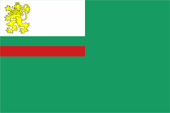
seit/since 1991, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
seit/since 1990, |
 |
seit/since 1997, |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
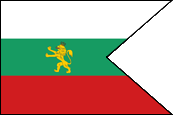
| 1.) 1878–1908 – Fürstentum Bulgarien – Principality of Bulgaria | |
 |
1877–1879, |
 |
1879–1908, |
 |
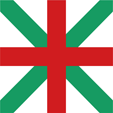
1879–1908, Kriegsflagge (Marineflagge) – war flag (naval flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1878–1908, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Lotsen(ruf)flagge – pilot flag (Pilot Call flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1878–1908, Standarte des Fürsten – standard of the Prince, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:6, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas |
| 2.) 1878–1908 – Wilajet Ostrumelien – Vilayet of Eastern Rumelia | |
 |
1878–1885 (?), |
 |
1885–1908 (?), |
| 3.) 1908–1946 – Königreich Bulgarien – Kingdom of Bulgaria | |
 |
1908–1947, |
 |
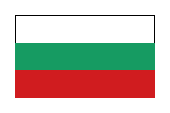
1908–1946, Staats-, Marine und Kriegsflagge – state and naval and war flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1908–1949, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1908–1946, Lotsen(ruf)flagge – pilot flag (Pilot Call flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas, FOTW, Diese Art Flaggen wurde im 20. Jahrhundert abgeschafft, heute gilt – This type of flag was abolished in the 20th century, today is: |
 |
1908–1918, Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Enzyklopädie |
 |
1918–1946, Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Enzyklopädie |
 |
1918–1946, Standarte des Königs zur See – standard of the King at Sea, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1908–1946, Flagge des Kriegsministers – flag of the War Minister, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas |
 |
1908–1946, Flagge des Chefs der Flotte – flag of the Navy Chief, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Europas |
 |
1944–1947, |
| 4.) 1947–1990 – Volksrepublik Bulgarien – People's Republic of Bulgaria | |
 |
1947–1948, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1948–1990, Nationalflagge – national flag, (mit kleinen Änderungen – with small changes), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1947–1990, Handelsflagge – merchant flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
1949–1955, Marineflagge – naval flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
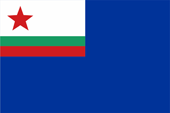
1955–1991, Marineflagge – naval flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen, Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1955–1990, Flagge der Hilfsschiffe – flag for aux ships, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
1955–1990, Flagge des Chefs der Flotte – flag of the Navy Chief, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1955–1990, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, 1:2 Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (BG) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die weiß-grün-rote Flagge Bulgariens wurde mit der ersten Verfassung von 1879 eingeführt. Die Nationalflagge trug nur in der Zeit der kommunistischen Herrschaft (1848–1990) ein Wappen, und zwar am Mast im weißen Streifen. Weiß steht für Freiheit und Frieden, Grün für die Wälder und die Landwirtschaft, Rot für das Blut, das zur Erlangung der Freiheit vergossen wurde. | The green-white-red flag of Bulgaria was introduced with the first constitution of 1879. The national flag was only in the period of communist rule (1848–1990) added by a coat of arms, and that on the mast in the white stripe. White stands for freedom and peace, green for the forests and the agriculture, red for the blood, which was shed for the attainment of the freedom. |
| Als Bulgarien in Folge des russisch-türkischen Krieges (1877–1878) als Fürstentum von der Türkei losgelöst wurde, und nach dem Friedensvertrag von San Stefano (03.03.1878) als Großbulgarien auferstand, wurde es nach dem Berliner Vertrag (13.07.1878) als türkischer Vasallenstaat in eine Teilunabhängigkeit entlassen, allerdings mit einem um ca. 60% der Landfläche reduzierten Territorium. Viele slawische Völker wählten sich nach 1848 Flaggen in den Farben Weiß, Blau und Rot, da sie Russland als Vorbild ansahen, denn die Russen waren die einzige freie slawische Nation. Alle anderen slawischen Völker lebten unter österreichischer, türkischer oder auch deutscher Herrschaft. Jene Politische Strömung, die versucht alle Slawen in einer Nation unter den Farben Weiß, Blau und Rot zu einen, wird Panslawismus genannt, und die Farben Weiß, Blau und Rot werden daher panslawische Farben genannt. Die Bulgaren verdankten den Russen ihre Freiheit, und führten eine Flagge ein, die der russischen ähnelte, jedoch wurde der blaue Streifen durch einen grünen ersetzt. Die Farben Weiß, Grün und Rot wurden allerdings inoffiziell schon seit 1862, also vor 1877/78 genutzt. Als Farben für die Flaggen werden heute angegeben: Grün = pt 347, Rot = pt 032 und Weiß. | As
Bulgaria in result of the Russian-Turkish war (1877–1878) was separated from
the Turkey as principality, and after the peace treaty from San Stefano (3rd
of march in 1878) re-rises as Great Bulgaria, it got after the Berlin treaty
(13th of July in 1878) dismissed in a partial independence as Turkish vassal
state, though with a by ca. 60% of the area reduced territory.
Many Slavic nations choose after 1848 flags in the colors white, blue and
red, because they saw in Russia a model, the Russians were the only free
Slavic nation. All other Slavic nations lived under Austrian, Turkish or
even German rule. The Bulgarians owe the Russians their freedom, and introduced a flag, which equals the Russian flag, however got the blue stripe substituted by a green. The colors white, blue and red were though unofficial in use already since 1862, so before 1877/78. The colors given for the flags today are: green = pt 347, red = pt 032 and white. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1997, Wappen von Bulgarien – coat of arms of Bulgaria, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (BG), Пакко, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1971–1990, Wappen von Bulgarien – coat of arms of Bulgaria, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen, Wikipedia (BG), Original: Unknown authorVectorization: Scroch, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen der Volksrepublik wurde 1946 angenommen und 1948, 1967 und 1971 in Details abgeändert. Der grundsätzliche Aufbau der Flagge war davon nicht betroffen. Im Jahr 1997 wurde ein neues, bürgerliches Wappen angenommen. Der Wappenschild ist rot, mit dem goldenen bulgarischen Löwen. Das Schild trägt eine Krone und wird von zwei Löwen gehalten, die auf Eichenzweigen stehen. Unterhalb ein Schriftband in den Landesfarben mit der Inschrift: "Saedinenieto pravi Silata" => "In der Einheit liegt die Stärke". | The coat
of arms of the People's Republic was adoped in 1946 and changed in details
in 1948, 1967 and 1971. The basic structure of the flag was not concerned in
this doing. In the year 1997 was introduced a new and civil coat of arms.
The blazon is red, with the golden Bulgarian lion. The shield carrys a crown
and is holded by two lions, which stand on oak twigs. Below a typeface
ribbon in the colors fo the land with the inscription: "Svedinenieto pravi
Silata" => "Unity provides strength". |
| Der goldene bulgarische Löwe auf rotem Grund ist das traditionelle Symbol Bulgariens. Er geht auf das 14. Jahrhundert zurück. Er erschien von Anfang an auf Staats- oder Militärflaggen. Zwischen 1948 und 1990 erschien er auch im Wappen auf der Nationalflagge und auf Marineflaggen wurde er in dieser Zeit vom roten Stern des Kommunismus verdrängt. | The
golden Bulgarian lion on red ground is the traditional symbol of Bulgaria.
He has its roots in the 14th century. It appeared from the beginning on the
state and military flags. Between 1948 and 1990 he also appeared in the emblem on the national flag, and on naval flags it was replaced in this time by the red star of communism. |
| Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Der Löwe in der Heraldik". Ausführungen, Varianten, Entwicklung sowie Panther und Leoparden. |
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
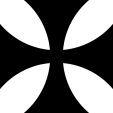 |
1915–1918, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1937–1941, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
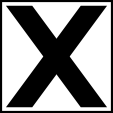 |
1941–1944, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1944–1946, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
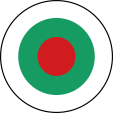 |
1946–1948, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (BG) |
 |
1948–1992, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
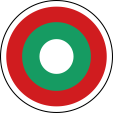 |
seit/since 1992, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
29–46 n.Chr. · die Region kommt an das Römische Reich 681–1018 · Erstes Bulgarisches Reich 1018–1185 · die Region gehört zum Byzantinischen Reich 1185–1396 · Zweites Bulgarisches Reich 1396–1878 · die Region gehört zum Osmanischen Reich 03.03.1878 · Drittes Bulgarisches Reich 13.07.1878 · errichtung des Fürstentums Bulgarien als türkischer Vasallenstaat, und des Wilajets Ostrumelien (Hauptstadt Plowdiw/Filibe) als autonome türkische Provinz unter einem christlichen Gouverneur 1908 · volle Unabhängigkeit, Gründung des Königreiches Bulgarien 1915–1918 · Teilnahme am Ersten Weltkrieg auf Seiten der Mittelmächte 1941–1944 · Teilnahme am Zweiten Weltkrieg auf Seiten der Achsenmächte 1944 · sowjetischer Einmarsch, kommunistischer Putsch 1946 · Sturz der Monarchie, Ausrufung der Republik 1947 · Ausrufung der Volksrepublik 1990 · Ausrufung der Republik 01.01.2007 · Bulgarien wird Mitglied der Europäischen Union |
History: |
|
29–46 A.D. · the region comes to the Roman Empire 681–1018 · 1st Bulgarian Empire 1018–1185 · the region belongs to the Byzantine Empire 1185–1396 · 2nd Bulgarian Empire 1396–1878 · the region belongs to the Ottoman Empire 3rd of March 1878 · 3rd Bulgarian Empire 13th of July 1878 · establish of the Principality of Bulgaria as a Turkish vassal state, and of the Vilayet of Eastern Rumelia (capital: Plovdiv/Filibe) as autonomous turkish province under a christian governor 1908 · full independence, foundation of the Kingdom of Bulgaria 1915–1918 · participation in the First World War on the side of the Middle Mights 1941–1944 · participation in the Second World War on the side of the Axis Mights 1944 · soviet invasion, communist revolt 1946 · overthrow of the monarchy, proclamation of the republic 1947 · proclamation of the people's republic 1990 · proclamation of the republic 1st of January 2007 · Bulgaria becomes a member of the European Union |
| Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Bulgarien" geht auf das Volk der Bulgaren zurück, einem Turkvolk aus dem Steppen Asiens. "Bulgare" bedeutet "Mischling", so dass Bulgarien das "Land der Mischlinge" ist. In der Tat sind die Bulgaren noch heute ein Mischvolk aus Thrakern, Slawen und Turk-Bulgaren. Mit der Bezeichnung Turk-Bulgaren sind nicht die in Bulgarien lebenden Türken gemeint, sondern die Ur-Bulgaren des frühen Mittelalters. | The name
"Bulgaria" comes from the people of the Bulgars, a Turkic people from the
steppes of Asia. "Bulgarian" means "half-breed" so that Bulgaria is the
"land of half-breeds". In fact, the Bulgarians are still a mixed population
of Thracians, Slavs and Turk-Bulgarians. The term Turk-Bulgarians means not
the Turks living in Bulgaria, but the original Bulgars of the early Middle
Ages. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Discovery '97 | |
|
Mit freundlicher Untersützung von: Kindly supported by: |
Jürgen Zens, Mario Schweigler |