Bolivien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Bolivien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
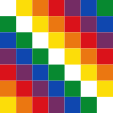 |
seit/since 2009, Wiphala-Flagge – Wiphala flag, = Nationalsymbol – national symbol, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
Staatsflagge – state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
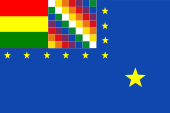
Kriegsflagge – war flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
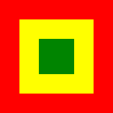
seit/since 2013, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
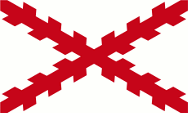 |
1548–1776, die Region gehört zum Spanischen Vizekönigreich Peru – the region belongs to the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
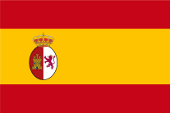 |
1776–1825, die Region gehört zum Spanischen Vizekönigreich Río de la Plata – the region belongs to the Spanish Viceroyalty of Río de la Plata, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1825–1826, Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen, FOTW |
 |
1825–1826, National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen, FOTW |
 |
1831–1851, Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
1831–1851 National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
1851–1888, Staatsflagge – state flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
1966-2013, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Das heutige Design der Flagge von Bolivien stammt vom 1851. Die heutige Variante wurde am 14.07.1888 eingeführt. Sie besteht aus drei waagerechten Streifen in Rot, Gelb und Grün. Rot steht für die Tierwelt, Gelb für den Mineralreichtum und Grün für die Vegetation und die Landwirtschaft. Rot symbolisiert aber auch den Mut und die Tapferkeit der bolivianischen Soldaten. Die Farben der Flagge gehen auf den ersten Präsidenten des Landes, Antonio José de Sucre (1795–1830) zurück. Er hatte 1826 eine Flagge in den Farben Gelb, Rot und Grün eingeführt, die sich an der Gestaltung der Flagge Großkolumbiens orientierte. Im Jahre 1851 wurde eine neue, bis heute beibehaltene, Reihenfolge der Farben festgelegt. | The
today's design of the flag of Bolivia descents from 1851. The today's
variant was introduced on the 14th of July, 1888. It consists of three
horizontal stripes, red, yellow and green. Red represents the fauna, yellow
the minerals resources, and green the vegetation and agriculture. Red also
symbolizes the bravery and valor of the Bolivian soldiers. The colors of the flag go back to the first president of the land, Antonio José de Sucre (1795–1830). He introduced in 1826 a flag with the colors yellow, red and green, which was modeled after the design of the flag of Greater Colombia. In 1851 the new sequence of colors was laid down. It has been maintained until now. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (ES), Translator of the English text: Joachim Nuthack | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1888, Wappen von Bolivien – coat of arms of Bolivia, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (ES) |
historische Wappen – historical Coats of Arms: |
|
 |
1825–1826, Wappen von Bolivien – coat of arms of Bolivia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
1826–1851, Wappen von Bolivien – coat of arms of Bolivia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
 |
1851–1888, Wappen von Bolivien – coat of arms of Bolivia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das heutige Staatswappen Boliviens wurde 1888 eingeführt, und geht im Wesentlichen auf das Wappen von 1825 zurück. Die Anzahl der Sterne im Wappen variierte immer mit der Anzahl der Departements/Provinzen. Es zeigte zuletzt neun Sterne. Im Jahre 1963 wurde der zehnte Stern zum Gedenken an das Departement Cobija hinzugefügt, welches Bolivien im Pazifischen Krieg (1879–1884) an Chile verlor. Das ovale Wappenschild zeigt den Berg von Potosí, er steht für Reichtum an Mineralien und Erzen, und eine Landschaft mit einem Alpaka, eine Garbe und eine Palme, welche für Naturreichtum stehen. Die Sonne ist ein Symbol der Inka, und der Kondor oberhalb des Schildes symbolisiert die Freiheit. | Today's
coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1888, and in substance goes back
to the coat of arms of 1825. The number of stars in the coat of arms always
varied with the number of departments/provinces. It last showed nine stars. In 1963 the tenth star was added in memory of the department Cobija, which Bolivia lost in the Pacific War (1879–1884) to Chile. The oval blazon shows the mountain of Potosí, it represents the riches of minerals and ores, and a scenery with a alpaca, a sheaf and a palm tree, which represent the abundance of nature. The sun is an Inca symbol, and the condor above the shield symbolizes freedom. |
| Das erste Wappen Boliviens wurde 1825 eingeführt und zeigte bereits die Elemente des heutigen Wappens: den Berg von Potosí, ein Alpaka, und eine Palme, umgeben von einem Palmen- und einem Ölzweig. Oberhalb des Schildes erschien eine Phrygische Mütze (ein Freiheitssymbol), und zwei allegorische Figuren die ein Band mit den Namen des Landes halten. Das zweite Wappen Boliviens wurde 1826 eingeführt und ähnelte bereits stark dem heutigen Wappen. Die Phrygische Mütze wurde 1851 durch einen Condor ersetzt. | The first coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1825 and showed already the elements of the today's coat of arms: the mountain of Potosi, an alpaca, and a palm tree, surrounded by a palm-twig and an oil-twig. Above the shield appeared a Phrygian Cap hold (a symbol of freedom), and two allegorical figures with a banner with the name of the country. The second coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1826 and resembled already the todays coat of arms. The Phrygian Cap was replaced by a Condor in 1851. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (ES), Translator of the English text (partial): Joachim Nuthack | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
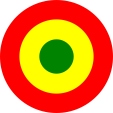 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
1471–1538
· der Westen des heutigen Landes ist Teil des Inkareiches 1538–1545 · Eroberung durch Spanien, die Region erhält den Namen Oberperu (Alto Perú) 1548 · Teil des Vizekönigreiches Peru 1776 · Teil des Vizekönigreiches Río de la Plata 1809 · Beginn des Befreiungskampfes 1816 · Oberperu wird wieder an Peru angegliedert 1825 · Oberperu wird Peruanischer Militärverwaltung unterstellt 06.08.1825 · Oberperu erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit 11.08.1825 · Proklamation der Bolivarischen Republik (República Bolívar) 18.05.1826 · Peru erkennt die Unabhängigkeit Boliviens an 1836–1839 · Konföderation Peru-Bolivien 1879–1884 · Pazifischer Krieg, Bolivien verliert seine Küstenprovinz, das Departement Cobija, an Chile 1899–1903 · Krieg gegen die abtrünnige Provinz Acre 1903 · Peru muss große Teile von Acre an Brasilien und Peru abtreten 1932–1935 · Krieg gegen Paraguay 18.03.2009 · die Republik Bolivien wird umbenannt in "Plurinationaler Staat Bolivien" |
History: |
|
1471–1538
· the West of the today's country is a part of the Inca-Empire 1538–1545 · conquest by Spain, the region gets the name Upper Peru (Alto Perú) 1548 · part of the Vice-Kingdom Peru 1776 · part of the Vice-Kingdom Río de la Plata 1809 · onset of the liberation fight 1816 · Upper Peru becomes re-incorporated to Peru 1825 · Upper Peru becomes subordinated under Peruan military gouvernment 6th of August 1825 · Upper Peru proclaims independence 11th of August 1825 · proclamation of the República Bolívar 18th of May 1826 · Peru recognizes Bolivian independence 1836–1839 · Confederation Peru-Bolivia 1879–1884 · Pacific War, Bolivia looses its coastal province, the Departement of Cobija, to Chile 1899–1903 · war against the renegading Province of Acre 1903 · Peru has to cede large parts of Acre to Brazil and Peru 1932–1935 · war against Paraguay 18th of March 2009 · the Republic of Bolivia becomes renamed in "Plurinational State of Bolivia" |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Die Region des heutigen Bolivien wurde in spanischer Zeit Oberperu, Charcas oder auch Chuquisaca genannt. Zu Ehren des Freiheitskämpfers Simón Bolívar wurde die 1825 unabhängig gewordene Republik "Bolivien" genannt. In der Indianerbevölkerung (Quechua und Aymara) wird das Land häufig "Qullasuyu" genannt. | The
region of the present-day Bolivia was called Upper Peru, Charcas or even
Chuquisaca in the Spanish time. In honor of the freedom fighter Simón
Bolívar, the in 1825 independent Republic was called "Bolivia" . In the
Indian population (Quechua and Aymara), the country is often called
"Qullasuyu". |
| Quelle/Source: World Statesmen, Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |