Pakistan |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Pakistan |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
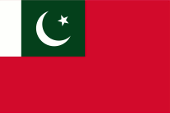
National- und Staatsflagge – national and state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Corel Draw 4   |
 |
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, using commons.wikimedia.org |
 |
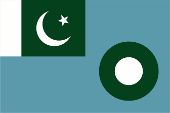
Flagge des Heeres – flag of the Army, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe – flag of the Air Force, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge für die Zivilluftfahrt – civil air ensign, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Präsidentenstandarte – Standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, using Zscout370, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
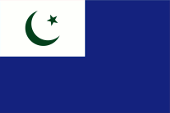
1947–1956, Flagge des Generalgouverneurs – flag of the Governor General, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flaggen Enzyklopädie |
 |
1956–1958, Handeslsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1956–1960, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1956–1967, Präsidentenstandarte – Standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, using Zscout370, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1967–2003, Präsidentenstandarte – Standard of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, using Zscout370, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons |
| Die Flagge Pakistans zeigt ein grünes Flaggentuch mit einem senkrechten weißen Streifen am Mast (1/4 der Fahnenfläche). In der Mitte der grünen Fläche ein geneigter weißer Halbmond mit einen fünfzackigen weißen Stern. Die Flagge wurde im Zusammenhang mit der Unabhängigkeit des Landes am 14.08.1947 erstmals offiziell gehisst. Sie geht auf die im Jahre 1906 geschaffene Parteiflagge der Moslemliga zurück, deren Ziel die Teilung Indiens in einen moslemischen und einen hinduistischen Staat war. Diese Flagge zeigte am Mast keinen weißen Streifen. Das Grün, der Stern und der Halbmond symbolisieren den Islam, während der weiße Streifen am Liek angeblich die im Land lebenden (aber stark unterdrückten) religiösen Minderheiten repräsentiert. In neuerer Auslegung steht die Farbe Weiß auf der Flagge für den Frieden. Die Farben der Flagge sind per Gesetz festgelegt, allerdings nur als "dunkelgrün". In der Praxis hat sich ein für das Grün durchgesetzt, der Pantone 357 nahekommt. | The flag
of Pakistans shows a green bunting with a vertical white stripe at the pole
(1/4 of the flag's surface). In the middle of the green area an inclined
white half-moon with a five-pointed white star. The flag was hoisted for the first time on 14th of August in 1947 in context with the independence of the country. It has its roots in the in 1906 created party flag of the Muslim Liga. Its target was the division of India in an Islamic and an Hindu state. That flag showed at the pole none white stripe. The colour green, the star and the half-moon symbolize the islam, while the white stripe on the leech ostensibly represents the in the country living (but toughly repressed) religious minorities. In a more recent interpretation, the colour white on the flag stands for peace. The colours of the flag are fixed by law, but only as "dark green". In practice, a colour close to Pantone 357 has become accepted for the green. |
| Pakistan orientiert sich teilweise am britischen Ensign-System. Das weist auf die früheren kolonialen Bindungen zu Großbritannien hin. | Pakistan is partially orientated in the British Ensign system. This point out to the former colonial connections to United Kingdom. |
Großbritannien führte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem ein, in dem:
|
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
|
| Der islamische Symbolismus, in Form von Halbmond und Stern, geht auf das Osmanische Reich zurück. Der letzte Kalif (aus dem Haus der Abbasiden) war 1258 hingerichtet worden. Der Kalif, Nachfolger Mohammeds, war religiöses und weltliches Oberhaupt des "Islamischen Reichs". Um 1460 wurde das Kalifat vom Herrscher des Osmanischen Reichs wiederbelebt. Diese Funktion wurde besonders wichtig als die Türken im Jahre 1517 die Stadt Mekka eroberten, und die Funktion der obersten Hüter und Bewahrer der heiligen Stätten übernahmen. Die Kontrolle über die heiligen Stätten ging während des Ersten Weltkriegs verloren (Mekka 1916, Medina 1918). Das Kalifat wurde 1924 von der türkischen Nationalversammlung abgeschafft. | The
islamic symbolism, with thw half-moon and the star, is from Ottoman origin.
The last Calif (from the house of the Abbaside's) was executed in 1258. The Calif – successor of Mohammed – was the religious and worldly head of the "Islamic Empire". About 1460 the Califate was revitalized by the ruler of the Ottoman Empire. This function became more important as the Turks conquered Mecca Town in 1517, as they became the supreme protectors and preservers of the holy places. The control over the holy places got lost during the First World War (Mecca 1916, Medina 1918). In 1924 the Califate became abolished by the Turkish national congregation. |
| So haben sich Halbmond und Stern als Symbole des Islam in der ganzen Welt verbreitet. Die Verbindung dieser Symbole mit grünen Flaggen hat ihren Ursprung im osmanischen Panislamismus. Als es in Teilen des Osmanischen Reiches zu Unabhängigkeitsbewegungen kam, setzte Abdul Hamid II. diesen Bewegungen erfolgreich das einigende Band des Panislamismus entgegen. Zum Symbol des Panislamismus machte er eine grüne Flagge (Farbe des Mantels des Propheten Mohammed), und setzte das türkische Wappen darauf. Die Flagge des Islam war erschaffen. | In this
way became half-moon and star spreaded in the whole world as the Symbols of
Islam. The coupling of that symbols with green flags has its roots in the
ottoman panislamism. As there arised independence movements in some regions of the Ottoman Empire, encounts Abdul Hamid II. these movements successful with the unifying string of panislamism. To the symbol of the panislamism he made the green flag (colour of the overcoat of the Prophet Mohammed), and layed above the Turkish coat of arms. The flag of the Islam was created. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Pakistan – coat of arms of Pakistan, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das pakistanische Staatswappen wurde 1955 eingeführt. Es ist einfarbig grün und zeigt, umgeben von einem Narzissenkranz, ein gevierteiltes Wappenschild mit landwirtschaftlichen Produkten: Baumwolle, Tee, Weizen und Jute. Über dem Wappenschild ein nach links geneigter Halbmond mit einem fünfzackigen Stern. Unter dem Wappen ein Spruchband mit dem Motto: "Glaube, Einheit, Disziplin". | The
Pakistani coat of arms was introduced in 1955. It is single coloured green
and shows surrounded by a narcissus-wreath a quartered blazon with
agricultural products: cotton, tea, wheat and jute. Above the blazon a to the left inclined half-moon with a five-pointed star. Under the coat of arms a banner with the motto: "religion, unity, discipline". |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
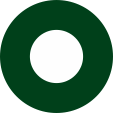 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ca. 3000
v.Chr. · Staat von Mohenjo Daro und Harappa 270–230 v.Chr. · zum indischen Mayurareich des Aschoka 326–323 v.Chr. · Eroberung durch Alexander dem Großen 3. Jhd. v.Chr. · Maurya-Reich ca. 400 · Staaten Sindh (Süden) und Gandhara (Norden) 711 · Eroberung und Islamisierung durch die Araber 11. Jhd. · zum Reich der Ghasnawiden 12. Jhd. · Staat Sindh 1526 · Eroberung durch das indische Mogulreich 1747 · zu Afghanistan 1843 · Unterwerfung von Sindh durch Großbritannien 1849 · Unterwerfung des Pandschab durch Großbritannien 1857 · der Mogul wird deportiert 1876 · Unterwerfung von Belutschistan durch Großbritannien 1930 · erste Forderungen nach einem eigenen islamischen Staat innerhalb Britisch-Indiens 14.08.1947 · Unabhängigkeit für Pakistan als britisches Dominion im Rahmen des Commonwealth of Nations, Teilung von ehemals Britisch-Indien, Gründung eines islamischen (Pakistan) und eines hindustischen Staats (Indien), erste Kämpfe in Kaschmir 1948 · erster Kaschmir-Krieg mit Indien 1954 · Beitritt zur SEATO 1955 · Beitritt zum Bagdad-Pakt (CENTO) 1956 · erste Verfassung, Proklamation der "Islamischen Republik Pakistan", das Land verbleibt jedoch im Commonwealth 1958–1969 · Militärdiktatur unter Ajub Khan 1962 · neue Verfassung als Präsidialregime, Gliederung in zwei Provinzen (West- und Ost-Pakistan) mit einer jeweils eigenen Provinzialregierung 1965 · zweiter Kaschmir-Krieg mit Indien 1969–1971 · Militärdiktatur unter Jahja Khan März 1971 · Forderungen nach mehr Autonomie in Ostpakistan, Militäraktionen 26.03.1971 · Proklamation der Unabhängigkeit von Ostpakistan durch Scheich Mujibur Rahman als Staat Bangladesch, Beginn des Unabhängigkeitskrieges, Bangladesch wird massiv von Indien unterstützt 17.04.1971 · Proklamation der Volksrepublik Bangladesch 16.12.1971 · Kapitulation Pakistans 20.12.1971 · Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto wird Staatspräsident 1972 · Austritt aus der SEATO 1973 · neue Verfassung, Bhutto wird Premierminister 05.07.1977 · Militärputsch, Machtübernahme durch General Zia ul-Haq, Ausrufung des Kriegsrechts 16.12.1978 · General Zia ul-Haq wird Staatspräsident 1979 · Auflösung der CENTO 04.04.1979 · Hinrichtung von Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto in Rawalpindi 1985 · Aufhebung des Kriegsrechts 1988 · General Zia ul-Haq kommt durch einen Flugzeugabsturz ums Leben, Wahlen zur Nationalversammlung: Benazir Bhutto (Tochter von Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto) wird Premierminister 1990–1993 · Mian Nawaz Sharif ist zwischenzeitlich Premierminister 1995 · Unruhen 1996 · Grenzstreitigkeiten zwischen Indien und Pakistan, Benazir Bhutto wird durch den Staatspräsident als Premierminister entlassen Mai 1998 · Pakistan zündet seine erste Atombombe 12.10.1999 · Militärputsch, Machtübernahme durch General Pervaiz Musharraf 18.10.1999 · die Commonwealth-Mitgliedschaft von Pakistan wird ausgesetzt 20.06.2001 · General Pervaiz Musharraf wird Staatspräsident 2007 · Ausnahmezustand 2008 · Pervaiz Musharraf tritt als Präsident zurück April/Mai 2025 · bewaffneter Konflikt zwischen Pakistan und Indien in der Kaschmir-Region |
| ca. 3000
B.C. · State of Mohenjo Daro and Harappa 270–230 B.C. · to the Indian Mayura Empire of Ashoka 326–323 B.C. · conquest by Alexander the Great 3rd cent. B.C. · Maurya Empire ca. 400 A.D. · States of Sindh (south) and Gandhara (north) 711 · conquest and islamization by the Arabs 11th cent. · to the Empire of the Ghaznavids 12th cent. · State of Sindh 1526 · conquest by the Indian Mughal Empire 1747 · to Afghanistan 1843 · subjection of Sindh by United Kingdom 1849 · subjection of Punjab by United Kingdom 1857 · the Mughal becomes deported 1876 · subjection of Balochistan by United Kingdom 1930 · first demands for an own Islamic state within British India 14th of August 1947 · independence for Pakistan as British Dominion in the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations, division of formerly British India, establishment of an Islamic (Pakistan) and an Hindu state (India), first conflicts in Kashmir 1948 · first Kashmir War with India 1954 · joining to the SEATO 1955 · joining to the Baghdad Pact (CENTO) 1956 · first constitution, proclamation of the "Islamic Republic of Pakistan", the country however remains in the Commonwealth 1958–1969 · military dictatorship under Ajub Khan 1962 · new constitution as Presidial Regime, structured in two provinces (Western and Eastern Pakistan) with own provincial governments 1965 · second Kashmir War with India 1969–1971 · military dictatorship under Jahja Khan March 1971 · claims for more autonomy in Eastern Pakistan, military campaigns 26th of March 1971 · proclamation of independence of Eastern Pakistan by Sheik Mujibur Rahman as State of Bangladesh, outbreak of the independence war, Bangladesh gets massive support by India 17th of April 1971 · proclamation of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh 16th of December 1971 · capitulation of Pakistan 20th of December 1971 · Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto becomes president 1972 · resignation out of the SEATO 1973 · new constitution, Bhutto becomes prime minister 5th of July 1977 · military coup d’état, seizure of power by General Zia ul-Haq, proclamation of the war right 16th of December 1978 · General Zia ul-Haq becomes president 1979 · dissolution of the CENTO 4th of April 1979 · execution of Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto in Rawalpindi 1985 · abolition of the war right 1988 · General Zia ul-Haq dies by a plane crash, elections to the national assembly: Benazir Bhutto (daughter of Zulfikar Ali Khan Bhutto) becomes prime minister 1990–1993 · Mian Nawaz Sharif is interim prime minister 1995 · riots 1996 · border quarrels between India and Pakistan, Benazir Bhutto gets fired as prime minister by the president May 1998 · Pakistan detonates its first atomic bomb 12th of October 1999 · military coup d’état, seizure of power by General Pervaiz Musharraf 18th of October 1999 · Pakistan's membership in the Commonwealth becomes suspended 20th of June 2001 · General Pervaiz Musharraf becomes president 2007 · state of emergency 2008 · Pervaiz Musharraf resigns as president April/May 2025 · armed conflict between Pakistan and India in the Kashmir region |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Wikipedia (DE) |
| Der Name "Pakistan" wurde durch Kombinieren von Anfangsbuchstaben bzw. Wortteilen seiner Landesteile gebildet: Pandschab, Afghanistan, Kaschmir, Sind und Belutschistan. Sehr gern wird "pak" als das persische Wort für "rein" interpretiert → "Land der Reinen". | The name
"Pakistan" was constructed by combination of initial letters and parts of
words of its countrysides: Punjab, Afghanistan, Kashmir, Sindh and Balochistan. With pleasure is the word "pak" interpreted as the Persian word for "pure" → "Land of the Pure". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |