Malta |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Malta |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
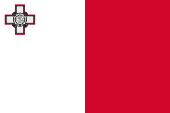 |
National-, Staats- und Marineflagge – national, state and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
seit/since 1988, Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
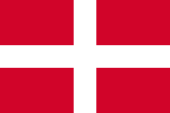 |
1530–1798, Flagge von Malta (Malteserorden) – flag of Malta (Order of Malta) Quelle/Source, nach/by: World Statesmen |
 |
1814–1954, |
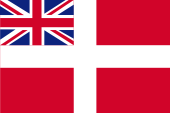 |
1814–1864, inoffizielle Handelsflagge – unofficial merchant flag Quelle/Source, nach/by: World Statesmen |
 |
1864–1921, |
 |
1875–ca.1898, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag) Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
ca.1898–1923, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag) Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1921–1943, Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, unsicher – uncertain, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
ca.1898–1943, inoffizielle National- und Handelsflagge – unofficial national and merchant flag Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1923–1943, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag) Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1943–1964, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag) Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1943–1964, Flagge des Gouverneurs – flag of the Governor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
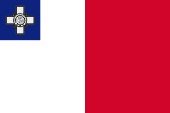 |
1943–1954, inoffizielle National- und Handelsflagge – unofficial national and merchant flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1954–1964, National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1967–1974, Flagge der Königin – flag of the Queen Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1964–1974, Flagge des Generalgouverneurs – flag of the Gouvernor General, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
| Die
Flagge Maltas ist weiß-rot senkrecht gestreift, mit einem
rotgeränderten Georgskreuz im Obereck. Sie wurde in dieser Form erstmals
offiziell anlässlich der Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit am 21.09.1964 gehisst. Die Farben Weiß und Rot gehen auf den Normannengrafen Roger II. (1095–1154) zurück, der die Insel im Jahre 1090 eroberte und von den Moslems befreite. Die Farben Weiß und Rot waren auf der Insel immer präsent und wurden wahrscheinlich ab 1898 als inoffizielle National- und Handelsflagge verwendet. |
The flag of Malta is vertically white and red striped with a red-bordered Cross of St. George in the upper staff quadrant. It was officially hoisted in this shape for the first time on the occasion of the achievement of independence on 21st of September in 1964. The colours white and red have their roots in the Norman's Count Roger II. (1095–1154), which conquers the island in the year 1090 and liberated it from the Muslims. The colors white and red have always been present on the island and were probably used as the unofficial national and trade flag from 1898 onwards. |
| In der britischen Kolonialzeit galt – jedoch nicht vor 1875 – die britische Dienstflagge, also ein Blue Ensign mit dem Badge der Inseln im fliegenden Ende der Flagge. | In the times of the British colony was in use – but not until 1875 – the British official flag, so a Blue Ensign with the badge of the islands in the flying end of the flag. |
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Handelsschiffe und seefahrende Privatpersonen aus Kolonien dürfen nur dann einen Red Ensign mit Badge führen, wenn von der britischen Admiralität eine entsprechende Erlaubnis für die Kolonie erteilt wurde. |
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. |
|
Ab 1921 durfte angeblich auch ein Red Ensign verwendet werden. Ein Nachweis
dafür ist nicht zu erbringen. Das Badge war ein weiß-rot gespaltener Schild
auf einer weißen Scheibe. Im Jahre 1943 wurde Malta durch König Georg IV.
das Georgskreuz als Anerkennung für die Tapferkeit der Malteser während der
Bombardierungen im Zweiten Weltkrieg verliehen. Diese Auszeichnung wurde in
einer blauen Oberecke auf dem Schild des Badges ergänzt. Die inoffizielle weiß-rote Flagge wurde darauf hin ebenfalls um die blaue Oberecke mit dem Georgskreuz ergänzt und ab dem 28.12.1943 so verwendet. Im Jahre 1954 soll diese Flagge offiziell zugelassen wurden sein. |
From 1921 it was said that a Red Ensign could also be used. It is not
possible to provide proof of this. The badge was a white-red shield in party
per pale on a white disk. In the year 1943 Malta was awarded by King George IV. the Cross of St. George as praise for the bravery of the Maltese during the bombardments in the Second World War. This distinction was added in a blue upper canten on the shield of the badge. The unofficial white and red flag was then also supplemented by the blue upper corner with the St. George's Cross and was used in this way from 28th of December in 1943. In 1954 this flag is said to have been officially approved. |
| Als Malta am 21.09.1964 unabhängig wurde, wurde die blaue Oberecke entfernt, und das Georgskreuz zur besseren Sichbarkeit mit einem roten Rand versehen. Es gibt Darstellungen der Flagge mit einem flächig blau, hellblau oder silbern (hellgrau) gefüllten Georgskreuz, oder es wird auf die Darstellung der Details (Der Heilige Georg tötet den Drachen) im Inneren des Kreuzes verzichtet. | As Malta became independent on 21st of September in 1964 was removed the blue upper canton and the Cross of St. George was added by a red border to distinguish it better. There are versions of the flag with a filled Cross of St. George in blue, pale blue or silvery (pale gray) or there is renounced for the representation of the minutiaes (the Holy George kills the dragon) in the interior of the cross. |
| Die Handelsflagge von Malta geht auf die Insignien des christlichen Johanniterordens (auch Malteserorden) zurück, der Inseln zwischen 1530 und 1798 beherrschte. Die Form des Kreuzes in der Flagge wird daher auch Malteserkreuz genannt. | The merchant flag of Malta has its roots in the insignias of the Christian Order of St. John (also Maltesian Order), which ruled the islands between 1530 and 1798. That shape of the cross in the flag is from there also named Maltesian Cross. |
| Zwischen 1964 und 1974 gehörte Malta nicht nur dem British Commonwealth of Nations an, sondern war auch keine Republik. Staatsoberhaupt war die britische Königin. Sie hatte in ihrer Funktion als maltesisches Staatsoberhaupt eine eigene Flagge. | Between
1964 and 1974 Malta belonged not only to the British Commonwealth of Nations
but was even not a republic. Chief of State was the British Queen. In hers function as Maltese Chief of State she had an own flag. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Enzyklopädie, Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1988, Wappen von Malta – coat of arms of Malta, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1975–1988, Wappen von Malta – coat of arms of Malta, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
| Das heutige Staatswappen erinnert an das im Jahre 1964 eingeführte Wappen. Dieses zeigte das weiß-rote (silbern-rote) Schild mit einer blauen Oberecke, und darin das Georgskreuz (→ siehe oben unter "Flagge"). Oberhalb ein goldener Helm mit weiß-roten Decken und einer goldenen Mauerkrone. Als Schildhalter dienten zwei Delphine. Unterhalb des Schildes erschien das Malteserkreuz sowie das Staatsmotto. | The
today's coat of arms remembers the in 1964 introduced coat of arms. That
showed the white-red (silvery-red) shield with a blue upper canton and in it
the Cross of St. George (→ look above among "flag"). Above a golden helmet with white-red covers and a golden wall-crown. As shield supporters served two dolphins. Below the shield arised the Maltesian Cross as well as the motto of the state. |
| Nachdem Malta 1974 Republik geworden war, meinte man ein neues Wappen einführen zu müssen. So wurde am 11.07.1975 ein Siegel als Staatswappen angenommen, das eine Küstenszene mit der aufgehenden Sonne zeigte, ein Fischerboot, eine Schaufel und eine Gabel. Darunter der neue Name des Staates: "Republikka Ta'Malta". | After Malta became republic in 1974, they thought they have to introduce a new coat of arms. In this way was adoped a seal as new coat of arms on 11th of July in 1975, which showed a coastal scene with the rising sun, a fishing boat, a shovel and a pitchfork. Underneath the new name of the state: "Republikka Ta'Malta". |
| Nach einem Machtwechsel wurde das Wappen am 19.10.1988 (nach anderen Quellen am 28.10.1988) erneut geändert. In seiner bis heute gültigen Form zeigt es wieder den weiß-roten Schild mit einem silbernen, rot umrandeten Georgskreuz im linken oberen Eck. Oberhalb des Schildes eine goldene Mauerkrone, und links und rechts des Schildes ein grüner Olivenzweig (links) und ein grüner Palmenzweig (rechts). Beide sind mit einem weißen Band verknüpft, welches als Inschrift den Namen des Staates trägt: "Republikka Ta'Malta". | After a
change of government the coat of arms was changed again on 19th of October
in 1988 (by other sources on 28th of October in 1988). In its until today
valid form it shows again the white-red shield with a silvery, with a red
bordered Cross of St. George in the left upper canton. Above the shield a golden wall-crown and to the left and to the right of the shield a green olive twig (left) and a green palm tree twig (right). Both are tied together with a white ribbon which carrys as inscription the name of the state: "Republikka Ta'Malta". |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Flaggen und Wappen, Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1980–1988, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 14. – 7.
Jhd. v. Chr. · phönizische Siedlung 7. Jhd. v. Chr. · zum Reich von Karthago 218 v. Chr. · als "Melita" zum Römischen Reich 395 n. Chr. · bei der Teilung des Römischen Reiches kommt Malta an das Weströmische Reich 533 · zum Oströmischen Reich (Byzanz) 870 · Eroberung durch Araber, Islamisierung 1090 · Eroberung durch die Normannen (Graf Roger von der Normandie), zum Königreich Sizilien, Rechristianisierung 1530 · der christliche Johanniterorden erhält Malta als Lehen von Kaiser Karl V. 1798 · Eroberung durch Truppen Napoléons 1800 · Befreiung der Inseln durch britische Truppen und Truppen des Königreichs Neapel 1814 · Wiener Kongress, Malta kommt an Großbritannien, wird britische Kronkolonie 14.04.1921 · Verfassung, beschränkte Selbstverwaltung 1940–1943 · Zweiter Weltkrieg, umfangreiche Bombardierungen 1947 · innere Autonomie 21.09.1964 · Unabhängigkeit (im Rahmen des British Commonwealth of Nations) 13.12.1974 · Malta wird Republik, verbleibt jedoch im Commonwealth 1965 · Beitritt zum Europarat 1979 · die letzten britischen Truppen verlassen das Land 2004 · Aufnhame in die Europäische Union (EU) |
| 14th –
7th cent. B.C. · phoenician settlement 7th cent. B.C. · to the Empire of Karthago 218 B.C. · as "Melita" to the Roman Empire 395 A.D. · at the partition of the Roman Empire Malta comes to the West Roman Empire 533 · to the East Roman Empire (Byzantium) 870 · conquest by Arabs, Islamization 1090 · conquest by the Normans (Count Roger of Normandy), to the Kingdom of Sicily, re-christianization 1530 · the Christian Order of St. John gets Malta as fiefdom from Emperor Charles V. 1798 · conquest by troops of Napoléons 1800 · liberation of the islands by British troops and troops of the Kingdom of Naples 1814 · Vienna Congress, Malta comes to United Kingdom, becomes a British crown colony 14th of April 1921 · constitution, limited autonomy 1940–1943 · Second World War, extensive bombardments 1947 · internal autonomy 21st of Sept. 1964 · independence (within the framework of the British Commonwealth of Nations) 13th of December 1974 · Malta becomes a republic but remains in the Commonwealth 1965 · joining to the European Council 1979 · the last British troops leave the country 2004 · joining to the European Union (EU) |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
| Der Name "Malta" stammt vom lateinischen "Melita", und dieses Wort dürfte noch älter sein, denn es stammt vom indoarischen Wort "mel", was "hoch" bedeutet. | The name "Malta" has its roots in the Latin "Melita", and that word should be real older because it comes from the Indo-Aryan word "mel", what means "high". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |