Jugoslawien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Jugoslawien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations  |
 |
Staatsflagge – state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, zweifelhaft – doubtful, |
 |
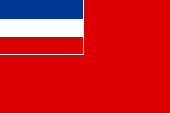
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: 1.) Wikipedia (EN), 2.) Wikipedia (EN)  |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
 |
Präsidentenstandarte – standard of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1992–2004, Flagge von Serbien – flag of Serbia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
 |
2004–2006, Flagge von Serbien – flag of Serbia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D)  |
 |
1992–2004, Flagge von Montenegro – flag of Montenegro, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
 |
2004–2006, Flagge von Montenegro – flag of Montenegro, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations   |
|
|
|
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
|
|
|
|
1.)
Königreich der Serben, Kroaten und Slowenen (1918–1929) – Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 2.) Königreich Jugoslawien (1929–1941) – Kingdom of Yugoslavia |
|
 |
National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national, state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)  |
 |
Marine und Kriegsflagge – naval and war flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1918–1929 (?), Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1929–1937 (?), Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
1937–1941 (?), Standarte des Königs – standard of the King, Variante - variant, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
|
|
|
3.)
Sozialistische Föderative Republik Jugoslawien (1946–1992) – Socialist Federal Republic Yugoslavia |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)    |
 |
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)    |
 |
1946–1992, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
1946–1992, Ehrenflagge der Marine – honour flag of the navy, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1956–1992 Flagge des Grenzschutzes – flag of the Border Guard, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1963–1991, Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1963–1992, Präsidentenstandarte – standard of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
Standarte des Oberkommandierenden der Streitkräfte – standard of the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
|
|
|
3.1.)
Bundesstaaten der SFR Jugoslawien (bis/till 1992) – Federal staates of the SFR Yugoslavia |
|
 |
Flagge Serbiens und Montenegros – flag of Serbia and Montenegro, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
Flagge Kroatiens – flag of Croatia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
Flagge Sloweniens – flag of Slovenia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
Flagge Bosnien-Herzegowinas – flag of Bosnia-Hercegovina, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
Flagge Makedoniens – flag of Macedonia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge des 1918 entstandenen Königreichs der Serben, Kroaten und Slowenen (1918–1929)zeigte die Farben Blau, Weiß und Rot (panslawische Farben) in waagerechter Anordnung. Die Marine- und Kriegsflagge zeigte zusätzlich noch das mittlere Wappen des Landes. | The flag of the in 1918 founded Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (1918–1929), showed the colors blue, white and red (Pan-Slavic
Colours) in an horizontal arrangement. The naval and war flag showed also the middle coat of arms of the country. |
| Über die Flagge des Königs findet man widersprüchliche Angaben und unterschiedliche Ausführungen. Als relativ sicher gilt eine blau-weiß-rote quadratische Flagge mit dem großen Wappen des Landes darin. Sie zeigte am Rand den von den Flaggen der Habsburger Monarchie her bekannten charakteristischen Rand aus Dreiecken, der sich in den Flaggen der Staatsoberhäupter einiger Nachfolgestaaten Jugoslawiens bis heute erhalten hat. | About the flag of the king we will find contradictory informations and different versions. As a relatively safe is a blue-white-red square flag with the great coat of arms of the country in the middle. It showed on the edge the characteristic edge of triangles known from the flags of the Habsburg monarchy, what had survived in the flags of the heads of state of some successor states of Yugoslavia until today. |
| Mindestens eine Quelle, das Flaggenbuch des Oberkommandos der Deutschen Kriegsmarine von 1939, zeigt für die 30-er Jahre in der Mitte der Flagge ein anderes Motiv, einen doppelköpfigen silbernen Adler unterhalb einer völlig anders gestalteten Krone mit einem Wappenschild auf der Brust, der anstelle der Symbolik von Bosnien diejenige von Slowenien (Krain) zeigt. Immerhin ist es möglich, dass diese Gestaltung im Jahre 1929 eingeführt wurde, als das Land in "Jugoslawien" umbenannt worden ist. | At least one source, the flag book of the High Command of the German Navy of 1939, shows another motif in the middle of the flag for the thirties of that century, a double-headed silvery eagle below a completely different shaped crown, with a blazon on the chest, which showed instead of the symbolism of Bosnia that of Slovenia (Krain). After all, it is possible that this design was introduced in 1929, when the country was renamed in "Yugoslavia". |
| Eine weitere, angeblich 1937 eingeführte Flagge des Königs zeigt außer dem leicht veränderten Dreiecks-Rand jetzt einen purpurfarbenen Hintergrund, in der Mitte ein großes silbernes Kreuz und darauf einen in seiner Gestalt veränderten silbernen Adler unter der üblichen Krone, mit dem üblichen Wappenschild auf der Brust. | Another, allegedly in 1937 introduced flag of the king shows in addition to the slightly altered triangle-edge now a purple background, in the middle of it a large silvery cross and on it an in its shape changed silvery eagle under the usual crown, with the usual blazon on the chest. |
| Der jugoslawische Staat zerfiel während des Zweiten Weltkrieges (1941) in drei Staaten (Serbien, Kroatien und Montenegro), bzw. wurden große Gebiete an Nachbarstaaten angegliedert. | The Yugoslav state disintegrates during the Second World War (1941) into three states (Serbia, Croatia and Montenegro), and large territories were ceded to neighbouring countries. |
| Im November 1945 hatten sich die kommunistischen Partisanen des Josip Broz Tito im Bürgerkrieg gegen Monarchisten, Republikaner und Nationalisten durchgesetzt, und proklamierten die "Föderative Volksrepublik Jugoslawien". Die Tito-Partisanen verwendeten seit 1941 einen goldumrandeten fünfzackigen roten Stern, welcher ab dem 21.01.1946 das bis dahin auf der Flagge verwendete Wappen ersetzte. Am 17.04.1963 wurde das land in "Sozialistische Föderative Republik Jugoslawien" umbenannt. Die Flagge blieb jedoch unverändert. | In November 1945 the communist partisans of Josip Broz Tito had exulted in the civil war against monarchists, republicans and nationalists, and proclaimed the "Federative People's Republic of Yugoslavia". The Tito partisans used since 1941 a golden bordered five-pointed red star, which replaced on 21st of January 1946 the until that point of time used coat of arms.
On 17th of April in 1963 the country was renamed into "Socialistic Federative Republic of Yugoslavia". The flag however remained unchanged. |
| Mit dem Zusammenbruch des sozialistischen Systems verließen zwischen 1991 und 1992 Slowenien, Kroatien, Makedonien und Bosnien-Herzegowina den jugoslawischen Staat. Am 27.04.1992 schlossen sich die beiden verbleibenden Staaten Serbien und Montenegro zur "Föderativen Republik Jugoslawien" zusammen, und der rote Stern wurde ersatzlos von der Nationalflagge entfernt und ein neues Staatswappen angenommen. Seit 2003 hieß das Land "Bundesrepublik Serbien und Montenegro". Am 03.06.2006 endete das Land mit dem Austritt Montenegros. | With the collapse of the socialist system, Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia and Bosnia-Hercegovina left the Yugoslav state between 1991 and 1992. On 27th of April in 1992 the two remaining states Serbia and Montenegro joined together to form the "Federative Republic of Yugoslavia", and the red star was removed from the national flag without substitution and a new coat of arms was further adopted. Since 2003 the country was called "Federal Republic of Serbia and Montenegro". On 3rd of June in 2006, the country ended with the withdrawal of Montenegro. |
| Die Mitgliedsstaaten Jugoslawiens nutzten die Panslawischen Farben ihrer jeweilige Nationalflagge, nur wurde je nach dem politischen System entweder ein Landeswappen oder ein roter Stern in der Mitte der Flagge verwendet. Lediglich Bosnien-Herzegowina und Makedonien haben in der Zeit des sozialistischen Jugoslawiens jeweils eine anders gestaltete Flagge verwendet. | The
membering countries of Yugoslavia always used the Panslavic Colours in their
respective national flag, but there were in use – depending on the political
system – either a coat of arms or a red star in the middle of the flag. Only Bosnia-Hercegovina and Macedonia used in the times of the socialistic Yugoslavia an in an other way designed flag. |
| Viele slawische Völker schufen sich in der Zeit nach 1848 (dem Jahr der Revolutionen) – im Zusammenhang mit einem erstarkenden slawischen Nationalismus – eigene Flaggen. Dabei spielte der Panslawismus eine bedeutende Rolle, eine politische Bewegung des 18./19. Jahrhunderts, die alle Slawen in einer Nation einen wollte. Die meisten slawischen Völker lebten jedoch in dieser Zeit unter österreichischer, türkischer oder auch deutscher Herrschaft. Der Panslawismus sah in Russland ein Vorbild, denn die Russen waren nahezu die einzige freie slawische Nation. Und so wurden die Farben der russischen Flagge zum Idol der Panslawisten, und letztlich farbliches Vorbild bei der Gestaltung der Flaggen vieler slawischer Nationen. Diese Flaggen trugen und tragen bis auf wenige Ausnahmen die russischen Farben Weiß, Blau und Rot als gemeinsames Merkmal. Daher wird diese Farbkombination "Panslawische Farben" genannt. | Many
Slavic nations created their own flags in the 19th century – in context with a
growing Slavic nationalism. The Panslavism played an important roll,
a political movement of the 18th/19th century, which would unite all Slavs
in one nation. The most Slavic nations however lived in this times
under Austrian, Turkish or even German rule. The Panslavism saw in Russia a model, because the Russians were nearly the only free Slavic nation. In this way the colours of the Russian flag became to an idol of the Panslavists, and in the end even a colour's pattern for the designing of the flags of many Slavic nations. Those flags carried and carry except few exceptions the Russian colours white, blue and red as mutual attribute. From there this colour's combination is called "Panslavic Colours". |
| Serbien hatte 1830 das osmanische Joch abgeworfen, und im Jahre 1835 die rot-blau-weiße Flagge angenommen. Montenegro (eine ursprünglich rein serbische Staatsgründung), 1852 vom Osmanischen Reich unabhängig geworden, verwendete zunächst eine rote Flagge mit einem silbernen Adler darin. Im Jahre 1860 schaffte Montenegro die rote Flagge mit dem Adler ab, und übernahm die Flagge Serbiens. | Serbia
had in 1830 thrown off the Ottoman yoke, and adoped in 1835 a red-blue-white
flag. Montenegro (an initially pure Serbian state`s foundation) used since 1852, when it became independent from the Ottoman Empire, initially a red flag with a silvery eagle on it. In the year 1860 Montenegro had abolished the red flag with the eagle and adoped the flag of Serbia. |
| Für die Einführung der Flagge Serbiens mit den russischen Farben wird zuweilen ein ganz konkreter Grund angeführt: Die Farben seien als Dank für die Waffenhilfe der Russen für die Serben im Freiheitskampf gegen die Türken angenommen worden. | For the introduction of the Serbian flag with the Russian colours is occasionally telled a real concrete reason: The colours have been adoped as gratitude for the Russian help in arms for the Serbs in the struggles for freedom against the Turks. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggenbuch 1939, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
|
|
|
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
1992–2006, Wappen von Jugoslawien (seit 2003: Serbien und Montenegro) – coat of arms of Yugoslavia (since 2003: Serbia and Montenegro), Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
|
|
|
historische Wappen – historical Coats of Arms: |
|
 |
1918–1941, Wappen von Jugoslawien – coat of arms of Yugoslavia |
 |
1943–1946, Wappen von Jugoslawien (im Untergrund) – coat of arms of Yugoslavia (in underground) |
 |
1946–1963, Wappen von Jugoslawien – coat of arms of Yugoslavia |
 |
1963–1992, Wappen von Jugoslawien – coat of arms of Yugoslavia |
| Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Wikipedia (EN) | |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen des im Jahre 1918 gegründeten "Königreichs der Serben, Kroaten und Slowenen" – das 1929 in "Königreich Jugoslawien" umbenannt wurde – zeigt den silbernen serbischen Doppeladler auf rotem Grund, denn die Könige Serbiens waren zugleich die Könige Jugoslawiens. Der Adler trägt ein halbgespaltenes und halbgeteiltes Brustschild mit der Heraldik Serbiens (Kreuz mit Feuerstählen), Kroatiens (weiß-rot geschacht) und Sloweniens (Halbmond mit drei Sternen). Oberhalb des Schildes die jugoslawische Krone. | The coat
of arms of the in 1918 established "Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and
Slovenes" – which was renamed in 1929 into "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" – showed
the silvery Serbian double-eagle on red ground, because the Kings of Serbia
were at the same time the Kings of Yugoslavia. The eagle carrys a half clefted and half divided breast-shield with the heraldry of Serbia (cross with fire steels), Croatia (white-red chessed) and Slovenia (half-moon with three stars). Above the shield the Yugoslav crown. |
| Das Wappen des sozialistischen Jugoslawiens zeigte sechs Fackeln, die für die einzelnen Teilstaaten des Landes standen. Bis 1963 waren es nur fünf Fackeln, welche für die fünf Nationen des Landes standen. Über den Fackeln der fünfzackige, goldumrandete rote Stern der Tito-Partisanen, das Zeichen des Kommunismus. Die Fackeln sind von einem Ährenkranz umgeben, der von einem blauen Band zusammengehalten wird. Das Band trägt in der Mitte das Datum 29.11.1943. An diesem Tag wurde das kommunistische Volksbefreiungskomitee gegründet. | The coat
of arms of the socialistic Yugoslavia showed six torchs, which stood for the
individual partial states of the country. Until 1963 there were only five torchs which stood for the five nations of the country. Above the torchs the five-point, gold-rimmed red star of the Tito-Partisans, the sign of communism. The torchs are surround by an ear wreath, which is bond by a blue ribbon. The ribbon carrys in the middle the date 29th of November in 1943. On this day was established the communist people's liberation committee. |
| Das bis zum Ende Jugoslawiens (seit 2003 Bundesrepublik Serbien und Montenegro) gültige Wappen zeigte wieder den serbischen (jugoslawischen) Doppeladler. Das viergeteilte Schild auf seiner Brust vereinte die Heraldik Serbiens (Kreuz mit Feuerstählen) und Montenegros (goldener schreitender Löwe). | The until the end of Yugoslavia (since 2003 Federal Republic of Serbia and Montenegro) used coat of arms showed again the Serbian (Yugoslav) double-eagle. The quartered shield on its chest combined the heraldry of Serbia (cross with fire-steels) and of Montenegro (golden gradient lion). |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (EN) | |
|
|
|
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1929–1941, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
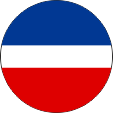
1945–1992, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1992–2006, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
|
|
|
| Landkarte – Map: |
| Die Staaten des früheren Jugoslawien – The countries of the former Yugoslavia |
|
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1830 ·
Serbien wird endgültig vom Osmanischen Reich unabhängig 1852 · Montenegro wird unabhängig 1878 · Beriner Kongress, Unabhängigkeit für Serbien und Montenegro wird bestätigt 1918 · Zusammenbruch der Habsburger Monarchie in Folge des Ersten Weltkrieges 01.12.1918 · Slowenen, Kroaten, Serben und Montenegriner schließen sich im "Königreich der Serben, Kroaten und Slowenen" zusammen, Bosnien-Herzegowina und Makedonien werden Provinzen, erster König wird Peter I. aus dem serbischen Königshaus Karadjordjevic 1921 · König Alexander I. folgt Peter I. auf den Thron 1929 · König Alexander I. errichtet eine Militärdiktatur, Umbenennung des Staats in "Königreich Jugoslawien" 1934 · König Alexander I. wird in Marseille ermordet, Thronfolger wird Peter II. 25.03.1941 · Jugoslawien erklärt seinen Beitritt zur den Achsenmächten (Achse), daraufhin Putsch serbischer Offiziere unter General Simovic, der Beitritt zur "Achse" wird widerrufen 06.04.1941 · Einmarsch deutscher und italienischer Truppen 17.04.1941 · Kapitulation Jugoslawiens, Jugoslawien wird aufgelöst: der König flieht ins Exil, einige Gebiete müssen an Nachbarstaaten abgetreten werden (Makedonien, Kosovo, Banat und Slowenien), die Provinz Bosnien-Herzegowina wird Kroatien angeschlossen, Kroatien und Montenegro werden unabhängig, Serbien kommt unter deutsche Militärverwaltung 15.06.1941 · Kroatien tritt der "Achse" bei 1941–1946 · Jugoslawien ist während des Zweiten Weltkriegs Schauplatz eines erbarmungslosen Partisanen- und Bürgerkriegs zwischen Kommunisten (unter J.P.Tito), Republikanern, Monarchisten und Nationalisten, die Kommunisten setzen sich durch 29.11.1945 · Ausrufung der "Föderativen Volksrepublik Jugoslawien" durch Tito 1945 · "Beistandspakt" mit der Sowjetunion 1948 · Bruch mit der Sowjetunion, Ablehnung deren Bevormundung, Entwicklung eines eigenen jugoslawischen Weges zum Sozialismus 17.04.1963 · Umbenennung in "Sozialistische Föderative Republik Jugoslawien" 04.05.1980 · Tod von J. B. Tito 1981 · Aufstände der Albaner im Kosovo, die Albaner fordern für die autonome serbische Provinz Kosovo den Republikstatus, die Aufstände werden niedergeschlagen 1990 · Wahl von Slobodan Milosevic zum Präsidenten Serbiens 1990 · Aufhebung des Autonomiestatus der serbischen Provinzen Kosovo und Wojvodina 25.06.1991 · Slowenien und Kroatien treten aus Jugoslawien aus und erklären ihre Unabhängigkeit 21.11.1991 · Makedonien tritt aus Jugoslawien aus und erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit 01.03.1992 · Bosnien-Herzegowina tritt aus Jugoslawien aus und erklärt seine Unabhängigkeit 27.04.1992 · Serbien und Montenegro proklamieren die "Bundesrepublik Jugoslawien" 1991–1995 · Krieg zwischen Jugoslawien und Kroatien/Bosnien-Herzegowina 1998 · im Kosovo forciert die UÇK (Albanische Befreiungsarme des Kosovo) ihren Kampf für die staaliche Unabhängigkeit des Kosovo, auf Grund der serbischen Gegenmaßnahmen fliehen viele Albaner aus Kosovo 1999 · die NATO ergreift einseitig Partei für die UÇK, greift in der Krieg Serbiens um seine territoriale Integrität ein, und bombardiert großangelegt serbische Ziele im Kosovo sowie in Serbien selbst, Besetzung des Kosovo durch KFOR-Truppen der NATO zum "Schutz vor Übergriffen jugoslawischer Truppen", Vertreibung der serbischen Bevölkerung aus dem Kosovo 2000 · Wahlen in Serbien, Vojislav Kostunica wird Nachfolger von Milosevics 28.06.2001 · die serbische Regierung verkauft Slobodan Milosevic gegen Wirtschaftshilfe und mehrere Millionen Dollar an das UN-Kriegsverbrechertribunal in Den Haag 2002 · die serbische Provinz Kosovo wählt einen "Präsidenten", Ibrahim Rugova 04.02.2003 · neue Verfassung, Jugoslawien wird durch die "Bundesrepublik Serbien und Montenegro" abgelöst 21.05.2006 · Volksabstimmung in Montenegro über eine Trennung Montenegros von Serbien, 55,4% Zustimmung zur Auflösung des Staatenbundes 13.07.2006 · Unabhängigkeitserklärung von Montenegro, Ende des Staatenbundes |
|
|
| 1830 ·
Serbia is irrevocably independent from Ottoman Empire 1852 · Montenegro is independent 1878 · Congress of Berlin, the independence for Serbia and Montenegro is confirmed 1918 · breakdown of the Habsburg's monarchy in result of the First World War 1st of December in 1918 · Slovenes, Croats, Serbs and Montenegrins join into the "Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes", Bosnia-Hercegovina and Macedonia become provinces, first King is Peter I. from the Serbian royal House Karadjordjevic 1921 · King Alexander I. succeeds Peter I. on the throne 1929 · King Alexander I. establishes a military dictatorship, the state is renamed into "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" 1934 · King Alexander I. gets murderd in Marseille, successor is Peter II. 25th of March in 1941 · Yugoslavia declares its joining to the Axis Mights (axis), because of that coup d'état of Serbian military officers under General Simovic, the joining to the "axis" is revoked 6th of April in 1941 · invasion of German and Italian troops 17th of April in 1941 · capitulation of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia becomes dissolved: the King escapes into exile, some territories have to cede territories to neighbouring states (Macedonia, Kosovo, Banat and Slovenia), the Province of Bosnia-Hercegovina gets incorporated into Croatia, Croatia and Montenegro get independent, Serbia comes under German military administration 15th of June in 1941 · Croatia joines to the "axis" 1941–1946 · Yugoslavia is during the Second World War a scene of a merciless partisan and civil war between communists (under J.P.Tito), republicans, monarchists and nationalists, the communists prevailed 29th of November in 1945 · proclamation of the "Federative People's Republic of Yugoslavia" by Tito 1945 · "support agreement" with the Soviet Union 1948 · break with the Soviet Union, dismissal of their patronizing, evolution of an own Yugoslav way to socialism 17th of April 1963 · renamed to "Socialistic Federative Republic of Yugoslavia" 4th of May in 1980 · death of J. B. Tito 1981 · riotings of the Albanians in Kosovo, the Albanians claim an autonomous status for the Serbian Province of Kosovo as a republic, the riotings get suppressed 1990 · election of Slobodan Milosevic to the President of Serbia 1990 · abolition of the autonomy status of the Serbian provinces Kosovo and Vojvodina 25th of June in 1991 · Slovenia and Croatia leave Yugoslavia and declaire their independence 21st of November in 1991 · Macedonia leaves Yugoslavia and declares its independence 1st of March in 1992 · Bosnia-Hercegovina leaves Yugoslavia and declares its independence 27th of April in 1992 · Serbia and Montenegro proclaim the "Federal Republic of Yugoslavia" 1991–1995 · war between Yugoslavia and Croatia/Bosnia-Hercegovina 1998 · in Kosovo the UÇK (Albanian Liberation Army of the Kosovo) forces its struggle for the independence of Kosovo, because of the Serbian counteractions many Albanians flee from the Kosovo 1999 · the NATO grasps unilateral party for the UÇK, intervenes in the war against Serbia for its territorial integrity and bombs extendedly Serbian targets in the Kosovo as well as in Serbia itself, occupation of the Kosovo by KFOR-troops of the NATO for "protection against encroachments of Yugoslav troops", assassination and expulsion of the Serbian population from the Kosovo 2000 · elections in Serbia, Vojislav Kostunica becomes successor of Milosevics 28th of June in 2001 · the Serbian government sells Slobodan Milosevic for economical support and several millions of dollars to the UN war crimes tribunal in Den Haag 2002 · the Serbian province Kosovo elects a "President", Ibrahim Rugova 4th of February in 2003 · new constitution, Yugoslavia is superseded by the "Federal Republic of Serbia and Montenegro" 21st of May in 2006 · plebiscite in Montenegro about the separation of Montenegro from Serbia, 55,4% agreement for the dissolution of the confederation 13th of July 2006 · declaration of independence of Montenegro, end of the confederation |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Discovery '97, Wikipedia (D) |
|
|