Kokosinseln |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Kokosinseln |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 1955, |
 |
seit/since 2003, Nationalflagge – national flag (inoffiziell–unofficial), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
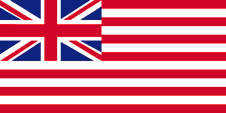 |
1857–1878, Flagge der Britischen Ostindienkompanie – flag of British East India Company, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: commons.wikimedia.org |
 |
1878–1955, Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge, |
 |
1878–1955, |
 |
1878–1886, Britisch-Ceylon, |
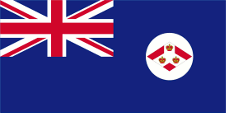 |
1886–1925, Straits Settlements, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen |
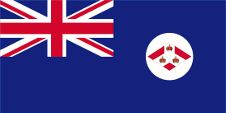 |
1886–1925, Straits Settlements, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen |
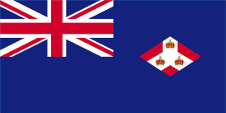 |
1925–1942, Straits Settlements, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: World Statesmen |
 |
1942–1946, Britisch-Ceylon, |
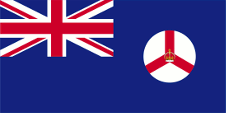 |
1946–1951, Britisch-Singapur, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge der Kokosinseln wurde 2003 eingeführt, jedoch hat sie nur inoffiziellen Charakter. | The today’s flag of Cocos-Islands was introduced in 2003, but it has only unofficial character. |
| Die Flagge ist einfarbig grün und zeigt in der Oberecke am Mast eine gelbe Scheibe mit einer Palme darin. In der Mitte der Flagge ein gelber Halbmond und im fliegenden Ende das Kreuz des Südens, gebildet aus gelben Sternen. | The flag is single-coloured green and shows in the upper staff quadrant near the pole a yellow disk with a palm tree in it. In the middle of the flag a yellow half-moon and in the flying end the Cross of the South formed by yellow stars. |
| Die Farben Gelb und Grün sind die Nationalfarben von Australien. Ebenso verweist das Kreuz des Südens auf die Verbindungen zu diesem Land. | The colours yellow and green are the national colours of Australia. Just as refers the Cross of the South to the connexions to that country. |
| Die Kokosinseln gehörten ab 1886 zur britischen Kronkolonie der Straits Settlements. | The Cocos Islands belonged since 1903 to the British crown colony of the Straits Settlements. |
| Im Jahre 1867 wurden die Straits Settlements eine britische Kronkolonie. Für diese wurde eine Flagge eingeführt, wie sie damals in britischen Kolonien üblich war. | In the year 1867 the Straits Settlements became a British crown colony. For that was introduced a flag how it was usual at that times for British colonies. |
Großbritannien hatte
in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. |
The United Kingdom
introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. |
| Das Badge der Straits Settlements war ein roter Rhombus mit einer weißen Deichsel, auf die drei Kronen aufgelegt waren. Diese standen für die drei Besitzungen Pinang, Malakka und Singapur. | The badge of the Straits Settlements was a red rhombus with a white shaft on which were layed down three crowns. That stood for the three places of Penang, Malacca and Singapore. |
| 1942 wurden die Inseln der Verwaltung von Britisch-Ceylon unterstellt und ab 1946 der von Britisch-Singapur. Die Verwaltung durch Britisch-Singapur endete 1951. | In 1942 the islands came under the administration of British Ceylon and from 1946 under that of British Singapore. The British Singapore administration ended in 1951. |
| An Land repräsentierten der einzelne Bürger und auch die Behörden ihren Status als Bürger oder Organe der britischen Nation, verkörpert im United Kingdom, durch die Verwendung des Union Jack, dann „Union Flag“ genannt. Zur See war somit für den britischen Bürger die britische Handelsflagge, der Red Ensign (Rote Flagge) vorgesehen. In einigen wenigen Fällen wurde den Bürgern einer Kolonie durch die Admiralität erlaubt, auf See einen Red Ensign mit dem Badge der Kolonie zu verwenden. |
On land, the individual
citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or
organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, through the
use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At sea, the British citizen was thus provided with the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were allowed by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea. |
| Die Verwaltung der Kokosinseln ging am 23.11.1955 auf Australien über, und auf der Insel wird offiziell nur die Flagge Australiens verwendet. | The administration of Christmas Island was handed over to Australia on 23rd of November in 1955 and on the island is officially in use only the Australian flag. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World, Volker Preuss | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen der Kokosinseln – coat of arms of Cocos-Islands, Quelle/Source: nach/by: Wikipedia (ES) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Wappen zeigt einen Schild zwischwen zwei Palmen. Das Schild was gevierteilt, Feld eins und vier zeigen einen silbernen Fisch auf blauem Untergrund, Feld zwei und drei einen Vogel auf silbernem Hintergrund. In der Mitte ein schwarzes "Z". Oberhalb des Schildes eine rot-weiße Wulst, daraus eine Hand mit einer roten Nelke darin. Unterhalb des Schildes erscheint ein goldenes Schriftband mit dem Motto "Pulu Kita Maju". Solange die Insel im Besitz der Familie Clunies-Ross gewesen war, stand dort das lateinische Motto "Pro Patria". Das Wappen ist vermutlich das Familienwappen der Clunies-Ross. Das Wappen könnte in der Tat das Familienwappen der Clunies-Ross sein. Dafür spricht das schwarze "Z" in der Mitte des Wappens. Es wird zwar als "Zobel" und "Säbel" bezeichnet, dürfte aber in Wirklichkeit eine abgewandelte Form einer Wolfsangel sein, die europäischer Heraldik entstammt. | The coat of arms schows a shield between two palm trees. The shield was quartered, field one and four show a silvery fish on a blue background, field two and three show a bird on a silvery background. In the middle appears a black "Z". Above the shield a red and white bead and out of it a hand with a red carnation in it. Below the shield appears a golden banner with the slogan "Pulu Kita Maju". As long as the island had been owned by the Clunies-Ross family, there was placed the Latin motto "Pro Patria". The arms are probably the family crest of the Clunies-Ross familyThe arms could be in fact the crest of the Clunies-Ross family. This is supported by the black "Z" in the middle of the crest. Although it is called "sable" and "saber", but it should be in reality a modified form of a wolf angel, a sign which comes from the European heraldry. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (ES), Volker Preuss | |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1609
· der englische Seefahrer William Keeling entdeckt die Kokosinseln 1826 · Besiedlung der Inseln durch Briten 1831 · der Schotte John Clunies-Ross ergreift Besitz von den Inseln 1857 · die Kokosinseln werden formell von der Britischen Ostindienkompanie in Besitz genommen 1878 · die Verwaltung der Kokosinseln geht auf den Britischen Gouverneur von Ceylon (Sri Lanka) über 1886 · die Kokosinseln werden den Straits Settlements angegliedert 1901 · Bau einer Kabelstation auf Direction Island 1910 · Bau einer Funkstation auf Direction Island 09.11.1914 · Erster Weltkrieg (1914–1918), deutsche Truppen landen auf Direction Island, verlassen aber wenig später die Kokosinseln 1942 · die Verwaltung der Kokosinseln geht wieder auf den Britischen Gouverneur von Ceylon (Sri Lanka) über 1942–1944 · japanische Luftangriffe im Zweiten Weltkrieg (1939–1945) 01.04.1946 · das Ende der Straits Settlements: Pinang und Malakka werden der Malaiischen Union (Malaya) angeschlossen, Singapur wird eine eigene britische Kronkolonie, die Kokosinseln und die Weihnachtsinsel werden Singapur angeschlossen, Labuan kommt an Britisch-Nordborneo 1951 · die Inseln werden von Singapur getrennt, verbleiben als britischer Besitz 23.11.1955 · die Verwaltung der Kokosinseln geht von Großbritannien auf Australien über 1978 · Australien kauft der Familie Clunies-Ross die Inseln fast vollständig ab 25.07.1979 · Australien gewährt Selbstverwaltung 1984 · Volksabstimmung, Mehrheit für Verbleib bei Australien |
History: |
| 1609
· the English seafarer William Keeling discovers the Cocos Islands 1826 · settlement of the islands by British 1831 · the Scotsman John Clunies-Ross appropriates the islands 1857 · the Cocos Islands become formally appropriated by the British East India Company 1878 · the administration of the Cocos Islands becomes handed over to the British Governor of Ceylon (Sri Lanka) 1886 · the Cocos Islands become annexed to the Straits Settlements 1901 · construction of a cable station on Direction Island 1910 · construction of a broadcast station on Direction Island 9th of November 1914 · First World War (1914–1918), German troops debark on Direction Island, but leave the Cocos Islands a little bit later 1942 · the administration of the Cocos Islands becomes handed over again to the British Governor of Ceylon (Sri Lanka) 1942–1944 · Japanese air strikes in the Second World War (1939–1945) 1st of April 1946 · the end of the Straits Settlements: Penang and Malacca become affiliated to the Malay Union (Malaya), but Singapore becomes an own British crown colony, the Cocos Islands and Christmas Island become annexed to Singapore, Labuan comes to British North Borneo 1951 · the islands become separated from Singapore, but remainin as a British possession 23rd of November 1955 · the administration of the Cocos Islands is transfered from the United Kingdom to Australia 1978 · Australia purchases the islands almost entirely from the Clunies-Ross family 25th of July 1979 · Australia grants autonomy 1984 · plebiscite, majority for a remaining at Australia |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Kokosinseln" (auch "Cocos-Inseln") bezieht sich wahrscheinlich auf die Kokospalmen der Inseln. Sie bildeten von 1826 bis 1987 die Haupterwerbsquelle der Inselbewohner (Herstellung von Palmöl und Kopra). Die Inseln werden auch "Keeling-Inseln" genannt, zu Ehren ihres Entdeckers, des englischen Seefahrers Kapitän William Keeling. | The name "Cocos
Islands" refers probably to the cocos palm trees on the islands. They had been from
1826 to 1987 the main source of income of the inhabitants of the islands (production of
palm oil and copra). The islands are also named "Keeling Islands" to honour their discoverer, the English seafarer Captain William Keeling. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuss | |