Äthiopien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Äthiopien |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
National- und Staats-
und Handelsflagge – national and state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1897–1936, National- und Staatsflagge – national and state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1941–1974, National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national, state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
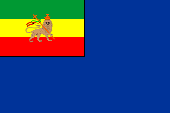 |
1941–1974, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1941–1974, Vorderseite der Kaiserflagge – flag of the Emperor (front), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 45:95, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1941–1974, Rückseite der Kaiserflagge – flag of the Emperor (reverse), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 45:95, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1974–1987, Staatsflagge – state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World, Flaggen und Wappen   |
 |
1987–1991, Staatsflagge – state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1941–1974, National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3 / 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1974–1996, National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge Äthiopiens zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Grün, Gelb und Rot. Im Zentrum – über allem – das Staatswappen, eine blaue Scheibe mit einem darauf liegendem gelbem Pentagramm. Das Grün steht für die Arbeit und die Fruchtbarkeit des Landes, das Gelb für Vaterlandsliebe und Gerechtigkeit, und Rot steht für Mut und das für die Unabhängigkeit vergossene Blut. | The today's flag of Ethiopia shows three horizontal stripes in green, yellow and red. In the center – above all – the coat of arms of the state, a blue disk with a thereupon lying down yellow pentagram. The green stands for the work and the fruitfulness of the land, the yellow for patriotism and justice, and red stands for bravery and the in the struggles for indpendence given blood. |
| Die Farben werden auch christlich gedeutet, und zwar als Symbol für die christliche Dreifaltigkeit: Grün steht für den Heiligen Geist, Gelb für Gott Vater, Rot für den Sohn. Ebenso werden die Farben mit christlichen Tugenden in Verbindung gebracht. Grün steht so für Hoffnung, Gelb für Nächstenliebe und Rot für den Glauben. | The colors are also
interpreted in a Christian way as a symbol of the Christian Trinity: Green stands for Holy
Spirit, yellow stands for God the Father, and red for the son. The colors are also associated with Christian virtues. Green in this way hope, yellow represents charity and red stands for the faith. |
| Erstmals wurde die Flagge Äthiopiens – in umgekehrter Farbfolge – im Jahre 1897 eingeführt. Die Farben der Flagge werden auf die Ausschmückung des Thronsaales des Kaisers Menelik II. (1889–1913) mit kleinen Wimpeln in diesen Farben zurückgeführt. Von 1935 bis 1941 war Äthiopien italienische Kolonie, und führte keine eigene Flagge. Nach Abzug der Italiener erfolgte die Wiedereinführung, diesmal in der heute üblichen Farbreihenfolge. In dieser Form blieb die Flagge unverändert, abgesehen von den verschiedenen Wappendarstellungen in der Mitte der Staatsflagge, und ist in der heutigen Form seit dem 06.02.1996 offiziell. | The flag of Ethiopia
was hoisted up for the first time – in inverted sequence of colors – in the year
1897. The colors of the flag have their roots in the trimming of the throne hall of
emperor Menelik II. (1889–1913) with little pennants in this colors. From 1935 till 1941 Ethiopia was an Italian colony, and has not an own flag. After the retreat of the Italians follows the reintroduction, this time in the today usual sequence of the colors. In this form the flag stays unchanged, irrespective of the diverse coats of arms in the middle of the state flag, and is in the today's form official since the 6th of February in 1996. |
| Die Farben der Flagge sind auch als die "Panafrikanischen Farben" bekannt: Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische und auch amerikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen, steht für die politische Einheit Afrikas, ja aller Schwarzen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. | The colors of the flag
are even known as the "Panafrican colors": Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of
the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used
many african and even american countries in their flags after the independence, stands for
the political unity of Africa, of all black People. |
| Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (D) | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Äthiopien – coat of arms of Ethiopia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
historische Wappen – historical Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
1974–1987, Wappen von Äthiopien – coat of arms of Ethiopia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1987–1991, Wappen von Äthiopien – coat of arms of Ethiopia, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Als Staatswappen Äthiopiens wurde von alters her der sogenannte Löwe von Juda benutzt. Dieser ist wahrscheinlich vom Armenischen Löwen entlehnt und übernommen worden. Der Löwe von Juda galt schon im Mittelalter als das Wappentier des sagenhaften Priesters Johannes. | As coat of arms of the state Ethiopia was in use since older times the so named lion of Juda. That is probably borrowed from the Armenian lion and gets assumed. The lion of Juda was already in the middle ages valid as the scutcheon animal of the legendary priest Johannes. |
| Mit dem Ende der Monarchie wurde 1975 ein neues Staatswappen eingeführt. Es zeigte eine große Sonne und ein Zahnrad (Industrie) auf einer blauen Scheibe, davor einen Pflug (Landwirtschaft). Das Ganze wurde von zwei Ölzweigen eingefasst. An dem Punkt, wo sich beide Ölzweige kreuzen, erschien ein Medaillon mit der Darstellung des Löwen von Juda. | With the end of the
monarchy was introduced a new coat of arms in 1975. It showed a large sun and a cogwheel
(industry) on a blue disk, in front a plow (agriculture). This all was bordered with two oil-twigs. On this point, where both oil-twigs are crossing, appeared a medallion with the depiction of the lion of Juda. |
| Mit der Annahme einer neuen Verfassung wurde 1987 ein neues Staatswappen eingeführt. Dieses zeigte eine Abbildung des Obelisken von Aksum, ein großes Zahnrad, und einen kreisfürmigen Schild mit dahinter liegenden Waffen, darüber ein roter Stern. Das Wappen war von Ölzweigen und Palmwedeln umgeben. | With the acceptance of a new constitution was introduced a new coat of arms in 1987. This showed a depiction of the obelisk of Aksum, a large cogwheel, and a circular shield with behind situated arms, above that a red star. The coat of arms was surrounded by oil-twigs and palm tree fronds. |
| Mit der Annahme der neuen Verfassung als föderative demokratische Republik wurde am 06.02.1996 ein neues Staatswappen eingeführt, nebst dem Beschluss, dieses auf der Nationalflagge zu führen. Es zeigt eine blaue Scheibe mit der goldenen Darstellung eines Pentagramms, des Siegels Salomos. Zwischen den fünf Zacken des Pentagramms erscheinen trapezfürmige Strahlen. Dieses Symbol soll durch seinen gleichfürmigen Aufbau die Gleichheit aller Nationalitäten und Religionen zeigen, und zugleich die Einheit der Einwohner Äthiopiens darstellen. Die goldenen Strahlen stehen für die Zukunft des Landes. | With the acceptance of
a new constitution as federative democratic republic was introduced a new coat of arms on
6th of february in 1996, together with the resolution to use this on the national flag. It
shows a blue disk with the golden depiction of a pentagram, the seal of Salomo. Between the five jags of the pentagram appear trapezoid beams. This symbol should shows the equality of all nationalities and religions by his regular construction, and at the same time portray the unity of the residents of Ethiopia. The golden beams stand for the future of the land. |
| Quelle/Source nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1941–1974, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
seit/since 1996, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarte – Map: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1. bis 5. Jhd.
· Aksumitisches Reich 13. bis 18. Jhd. · erstes Kaiserreich 1855 · zweites Kaiserreich 1935–1941 · italienische Kolonie 1974 · Ende der Monarchie 1977–1982 · Ogaden-Krieg geg. Somalia 1993 · Sezession von Eritrea 2001 · Krieg gegen Eritrea 2018 · Friedensvertrag zwischen Äthiopien und Eritrea |
History: |
| 1st to 5th
cent. · Aksumitic Empire 13th to 18th cent. · first empire 1855 · second empire 1935–1941 · Italian colony 1974 · end of the monarchy 1977–1982 · Ogaden war against Somalia 1993 · secession of Eritrea 2001 · war against Eritrea 2018 · peace treaty between Ethiopia and Eritrea |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name des Landes geht auf die antike griechische Bezeichnung "aithiops" zurück, was "verbranntes Gesicht" heißt, und sich auf die dunkelhäutigen Bewohner Afrikas bezog. | The name of the country goes back to the ancient Greek name "aithiops", which means "burnt face", and referred to the dark-skinned inhabitants of Africa. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |